The homeroom system promotes stronger student-teacher relationships by assigning students to a single teacher who manages academic and behavioral progress, enhancing personalized support and continuity. In contrast, the departmental system divides instruction among subject specialists, allowing for deeper content expertise but often resulting in less personalized student engagement. Selecting between these systems depends on balancing the benefits of focused expertise against the need for holistic student development and consistent mentorship.
Table of Comparison
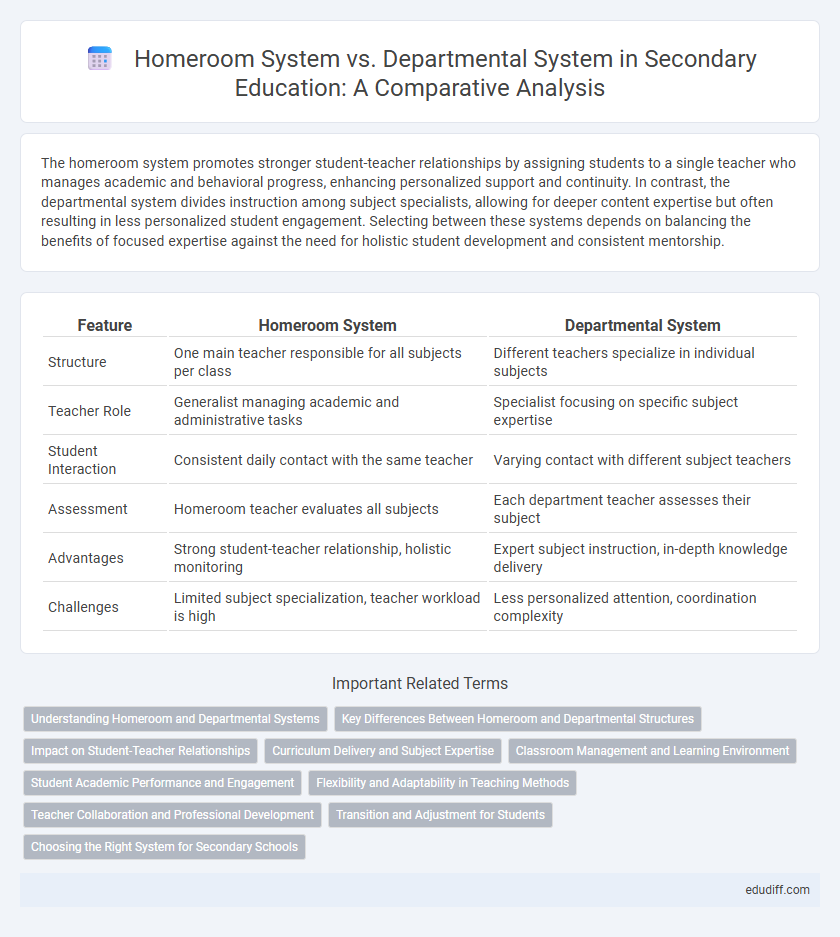
| Feature | Homeroom System | Departmental System |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | One main teacher responsible for all subjects per class | Different teachers specialize in individual subjects |
| Teacher Role | Generalist managing academic and administrative tasks | Specialist focusing on specific subject expertise |
| Student Interaction | Consistent daily contact with the same teacher | Varying contact with different subject teachers |
| Assessment | Homeroom teacher evaluates all subjects | Each department teacher assesses their subject |
| Advantages | Strong student-teacher relationship, holistic monitoring | Expert subject instruction, in-depth knowledge delivery |
| Challenges | Limited subject specialization, teacher workload is high | Less personalized attention, coordination complexity |
Understanding Homeroom and Departmental Systems
The homeroom system assigns students to a single teacher who manages multiple subjects, fostering consistent teacher-student relationships and personalized attention. The departmental system divides instruction among specialized teachers for each subject, promoting expertise and subject-focused teaching. Understanding these systems highlights different educational approaches impacting classroom management, student engagement, and curriculum delivery.
