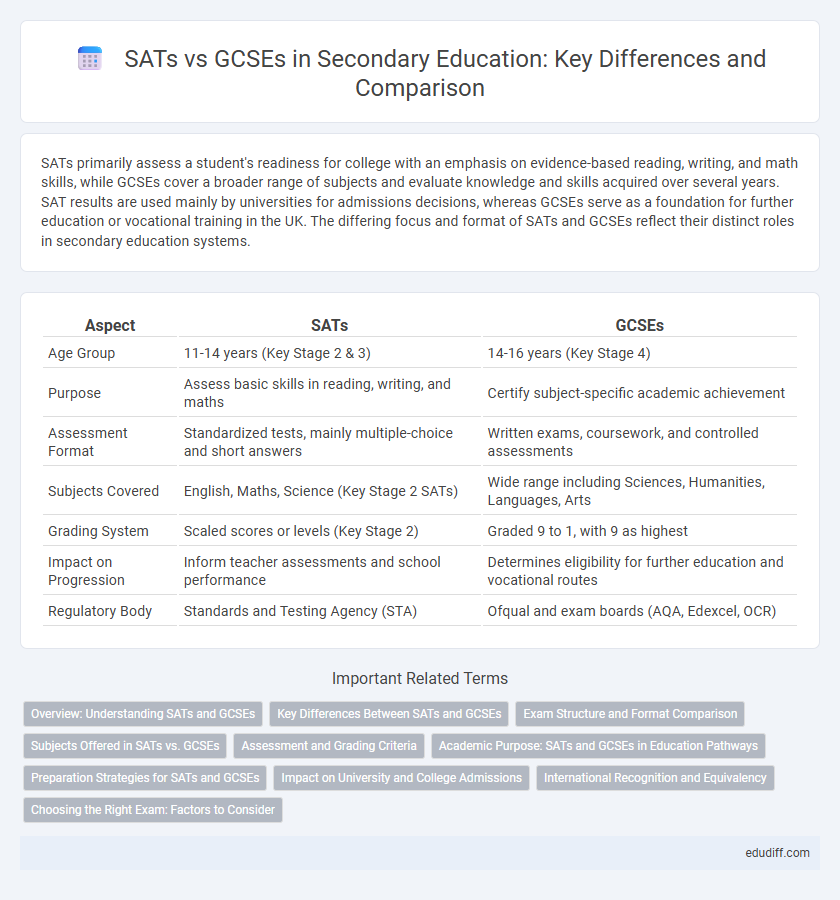
SATs primarily assess a student's readiness for college with an emphasis on evidence-based reading, writing, and math skills, while GCSEs cover a broader range of subjects and evaluate knowledge and skills acquired over several years. SAT results are used mainly by universities for admissions decisions, whereas GCSEs serve as a foundation for further education or vocational training in the UK. The differing focus and format of SATs and GCSEs reflect their distinct roles in secondary education systems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | SATs | GCSEs |
|---|---|---|
| Age Group | 11-14 years (Key Stage 2 & 3) | 14-16 years (Key Stage 4) |
| Purpose | Assess basic skills in reading, writing, and maths | Certify subject-specific academic achievement |
| Assessment Format | Standardized tests, mainly multiple-choice and short answers | Written exams, coursework, and controlled assessments |
| Subjects Covered | English, Maths, Science (Key Stage 2 SATs) | Wide range including Sciences, Humanities, Languages, Arts |
| Grading System | Scaled scores or levels (Key Stage 2) | Graded 9 to 1, with 9 as highest |
| Impact on Progression | Inform teacher assessments and school performance | Determines eligibility for further education and vocational routes |
| Regulatory Body | Standards and Testing Agency (STA) | Ofqual and exam boards (AQA, Edexcel, OCR) |
Overview: Understanding SATs and GCSEs
SATs and GCSEs serve distinct roles in the UK education system, with SATs typically administered to primary school students in Year 6 to assess core skills in English and math. GCSEs are more comprehensive exams taken at the end of secondary education, usually in Year 11, covering a wide range of subjects including sciences, humanities, and languages. These assessments help gauge student progress, inform educational pathways, and influence future academic and career opportunities.
