Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering personalized pacing and diverse resources that enhance student engagement in secondary education. Face-to-face learning provides direct interaction, immediate feedback, and a structured environment that fosters social skills and discipline. Combining both approaches can maximize educational outcomes by balancing flexibility with the benefits of in-person collaboration.
Table of Comparison
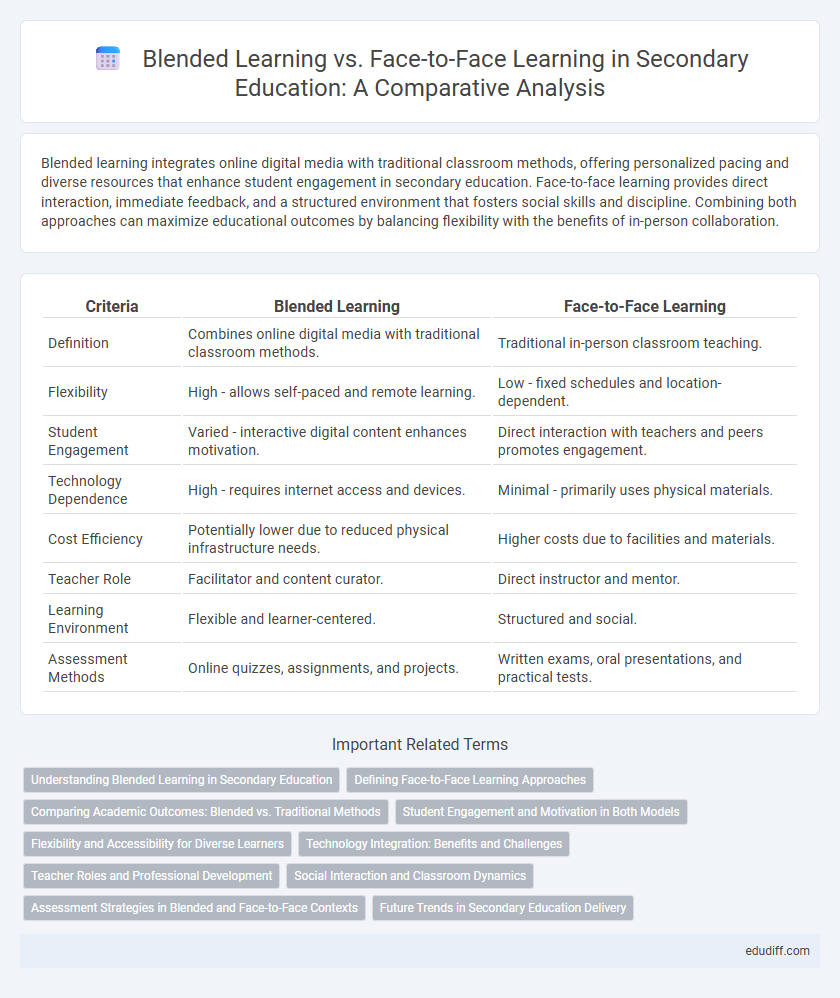
| Criteria | Blended Learning | Face-to-Face Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods. | Traditional in-person classroom teaching. |
| Flexibility | High - allows self-paced and remote learning. | Low - fixed schedules and location-dependent. |
| Student Engagement | Varied - interactive digital content enhances motivation. | Direct interaction with teachers and peers promotes engagement. |
| Technology Dependence | High - requires internet access and devices. | Minimal - primarily uses physical materials. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower due to reduced physical infrastructure needs. | Higher costs due to facilities and materials. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and content curator. | Direct instructor and mentor. |
| Learning Environment | Flexible and learner-centered. | Structured and social. |
| Assessment Methods | Online quizzes, assignments, and projects. | Written exams, oral presentations, and practical tests. |
Understanding Blended Learning in Secondary Education
Blended learning in secondary education combines traditional face-to-face instruction with digital resources, enhancing personalized learning experiences and increasing student engagement. Integrating online platforms allows for flexible pacing and diverse content delivery, catering to varied learning styles and improving outcomes. This hybrid approach supports skill development in technology use while maintaining critical interpersonal interactions essential for adolescent growth.