Key Differences Between Homeroom and Departmental Structures
The homeroom system assigns students to a single teacher for most subjects, fostering stronger teacher-student relationships and individualized attention, while the departmental system divides instruction among specialized subject teachers, enhancing subject expertise but reducing consistent teacher contact. In the homeroom structure, teachers handle classroom management and student assessments across subjects, whereas the departmental system delegates these roles to multiple educators specialized in different disciplines. Scheduling flexibility contrasts as the homeroom system follows a fixed routine for the entire day, and the departmental system allows varied class periods tailored to different subjects, impacting student learning dynamics and administrative efficiency.
Impact on Student-Teacher Relationships
The homeroom system fosters stronger student-teacher relationships by providing a consistent primary teacher who monitors academic progress and emotional well-being, enhancing personalized support. In contrast, the departmental system limits interaction frequency between students and individual teachers, potentially weakening rapport and continuity in mentorship. This difference in structural design significantly influences students' sense of belonging and their academic motivation through the quality of relationships formed.
Curriculum Delivery and Subject Expertise
The Homeroom System enhances curriculum delivery by fostering a consistent learning environment, allowing teachers to manage a broad range of subjects and maintain strong student-teacher relationships. In contrast, the Departmental System prioritizes subject expertise, enabling specialized instructors to deliver in-depth knowledge and tailored instruction for each discipline. This specialization often results in higher academic rigor and improved mastery in complex subject areas.
Classroom Management and Learning Environment
The homeroom system enhances classroom management by providing consistent teacher-student interaction, fostering stronger relationships and personalized discipline strategies. In contrast, the departmental system, with multiple subject teachers, may cause fragmented student supervision but offers specialized instruction that can improve the learning environment's academic rigor. Balancing these approaches impacts student engagement, classroom order, and overall educational outcomes.
Student Academic Performance and Engagement
The homeroom system fosters stronger student-teacher relationships, leading to improved academic performance and higher engagement due to consistent mentorship and personalized support. The departmental system offers specialized instruction by subject experts, enhancing content mastery but may reduce the continuity of student-teacher interactions, potentially impacting engagement levels. Studies indicate that a hybrid approach balancing homeroom stability with departmental expertise optimizes student achievement and involvement.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Teaching Methods
The Homeroom System offers greater flexibility by allowing teachers to adapt teaching methods to the diverse learning needs of a single group of students throughout the day. In contrast, the Departmental System emphasizes subject specialization, which can limit adaptability as students switch teachers and teaching styles for each subject. Flexibility in the Homeroom System supports personalized learning and continuous assessment, enhancing student engagement and academic progress.
Teacher Collaboration and Professional Development
The Homeroom System fosters consistent teacher collaboration through daily interaction with the same group of students, enabling targeted professional development tailored to shared classroom challenges. In contrast, the Departmental System encourages specialization, promoting subject-specific collaboration and advanced skill-building within disciplines. Both systems support effective teacher development, but the Homeroom model emphasizes holistic student support, while the Departmental model focuses on subject mastery and instructional expertise.
Transition and Adjustment for Students
Transitioning from a homeroom system to a departmental system requires students to adapt to multiple teachers and diverse instructional styles, which can initially increase cognitive load and organizational challenges. Adjustment involves developing time management skills and effective communication strategies to navigate different subject expectations. Support through orientation programs and mentoring can facilitate smoother adaptation and foster academic resilience during this systemic shift.
Choosing the Right System for Secondary Schools
Evaluating the homeroom and departmental systems reveals distinct benefits for secondary schools, with the homeroom system fostering stronger student-teacher relationships through consistent mentorship while the departmental system enhances subject specialization by dividing instruction among expert teachers. Secondary schools aiming for personalized student support and holistic development may favor the homeroom approach, whereas those prioritizing academic rigor and subject proficiency often adopt the departmental system. Key factors influencing the decision include school size, available faculty expertise, and the desired balance between student engagement and curriculum depth.
Homeroom System vs Departmental System Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com