Key Differences Between SATs and GCSEs
SATs primarily assess students in the US at the high school level for college admissions, focusing on math, evidence-based reading, and writing skills. GCSEs, taken in the UK usually at age 16, cover a broader range of subjects including sciences, humanities, languages, and arts, reflecting comprehensive secondary education. The SAT is a standardized test emphasizing reasoning and problem-solving, while the GCSE evaluates subject-specific knowledge through coursework and exams.
Exam Structure and Format Comparison
The SATs feature a structured format with sections in Math, Evidence-Based Reading, and Writing, each divided into multiple-choice and grid-in questions, emphasizing problem-solving and critical reading skills. In contrast, GCSEs offer subject-specific exams, combining written papers, coursework, and practical assessments, which vary significantly across subjects like English, Science, and Mathematics. The SAT's standardized timing and format deliver a uniform assessment model, whereas GCSEs provide a diverse evaluation approach tailored to different academic disciplines.
Subjects Offered in SATs vs. GCSEs
SATs primarily assess core subjects such as Math, Evidence-Based Reading, and Writing, emphasizing fundamental skills for college readiness in the United States. GCSEs in the United Kingdom offer a broader range of subjects, including Sciences, Humanities, Languages, and Arts, allowing students to specialize in areas of interest alongside mandatory core subjects like English, Math, and Science. This variation reflects the differing educational priorities, with SATs focusing on standardized assessment for university admission, while GCSEs provide a more comprehensive academic foundation for further education or vocational pathways.
Assessment and Grading Criteria
SATs primarily assess students' proficiency in core subjects like English and Mathematics through standardized tests, using a scaled scoring system from 400 to 1600. GCSEs evaluate a broader range of subjects with a mix of written exams, coursework, and practical assessments, graded on a numerical scale from 9 to 1. The SAT's focus is on college readiness, while GCSEs emphasize subject-specific knowledge and skills for secondary education progression.
Academic Purpose: SATs and GCSEs in Education Pathways
SATs primarily assess critical reading, math, and writing skills to support university admissions, reflecting students' readiness for higher education. GCSEs provide a broad foundation across multiple subjects, ensuring comprehensive secondary education and qualification for advanced studies or vocational training. Both exams serve distinct academic purposes, guiding students through critical educational milestones and influencing their future academic pathways.
Preparation Strategies for SATs and GCSEs
Effective preparation for SATs emphasizes mastery of core subjects such as mathematics, English reading, and writing through practice papers and timed exercises that enhance exam technique and time management skills. GCSEs require a broader subject focus, demanding consistent revision across multiple disciplines, incorporating past papers, revision guides, and active recall methods to improve retention. Tailoring study plans to individual strengths and weaknesses while integrating regular assessment feedback optimizes performance for both SATs and GCSEs.
Impact on University and College Admissions
University and college admissions often prioritize GCSE results as a baseline for academic readiness, while SAT scores are heavily weighted in countries like the United States for evaluating applicants' aptitude and potential. High GCSE grades demonstrate consistent academic performance across multiple subjects, which can influence offers from UK universities, whereas top SAT scores can enhance competitiveness in international admissions. Differences in emphasis reflect varied educational systems, with GCSEs affecting domestic acceptance and SATs impacting global opportunities.
International Recognition and Equivalency
SATs hold widespread international recognition, often used by universities worldwide as a standard measure for college admissions, especially in the United States and increasingly in other countries. GCSEs are primarily recognized within the UK and Commonwealth countries, with their equivalency to other qualifications varying by region and institution. The SAT's global acceptance makes it a preferred option for students aiming to study abroad, while GCSEs provide a solid academic foundation for secondary education within specific educational systems.
Choosing the Right Exam: Factors to Consider
Evaluate academic goals, subject strengths, and future university requirements when choosing between SATs and GCSEs, as each exam serves different educational pathways. Consider the SAT for U.S. college admissions emphasizing critical reading and math skills, while GCSEs assess broader UK curriculum knowledge across diverse subjects. Assess exam format, grading systems, and recognition by target institutions to align exam choice with long-term academic and career objectives.
SATs vs GCSEs Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com