IB Diploma offers a holistic curriculum with a focus on interdisciplinary learning, critical thinking, and global perspectives, while A-levels provide specialized subject depth tailored to students' strengths and university requirements. The IB program requires students to complete core components like the Extended Essay and Theory of Knowledge, promoting research and analytical skills beyond traditional exams. A-levels, on the other hand, allow for more flexibility in subject choices and often align closely with specific academic or career paths.
Table of Comparison
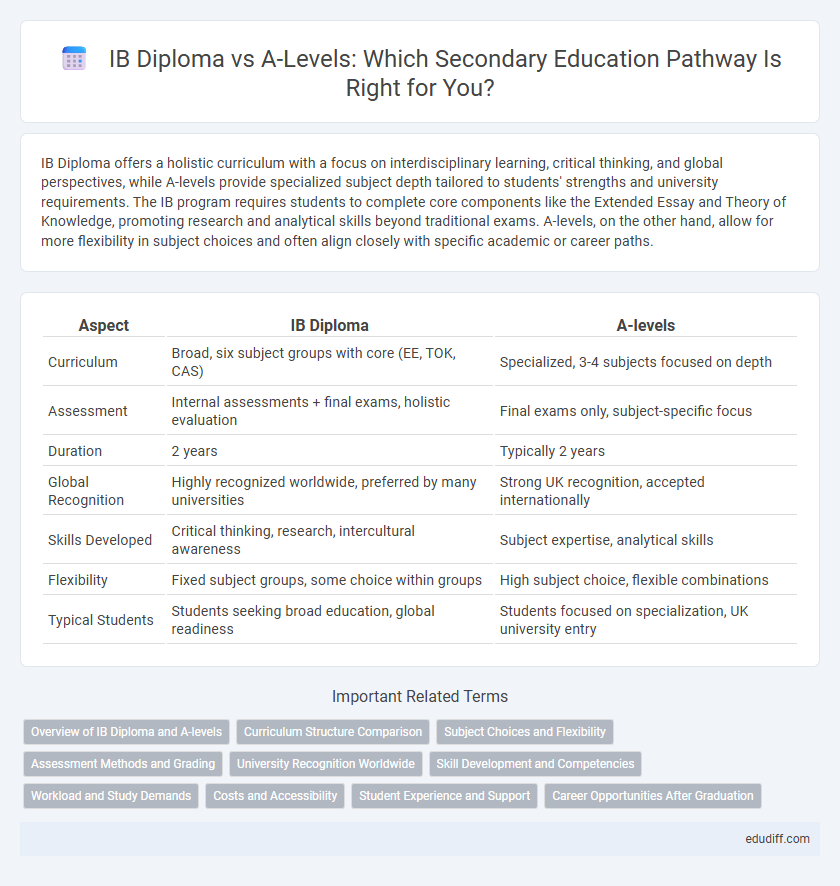
| Aspect | IB Diploma | A-levels |
|---|---|---|
| Curriculum | Broad, six subject groups with core (EE, TOK, CAS) | Specialized, 3-4 subjects focused on depth |
| Assessment | Internal assessments + final exams, holistic evaluation | Final exams only, subject-specific focus |
| Duration | 2 years | Typically 2 years |
| Global Recognition | Highly recognized worldwide, preferred by many universities | Strong UK recognition, accepted internationally |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, research, intercultural awareness | Subject expertise, analytical skills |
| Flexibility | Fixed subject groups, some choice within groups | High subject choice, flexible combinations |
| Typical Students | Students seeking broad education, global readiness | Students focused on specialization, UK university entry |
Overview of IB Diploma and A-levels
The IB Diploma offers a balanced curriculum requiring students to study six subjects across diverse disciplines, alongside core components such as Theory of Knowledge, Extended Essay, and Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS). A-levels allow for deeper specialization by focusing on three to four subjects, enabling students to develop in-depth knowledge in their chosen fields. Both qualifications are internationally recognized and accepted by universities, but the IB Diploma emphasizes interdisciplinary learning and critical thinking, while A-levels prioritize subject mastery.
