Vocational pathways prioritize hands-on skills and practical experience, preparing students directly for specific trades or careers through technical training and apprenticeships. Academic pathways emphasize theoretical knowledge and critical thinking, often leading to higher education opportunities and a broader range of career options. Choosing between vocational and academic routes depends on individual interests, career goals, and preferred learning styles.
Table of Comparison
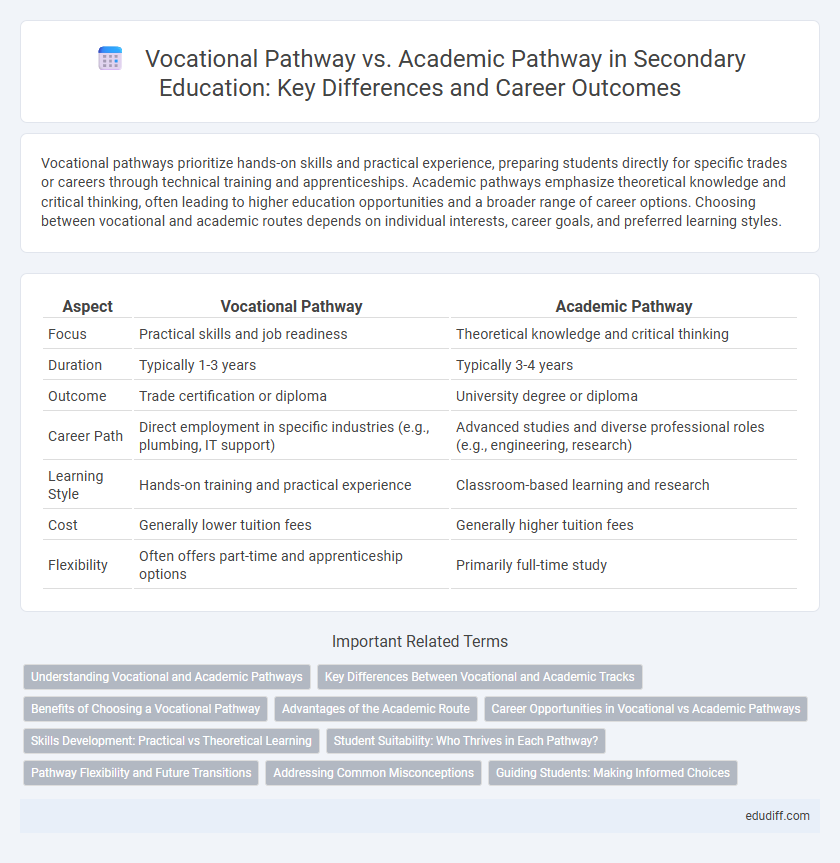
| Aspect | Vocational Pathway | Academic Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Practical skills and job readiness | Theoretical knowledge and critical thinking |
| Duration | Typically 1-3 years | Typically 3-4 years |
| Outcome | Trade certification or diploma | University degree or diploma |
| Career Path | Direct employment in specific industries (e.g., plumbing, IT support) | Advanced studies and diverse professional roles (e.g., engineering, research) |
| Learning Style | Hands-on training and practical experience | Classroom-based learning and research |
| Cost | Generally lower tuition fees | Generally higher tuition fees |
| Flexibility | Often offers part-time and apprenticeship options | Primarily full-time study |
Understanding Vocational and Academic Pathways
Vocational pathways emphasize practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades or careers, enabling students to enter the workforce directly after secondary education. Academic pathways focus on theoretical knowledge and critical thinking, preparing students for higher education and research-oriented careers. Understanding these pathways helps students align their education with career goals, balancing skill acquisition with academic advancement.
Key Differences Between Vocational and Academic Tracks
Vocational pathways emphasize practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades or careers, while academic pathways focus on theoretical knowledge and prepare students for higher education. Vocational tracks often lead to certifications or diplomas enabling immediate employment, whereas academic tracks culminate in degrees facilitating further study and research opportunities. Assessment methods differ, with vocational programs prioritizing competency-based evaluations and academic programs relying on exams and essays measuring conceptual understanding.
Benefits of Choosing a Vocational Pathway
Choosing a vocational pathway offers practical skills and hands-on experience that directly align with industry demands, leading to faster employment opportunities and higher job security in skilled trades and technical fields. Vocational education emphasizes specialized training in areas like healthcare, information technology, and engineering, often resulting in lower tuition costs and shorter completion times compared to traditional academic routes. This pathway cultivates industry certifications and apprenticeships, enhancing career readiness and earning potential for students seeking immediate entry into the workforce.
Advantages of the Academic Route
The academic pathway offers comprehensive theoretical knowledge, preparing students for university degrees and advanced research opportunities. It cultivates critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a broad understanding of various disciplines, which are essential for professions like medicine, law, and engineering. This route also enhances opportunities for scholarships and global mobility in higher education.
Career Opportunities in Vocational vs Academic Pathways
Vocational pathways offer direct entry into specialized trades and technical careers such as healthcare, construction, and information technology, providing practical skills with immediate workforce applicability. Academic pathways open opportunities in professions requiring higher education degrees, including law, engineering, and research, often leading to broader career advancement and higher earning potential. Both pathways contribute significantly to the economy, catering to diverse industry demands and workforce needs.
Skills Development: Practical vs Theoretical Learning
Vocational pathways emphasize hands-on skills development through practical training in trades such as carpentry, healthcare, and information technology, preparing students for immediate workforce entry. Academic pathways focus on theoretical learning, critical thinking, and conceptual understanding in subjects like mathematics, science, and literature, fostering analytical skills and long-term educational advancement. Combining practical skill acquisition with theoretical knowledge enhances overall competency and adaptability in diverse career environments.
Student Suitability: Who Thrives in Each Pathway?
Students with hands-on learning preferences and a focus on practical skills thrive in vocational pathways, where industries such as healthcare, technology, and trades provide direct career opportunities. Academic pathways suit students excelling in theoretical knowledge and critical thinking, preparing them for university studies in fields like science, humanities, and engineering. The suitability depends on individual learning styles, career goals, and strengths, emphasizing personalized education to maximize student success and engagement.
Pathway Flexibility and Future Transitions
Vocational pathways offer practical skills and hands-on experience, enabling students to enter the workforce quickly, while academic pathways emphasize theoretical knowledge and critical thinking, preparing students for university studies. Flexibility in academic pathways often includes options to change majors or pursue postgraduate education, whereas vocational pathways provide credentials that can lead to specialized career certifications or apprenticeships. Future transitions from vocational training to higher education institutions are increasingly supported through credit recognition and bridging programs, enhancing pathway interoperability and lifelong learning opportunities.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Misconceptions that vocational pathways are less challenging or offer limited career prospects persist despite data showing strong employment rates and skill demand in trades and technical fields. Academic pathways do not guarantee immediate job placement, whereas vocational training often includes hands-on experience and apprenticeships that enhance job readiness. Employers increasingly value specialized skills and certifications obtained through vocational education, contradicting the belief that academic routes are superior for long-term success.
Guiding Students: Making Informed Choices
Vocational pathways provide students with practical skills and industry-specific training that enhance employability in technical fields, while academic pathways emphasize theoretical knowledge and prepare students for tertiary education. Guiding students involves assessing their strengths, interests, and career goals to align choices with future job market demands and lifelong learning opportunities. Informed decisions are supported by comprehensive counseling, exposure to real-world work environments, and integration of labor market data.
Vocational pathway vs Academic pathway Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com