Matriculation programs provide a rigorous pathway emphasizing core academic subjects that prepare students for advanced studies, while foundation courses offer a broader introduction to various disciplines aimed at easing the transition into higher education. Matriculation is often preferred by students targeting specialized professional courses due to its comprehensive curriculum and recognized certification. Foundation courses prioritize skill development and flexibility, catering to learners seeking a less intensive, adaptable approach to post-secondary education.
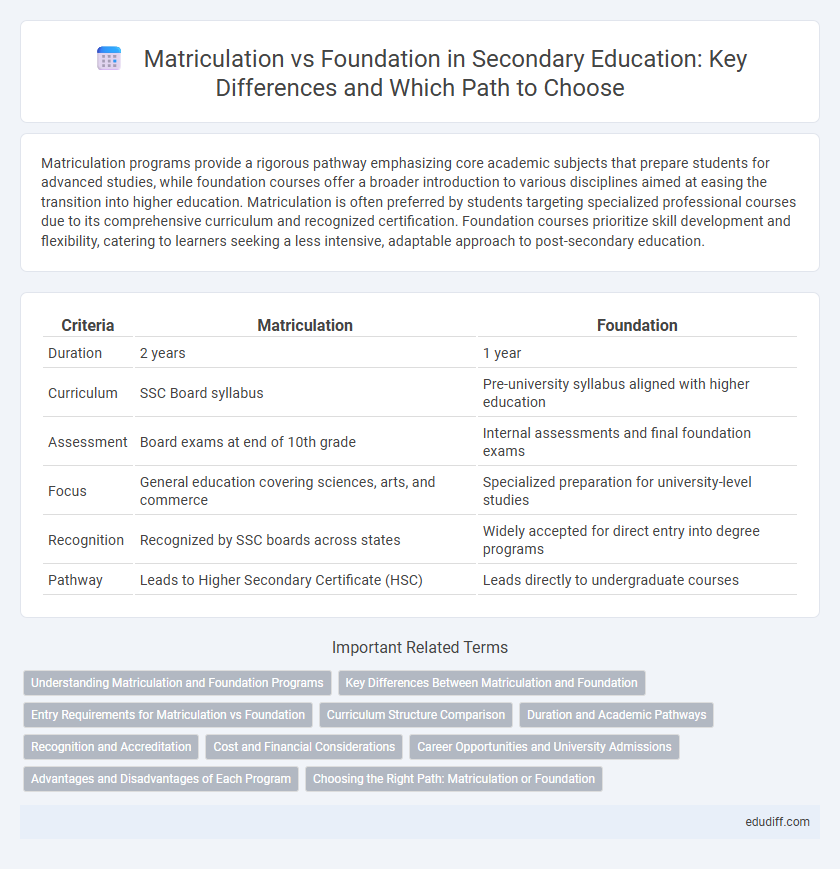
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Matriculation | Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 2 years | 1 year |
| Curriculum | SSC Board syllabus | Pre-university syllabus aligned with higher education |
| Assessment | Board exams at end of 10th grade | Internal assessments and final foundation exams |
| Focus | General education covering sciences, arts, and commerce | Specialized preparation for university-level studies |
| Recognition | Recognized by SSC boards across states | Widely accepted for direct entry into degree programs |
| Pathway | Leads to Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC) | Leads directly to undergraduate courses |
Understanding Matriculation and Foundation Programs
Matriculation programs typically serve as a streamlined pre-university course designed to prepare secondary students for higher education by covering core subjects like Mathematics, Science, and Bahasa Malaysia. Foundation programs offer a broader academic preparation with specialized streams such as Science, Engineering, or Business, aimed at equipping students with in-depth knowledge and skills for university degree courses. Understanding the distinct curriculum focus and assessment methods of both matriculation and foundation pathways helps students select the most suitable route for their academic and career goals.