Defining Face-to-Face Learning Approaches
Face-to-face learning approaches involve direct, in-person interaction between teachers and students within a traditional classroom setting, emphasizing real-time communication and immediate feedback. This method supports hands-on activities and social engagement, which enhance collaborative learning and critical thinking skills. Typical face-to-face learning environments foster structured schedules, facilitating deeper teacher-student relationships and personalized instruction.
Comparing Academic Outcomes: Blended vs. Traditional Methods
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, enhancing student engagement and often resulting in improved academic outcomes compared to face-to-face learning alone. Studies reveal that students in blended environments tend to achieve higher retention rates and better test scores due to personalized pacing and interactive content. However, face-to-face learning remains valuable for developing social skills and immediate feedback, making the choice dependent on specific educational goals and learner needs.
Student Engagement and Motivation in Both Models
Blended learning combines digital tools with traditional classroom instruction, enhancing student engagement through interactive content and personalized pacing, which boosts motivation by catering to diverse learning styles. Face-to-face learning fosters immediate social interaction and real-time feedback, contributing to motivation through direct teacher support and peer collaboration. Both models impact engagement differently, with blended learning promoting autonomy and face-to-face learning strengthening community and accountability.
Flexibility and Accessibility for Diverse Learners
Blended learning enhances flexibility by allowing secondary students to access course materials anytime, accommodating diverse schedules and learning paces. Face-to-face learning provides structured, immediate interaction, which benefits learners requiring direct guidance and real-time feedback. Combining both methods maximizes accessibility, supporting varied learning preferences and promoting inclusive education.
Technology Integration: Benefits and Challenges
Blended learning integrates digital tools with traditional classroom instruction, enhancing student engagement and enabling personalized learning paths through technologies like learning management systems and interactive content. Face-to-face learning benefits from in-person interaction but may lack the flexibility and resource accessibility that technology provides. Challenges in blended learning include ensuring equitable access to devices and reliable internet, as well as training educators to effectively combine technological tools with pedagogical strategies.
Teacher Roles and Professional Development
Teacher roles in blended learning evolve to facilitators of personalized learning experiences, integrating digital tools to enhance student engagement and autonomy. Professional development prioritizes digital literacy, instructional design skills, and adaptive teaching strategies to effectively blend online and face-to-face modalities. Face-to-face learning emphasizes direct interaction and real-time feedback, requiring teachers to excel in classroom management and immediate student support.
Social Interaction and Classroom Dynamics
Blended learning enhances social interaction by integrating online collaboration tools that complement face-to-face discussions, creating a dynamic classroom environment that fosters diverse communication channels. Face-to-face learning relies heavily on immediate verbal and non-verbal cues, promoting spontaneous interactions and stronger peer connections essential for social development. Classroom dynamics in blended settings shift towards more flexible participation, allowing students to engage at their own pace while benefiting from real-time feedback during in-person sessions.
Assessment Strategies in Blended and Face-to-Face Contexts
Assessment strategies in blended learning combine digital tools such as online quizzes, interactive simulations, and automated feedback systems with traditional methods like in-person exams and essays to provide a comprehensive evaluation of student understanding. Face-to-face learning primarily relies on direct observation, classroom discussions, and written tests, allowing for immediate teacher intervention and personalized feedback. Incorporating formative assessments through learning management systems enhances data-driven insights in blended environments, supporting adaptive instruction that caters to diverse secondary education learners.
Future Trends in Secondary Education Delivery
Blended learning in secondary education integrates digital tools with traditional classroom methods, enhancing personalized learning and flexible pacing for diverse student needs. Future trends indicate increased use of AI-driven platforms and virtual reality to create immersive, adaptive learning environments that supplement face-to-face instruction. This hybrid approach is expected to improve student engagement, collaboration, and academic outcomes while preparing learners for a technology-rich world.
Blended Learning vs Face-to-Face Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com