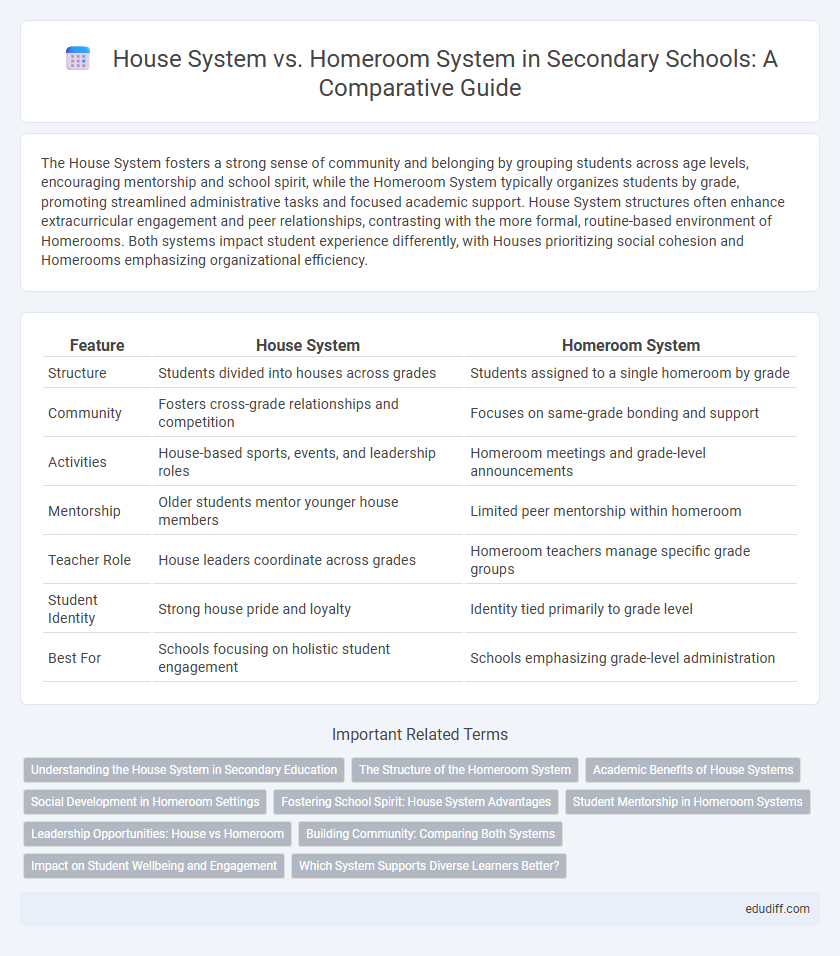
The House System fosters a strong sense of community and belonging by grouping students across age levels, encouraging mentorship and school spirit, while the Homeroom System typically organizes students by grade, promoting streamlined administrative tasks and focused academic support. House System structures often enhance extracurricular engagement and peer relationships, contrasting with the more formal, routine-based environment of Homerooms. Both systems impact student experience differently, with Houses prioritizing social cohesion and Homerooms emphasizing organizational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | House System | Homeroom System |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Students divided into houses across grades | Students assigned to a single homeroom by grade |
| Community | Fosters cross-grade relationships and competition | Focuses on same-grade bonding and support |
| Activities | House-based sports, events, and leadership roles | Homeroom meetings and grade-level announcements |
| Mentorship | Older students mentor younger house members | Limited peer mentorship within homeroom |
| Teacher Role | House leaders coordinate across grades | Homeroom teachers manage specific grade groups |
| Student Identity | Strong house pride and loyalty | Identity tied primarily to grade level |
| Best For | Schools focusing on holistic student engagement | Schools emphasizing grade-level administration |
Understanding the House System in Secondary Education
The House System in secondary education organizes students into smaller communities that foster a sense of belonging and promote peer support, enhancing social interaction beyond academic groups. Unlike the Homeroom System, which primarily serves administrative and organizational functions, the House System emphasizes holistic development through inter-house competitions, leadership opportunities, and mentorship programs. This approach cultivates school spirit and encourages teamwork, contributing to improved student engagement and well-being.
The Structure of the Homeroom System
The Homeroom System is structured around assigning students to a single homeroom teacher who oversees administrative tasks, attendance, and pastoral care, providing consistent daily supervision. This system emphasizes personalized support and fosters strong student-teacher relationships, enhancing academic monitoring and addressing individual needs. Homerooms typically consist of students from the same grade level, streamlining communication between staff, students, and parents.
Academic Benefits of House Systems
House systems in secondary education foster academic collaboration by grouping students across different year levels, promoting peer mentoring and support. This structure enhances student engagement through inter-house academic competitions and shared learning experiences, resulting in improved motivation and academic achievement. Research shows that house systems boost a sense of belonging, which correlates with higher attendance rates and better overall academic performance.
Social Development in Homeroom Settings
Homeroom systems foster social development by creating consistent daily interaction within a stable peer group, promoting deeper relationships and stronger community bonds among students. This regular engagement enhances communication skills, emotional support, and collaborative learning opportunities essential for adolescent growth. Compared to house systems, homerooms offer focused environments that address individual student needs and social dynamics more effectively.
Fostering School Spirit: House System Advantages
The House System significantly enhances school spirit by promoting a sense of belonging and friendly competition among students through team-based activities and events. Unlike the Homeroom System, which primarily focuses on administrative tasks, the House System creates lasting social bonds and encourages active participation in school traditions. This communal environment fosters pride and motivation, contributing to improved student engagement and school-wide unity.
Student Mentorship in Homeroom Systems
Homeroom systems provide a dedicated environment for student mentorship by assigning each student to a consistent mentor who supports academic, social, and emotional development. This sustained relationship fosters personalized guidance and timely intervention, enhancing student well-being and academic success. Compared to house systems, homeroom systems offer a more focused approach to individual student needs through regular, one-on-one interaction with mentors.
Leadership Opportunities: House vs Homeroom
The House System fosters diverse leadership roles, allowing students to represent their houses in various competitions and community activities, enhancing teamwork and responsibility. In contrast, the Homeroom System primarily offers leadership within a single class environment, limiting opportunities to lead across a wider peer group. Schools adopting the House System benefit from a structured framework that encourages student involvement and leadership development on a broader scale.
Building Community: Comparing Both Systems
The House System fosters a strong sense of identity and belonging by grouping students across different grades into supportive, competitive teams, enhancing peer mentorship and school spirit. In contrast, the Homeroom System centers on daily administrative tasks and stability, providing a consistent environment for academic and emotional support within a single grade level. Schools prioritizing community-building often find the House System more effective in promoting cross-age relationships and long-term engagement.
Impact on Student Wellbeing and Engagement
The House System fosters a strong sense of community by grouping students across year levels, promoting mentorship, and increasing peer support, which positively impacts student wellbeing. In contrast, the Homeroom System offers consistent relationships within a single grade, aiding targeted emotional support and academic engagement. Studies show that students in House Systems report higher engagement and a greater sense of belonging, contributing to improved mental health and reduced absenteeism.
Which System Supports Diverse Learners Better?
The House System supports diverse learners better by fostering a sense of belonging through smaller, cross-grade communities that promote peer mentoring and personalized support. It encourages collaboration among students with varying strengths, enhancing social-emotional development and inclusivity. Homeroom Systems, while structured for administrative efficiency, often lack the dynamic support networks essential for addressing diverse learning needs.
House System vs Homeroom System Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com