Inclusion fosters a learning environment where students with diverse needs participate fully in all classroom activities, emphasizing belonging and equal opportunities. Integration often places students with special needs in mainstream settings but may not guarantee active participation or adaptation to their unique requirements. Effective inclusion promotes tailored support and collaborative teaching strategies that enhance educational outcomes for all students.
Table of Comparison
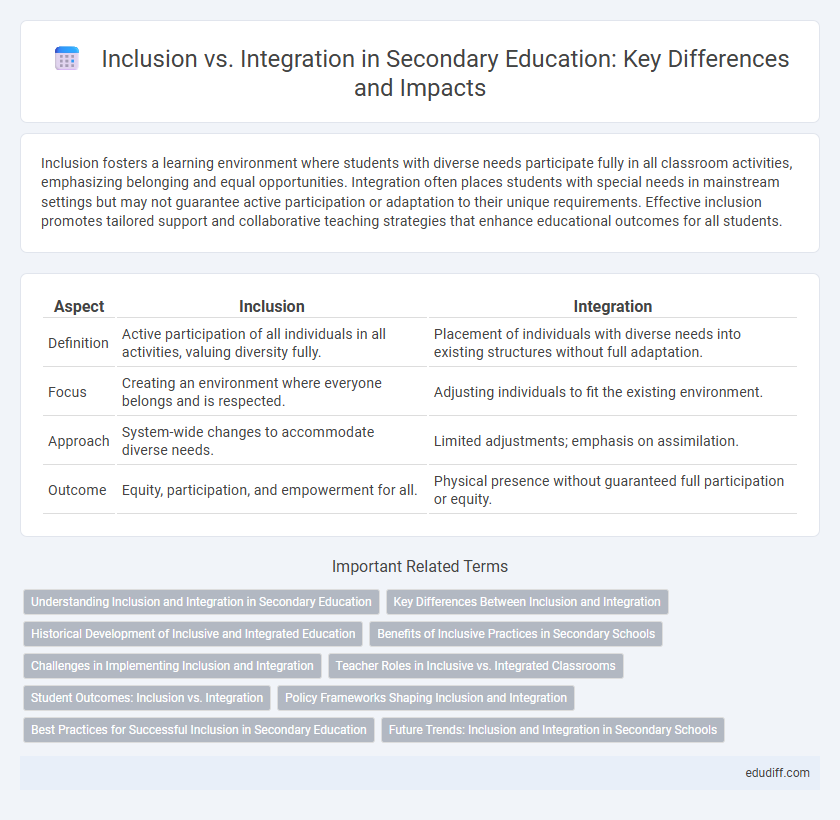
| Aspect | Inclusion | Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation of all individuals in all activities, valuing diversity fully. | Placement of individuals with diverse needs into existing structures without full adaptation. |
| Focus | Creating an environment where everyone belongs and is respected. | Adjusting individuals to fit the existing environment. |
| Approach | System-wide changes to accommodate diverse needs. | Limited adjustments; emphasis on assimilation. |
| Outcome | Equity, participation, and empowerment for all. | Physical presence without guaranteed full participation or equity. |
Understanding Inclusion and Integration in Secondary Education
In secondary education, inclusion involves creating learning environments where students with diverse abilities participate fully in general education classrooms with appropriate support, promoting equity and belonging. Integration traditionally refers to placing students with special needs into existing classrooms without necessarily providing tailored resources to meet their individual educational requirements. Understanding the distinctions between inclusion and integration is essential for educators to implement effective strategies that support academic success and social development for all learners.
Key Differences Between Inclusion and Integration
Inclusion emphasizes full participation and equal access for all students within mainstream classrooms, promoting diverse learning environments where individual needs are met. Integration typically places students with disabilities in general education settings but often requires them to adapt to the existing structure, sometimes without adequate support. Key differences include the level of support, curriculum adaptation, and the goal of fostering belonging versus mere physical placement.
Historical Development of Inclusive and Integrated Education
The historical development of inclusive and integrated education dates back to the mid-20th century, evolving from segregated special education models towards more unified classrooms. Early integration efforts in the 1960s and 1970s primarily placed students with disabilities in general education settings without significant support, highlighting the need for inclusive strategies. By the 1990s, inclusive education emphasized adapting curricula and teaching methods to meet diverse learners' needs, promoting equal access and participation for all students.
Benefits of Inclusive Practices in Secondary Schools
Inclusive practices in secondary schools promote equity by addressing diverse learning needs and fostering a supportive environment that enhances academic achievement and social development. Students in inclusive settings demonstrate improved communication skills, higher self-esteem, and greater acceptance of differences among peers. Evidence shows that inclusive education reduces behavioral issues and dropout rates, contributing to a more positive and collaborative school culture.
Challenges in Implementing Inclusion and Integration
Implementing inclusion and integration in secondary education faces challenges such as insufficient teacher training and lack of adaptive resources for diverse learning needs. Resistance from staff and students often hinders the creation of truly inclusive environments. Limited funding and inadequate policy support further exacerbate difficulties in accommodating students with disabilities or special needs.
Teacher Roles in Inclusive vs. Integrated Classrooms
In inclusive classrooms, teachers adopt a facilitator role, adapting instruction to meet diverse student needs and promoting collaboration among all learners. In integrated classrooms, teachers primarily deliver content with some accommodations for students with disabilities, focusing on physical placement rather than full participation. Effective inclusion requires teachers to use differentiated strategies, continuous assessment, and flexible grouping to ensure equitable access and meaningful engagement.
Student Outcomes: Inclusion vs. Integration
Inclusion in secondary education fosters higher student outcomes by promoting social-emotional growth and academic achievement through full participation in general classrooms. Integration often results in minimal peer interaction and limited access to grade-level curriculum, hindering skill development and self-esteem. Research indicates inclusive settings increase engagement, improve communication skills, and enhance long-term success for students with diverse learning needs.
Policy Frameworks Shaping Inclusion and Integration
Policy frameworks governing inclusion and integration emphasize the importance of equitable access to education, social services, and employment for marginalized groups. They prioritize removing systemic barriers and promoting cultural sensitivity, ensuring that diverse populations participate fully in social and economic life. Effective policies incorporate community engagement, anti-discrimination laws, and resource allocation to create inclusive environments rather than merely integrating individuals into existing structures.
Best Practices for Successful Inclusion in Secondary Education
Successful inclusion in secondary education requires tailored instructional strategies that address diverse learning needs, such as differentiated instruction and co-teaching models. Collaborative planning among general and special education teachers, supported by ongoing professional development, enhances student engagement and academic outcomes. Access to assistive technologies and individualized accommodations ensures equitable participation and fosters a supportive learning environment.
Future Trends: Inclusion and Integration in Secondary Schools
Future trends in secondary schools emphasize inclusive education models that prioritize personalized learning and social-emotional development to accommodate diverse student needs effectively. Integration efforts will increasingly leverage technology to create adaptive learning environments fostering collaboration among students with varying abilities. Data-driven approaches will guide policy and classroom practices, promoting equity and reducing achievement gaps through tailored support systems.
Inclusion vs Integration Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com