Curriculum Structure Comparison
The IB Diploma features a comprehensive curriculum requiring students to study six subjects from different groups, promoting a broad academic foundation, while A-levels allow specialization in three to four subjects for in-depth study. IB includes core components like Theory of Knowledge, the Extended Essay, and Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS), fostering critical thinking and holistic development, unlike A-levels which focus strictly on subject content. This structural difference influences university preparation, with IB encouraging interdisciplinary learning and A-levels enabling expertise in chosen fields.
Subject Choices and Flexibility
The IB Diploma offers a broad curriculum requiring students to study six subjects across multiple disciplines, ensuring a balanced education in languages, sciences, humanities, and mathematics. In contrast, A-levels allow for more specialization by selecting three to four subjects, enabling students to focus deeply on their areas of interest. This flexibility in A-levels suits students aiming for targeted university pathways, while the IB's structured diversity supports interdisciplinary skills and global recognition.
Assessment Methods and Grading
IB Diploma assessment emphasizes a combination of internal assessments, extended essays, and final exams, promoting critical thinking and research skills, with grades awarded on a scale of 1 to 7 for each subject. A-levels rely primarily on terminal exams taken at the end of the two-year course, graded from A* to E, focusing on content mastery and exam techniques. IB's holistic approach contrasts with A-levels' specialization, affecting how students demonstrate their academic proficiency and readiness for university.
University Recognition Worldwide
Universities worldwide recognize both the IB Diploma and A-levels, valuing their rigor and depth in preparing students for higher education. The IB Diploma is often preferred for its comprehensive curriculum, promoting critical thinking and global awareness, making it attractive to universities with holistic admission processes. A-levels offer subject specialization, which aligns well with universities seeking expertise in specific fields, particularly in the UK and Commonwealth countries.
Skill Development and Competencies
The IB Diploma emphasizes critical thinking, global awareness, and interdisciplinary research skills, fostering analytical and reflective competencies essential for higher education. A-levels focus more intensely on subject-specific knowledge and in-depth expertise, promoting specialized skills and mastery within chosen disciplines. Both curricula develop strong academic skills, but the IB's holistic approach nurtures broader cognitive and communication abilities, while A-levels refine detailed subject proficiency.
Workload and Study Demands
The IB Diploma demands consistent study across six subjects with an extended essay and Theory of Knowledge course, creating a continuous workload throughout the two years. A-levels allow students to specialize in three to four subjects, resulting in a concentrated but intense study period primarily toward final exams. The IB's balanced workload supports skill development and time management, while A-levels emphasize depth in chosen subjects with a more exam-focused assessment style.
Costs and Accessibility
IB Diploma programs often entail higher costs due to mandatory fees for exams and core components like the Extended Essay and CAS activities, whereas A-levels generally have lower examination fees and fewer compulsory projects, making them more affordable. Accessibility varies as IB programs require authorized schools with trained coordinators, limiting availability primarily to international or private schools, while A-levels are widely offered in many public and private institutions. Funding options and scholarships for the IB Diploma are less common compared to A-levels, which benefit from broader government support and examination subsidies.
Student Experience and Support
IB Diploma students benefit from a holistic educational approach emphasizing critical thinking, interdisciplinary learning, and global awareness, which enhances their academic engagement and personal growth. In contrast, A-levels offer more subject specialization, allowing students to dive deeply into their chosen disciplines with tailored support from subject-specific teachers. Both programs provide structured guidance and counseling services, but IB's continuous assessment fosters ongoing feedback, contributing to a supportive and interactive student experience.
Career Opportunities After Graduation
IB Diploma graduates demonstrate strong critical thinking and global awareness, making them attractive to multinational companies and competitive universities worldwide. A-level students benefit from subject specialization, providing deep expertise that aligns well with specialized career paths and professional degrees. Both qualifications offer pathways to diverse career opportunities, though IB's interdisciplinary approach suits roles requiring adaptability, while A-levels cater to focused academic and vocational pursuits.
IB Diploma vs A-levels Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com