Detentions offer a constructive alternative to suspensions by promoting accountability while keeping students engaged in the learning environment. Suspensions remove students from school, often leading to missed academic opportunities and increased risk of disengagement. Effective disciplinary strategies balance consequences with support to maintain student involvement and encourage positive behavior.
Table of Comparison
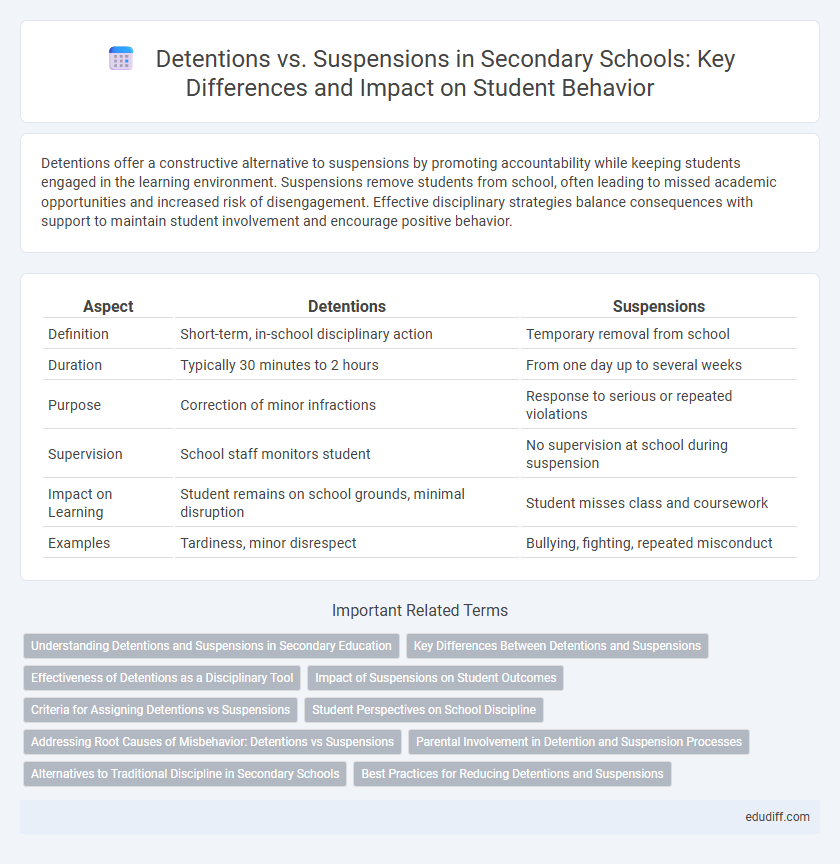
| Aspect | Detentions | Suspensions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, in-school disciplinary action | Temporary removal from school |
| Duration | Typically 30 minutes to 2 hours | From one day up to several weeks |
| Purpose | Correction of minor infractions | Response to serious or repeated violations |
| Supervision | School staff monitors student | No supervision at school during suspension |
| Impact on Learning | Student remains on school grounds, minimal disruption | Student misses class and coursework |
| Examples | Tardiness, minor disrespect | Bullying, fighting, repeated misconduct |
Understanding Detentions and Suspensions in Secondary Education
Detentions in secondary education serve as a disciplinary measure where students remain after school or during breaks to reflect on their behavior, often lasting from 15 minutes to several hours. Suspensions involve temporarily removing students from the school environment for more serious infractions, ranging from a day to several weeks, impacting their academic progress and social engagement. Both detentions and suspensions aim to correct misconduct, but suspensions carry more severe consequences and require reintegration strategies to support students' return.
Key Differences Between Detentions and Suspensions
Detentions are short-term disciplinary actions requiring students to remain after school or during breaks, often used for minor infractions, whereas suspensions involve temporary removal from school due to more serious offenses. Detentions aim to correct behavior through supervised reflection, while suspensions restrict student access to academic and social activities, signaling more severe consequences. The length of suspensions varies from days to weeks, significantly impacting student attendance compared to the typically brief duration of detentions.
Effectiveness of Detentions as a Disciplinary Tool
Detentions are often more effective than suspensions in addressing student behavior as they maintain the student's engagement with the school environment while reinforcing accountability. Research shows that detentions provide immediate consequences, which can reduce repeat offenses and support behavior correction without removing students from the learning process. Schools implementing structured detention programs report lower rates of chronic misbehavior compared to those relying primarily on suspensions.
Impact of Suspensions on Student Outcomes
Suspensions often lead to increased absenteeism and lower academic achievement among secondary students, contributing to higher dropout rates. Research shows that students who are suspended are more likely to experience disengagement from school and decreased graduation rates. Schools implementing restorative practices report improved student behavior and academic outcomes compared to traditional suspension methods.
Criteria for Assigning Detentions vs Suspensions
Criteria for assigning detentions versus suspensions in secondary schools depend on the severity and frequency of the misconduct. Detentions are typically assigned for minor infractions such as tardiness, talking in class, or minor disruptions, emphasizing corrective measures and behavior reinforcement. Suspensions are reserved for more serious offenses like violence, drug possession, or repeated violations, prioritizing safety and enforcing school policies through temporary removal from the learning environment.
Student Perspectives on School Discipline
Students often view detentions as less disruptive and more conducive to reflecting on their behavior compared to suspensions, which remove them from the learning environment entirely. Many express that suspensions can lead to feelings of alienation and academic setbacks, whereas detentions allow for continued engagement with schoolwork and peer interactions. This perspective highlights the importance of disciplinary measures that support student accountability while minimizing educational disruption.
Addressing Root Causes of Misbehavior: Detentions vs Suspensions
Detentions and suspensions serve distinct roles in addressing student misbehavior, with detentions focusing on correcting specific actions through immediate consequences, while suspensions remove students from the school environment to signal serious infractions. Addressing root causes requires a comprehensive approach that includes behavioral interventions, counseling, and restorative practices to reduce repeat offenses and improve student outcomes. Research shows that proactive strategies alongside detentions can mitigate disruptions without the negative impact on academic achievement associated with suspensions.
Parental Involvement in Detention and Suspension Processes
Parental involvement in detention and suspension processes significantly influences student outcomes by fostering communication and accountability between schools and families. Active engagement from parents during disciplinary actions promotes transparency, encourages behavioral improvements, and supports students' academic success. Schools that implement structured systems for parental notification and collaboration during detentions and suspensions see reduced recidivism and stronger home-school partnerships.
Alternatives to Traditional Discipline in Secondary Schools
Restorative justice programs and positive behavioral interventions offer effective alternatives to traditional detentions and suspensions in secondary schools by addressing underlying issues and promoting accountability. Implementing peer mediation and counseling services reduces repeat offenses and improves student relationships, fostering a supportive school environment. Data from the U.S. Department of Education indicates that schools adopting these alternatives see a significant decrease in exclusionary discipline and enhanced academic engagement.
Best Practices for Reducing Detentions and Suspensions
Implementing restorative justice programs and providing social-emotional learning support significantly reduce detentions and suspensions in secondary schools. Emphasizing positive behavioral interventions and consistent communication between staff, students, and families fosters a supportive school climate that addresses underlying issues. Data-driven approaches to monitor disciplinary actions ensure equitable treatment and help tailor interventions effectively.
Detentions vs Suspensions Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com