Key Differences Between Matriculation and Foundation
Matriculation is a pre-university qualification equivalent to Grade 11 and 12, usually involving a national standardized curriculum, while Foundation courses are university-specific preparatory programs designed to bridge the gap between secondary education and degree-level study. Matriculation emphasizes broad subject coverage and national exams, whereas Foundation focuses on subject specialization and university admission requirements. Duration varies, with Matriculation commonly spanning two years and Foundation programs lasting one year, tailored for direct entry into undergraduate degrees.
Entry Requirements for Matriculation vs Foundation
Matriculation entry requirements typically demand completion of SPM or equivalent qualifications with a minimum of five credits, including core subjects like Bahasa Malaysia and English. Foundation programmes often require SPM or O-Level certification with passes in specific subjects related to the chosen field of study. Both pathways emphasize academic performance but differ in subject focus and flexibility to accommodate diverse student backgrounds.
Curriculum Structure Comparison
Matriculation curriculum emphasizes a traditional subject-based structure with a strong focus on sciences, mathematics, and languages, designed to prepare students for higher secondary education through national exams. Foundation programs offer a more flexible and interdisciplinary approach, integrating core subjects with skills development like critical thinking and communication, aimed at easing the transition to university-level studies. The Matriculation system follows a standardized syllabus mandated by educational boards, whereas Foundation courses often incorporate international or modular content tailored to specific academic pathways.
Duration and Academic Pathways
Matriculation programs typically span two years and lead directly to pre-university qualifications recognized for entry into universities, focusing on a broad range of subjects. Foundation courses, usually lasting one year, offer specialized academic pathways tailored to specific fields such as engineering or business, providing a more direct route to related degree programs. Both pathways serve as essential stepping stones for secondary school graduates aiming to pursue higher education.
Recognition and Accreditation
Matriculation programs generally receive widespread recognition and accreditation from national education boards such as the Malaysian Ministry of Education, ensuring eligibility for local university admissions. Foundation programs often hold accreditation from individual universities or private institutions, which can limit recognition primarily to those specific universities or regions. The choice between matriculation and foundation depends on targeted university recognition and the intended academic pathway.
Cost and Financial Considerations
Matriculation programs often have lower tuition fees compared to foundation courses, making them a more budget-friendly option for secondary students. Foundation programs may involve additional costs such as higher lab fees and course materials, impacting the overall financial commitment. Scholarships and financial aid opportunities can vary significantly between matriculation and foundation pathways, influencing the total expenditure for students and families.
Career Opportunities and University Admissions
Matriculation offers broad-based secondary education recognized by public universities, providing direct access to various degree programs, especially in engineering, medicine, and law, while Foundation programs, often specific to private universities, tailor curricula to particular fields with streamlined admission paths. Career opportunities following Matriculation are diverse, benefiting from well-established recognition and acceptance in both local and international institutions, whereas Foundation students may find faster entry into specialized sectors aligned with their foundation studies. Universities typically view Matriculation certifications as standardized benchmarks allowing flexible degree options, while Foundation qualifications serve as focused preparatory routes enhancing students' readiness for niche academic disciplines and career tracks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Program
Matriculation programs offer a standardized curriculum recognized nationwide, providing students with solid preparation for local universities but may limit exposure to international subjects. Foundation programs deliver specialized courses aligned with specific fields or institutions, enabling smoother transition to targeted degree programs but sometimes lacking broad subject coverage. Choosing between Matriculation and Foundation depends on career goals, learning preferences, and desired university pathways.
Choosing the Right Path: Matriculation or Foundation
Choosing between Matriculation and Foundation programs depends on your academic goals and preferred learning style. Matriculation offers a structured and comprehensive syllabus recognized by local universities, ideal for students seeking a traditional pathway to pre-university education. Foundation programs provide specialized curriculum flexibility, often linked to specific universities or professional fields, making them suitable for students aiming for tailored expertise and smoother transition into degree courses.
Matriculation vs Foundation Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com