State schools offer free education funded by the government, ensuring accessibility for all children, while independent schools charge tuition fees and often provide specialized programs and smaller class sizes. Independent schools may have more resources for extracurricular activities and higher academic standards, but state schools benefit from diverse student populations and government support. Choosing between the two depends on factors such as financial capacity, desired educational environment, and individual student needs.
Table of Comparison
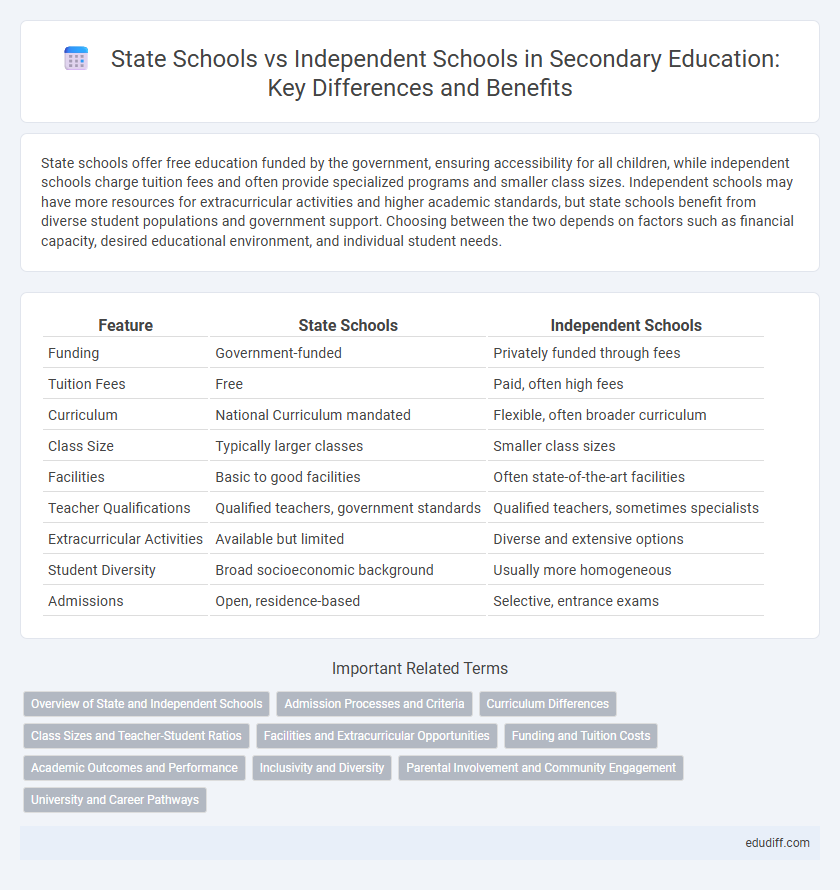
| Feature | State Schools | Independent Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government-funded | Privately funded through fees |
| Tuition Fees | Free | Paid, often high fees |
| Curriculum | National Curriculum mandated | Flexible, often broader curriculum |
| Class Size | Typically larger classes | Smaller class sizes |
| Facilities | Basic to good facilities | Often state-of-the-art facilities |
| Teacher Qualifications | Qualified teachers, government standards | Qualified teachers, sometimes specialists |
| Extracurricular Activities | Available but limited | Diverse and extensive options |
| Student Diversity | Broad socioeconomic background | Usually more homogeneous |
| Admissions | Open, residence-based | Selective, entrance exams |
Overview of State and Independent Schools
State schools in the UK are government-funded institutions providing free education to all students, following the national curriculum and regulated by Ofsted to ensure consistent standards. Independent schools, also known as private schools, operate independently of government funding, charging fees and often offering specialized curricula, such as the International Baccalaureate or advanced vocational programs. The key differences lie in funding sources, governance, curriculum flexibility, and sometimes access to resources and extracurricular opportunities.
Admission Processes and Criteria
State schools primarily admit students based on catchment area residency, often requiring proof of address for enrollment, ensuring local community access to education. Independent schools utilize selective admission criteria, including entrance exams, interviews, and previous academic records, to assess student suitability and potential. Both systems emphasize adherence to their respective policies and deadlines, but independent schools tend to have more rigorous and competitive procedures.
Curriculum Differences
State schools in the UK follow the National Curriculum, which ensures a standardized education framework emphasizing core subjects like English, Mathematics, and Science, with a focus on accessibility and government-regulated assessments such as GCSEs and A-levels. Independent schools have the flexibility to design bespoke curricula, often incorporating the International Baccalaureate, Advanced Placement courses, or specialized programs that foster critical thinking and tailored academic enrichment. Curriculum differences highlight state schools' uniformity and inclusivity, contrasted with independent schools' adaptability and emphasis on broad, often internationally recognized qualifications.
Class Sizes and Teacher-Student Ratios
State schools typically have larger class sizes, averaging around 25-30 students per class, which can impact individual student attention and personalized learning. Independent schools often maintain smaller class sizes, usually between 10-15 students, allowing for lower teacher-student ratios and enhanced individualized support. Research indicates that lower teacher-student ratios contribute to improved academic outcomes and higher student engagement.
Facilities and Extracurricular Opportunities
Independent schools often boast superior facilities, including advanced science labs, sports complexes, and performing arts centers, which enhance student learning experiences. State schools may face budget constraints limiting access to specialized equipment and extracurricular programs, but many still offer diverse clubs, sports teams, and arts activities to support student development. Access to high-quality resources and a broad range of extracurricular opportunities plays a crucial role in student engagement and skill-building across both school types.
Funding and Tuition Costs
State schools receive government funding, significantly reducing or eliminating tuition costs for students, making education more accessible to a wider population. Independent schools rely primarily on tuition fees paid by families, resulting in higher costs but often more resources and facilities per student. The disparity in funding sources directly impacts student demographics, academic offerings, and overall school experience in secondary education.
Academic Outcomes and Performance
State schools often demonstrate strong academic outcomes due to standardized curricula and government oversight, which ensures consistent performance metrics. Independent schools typically report higher exam results and university admission rates, attributed to smaller class sizes and enhanced resources. Research indicates that socio-economic factors heavily influence academic performance across both school types, highlighting the importance of personalized learning approaches.
Inclusivity and Diversity
State schools often demonstrate greater inclusivity and diversity by serving a broader demographic, including students from various socioeconomic backgrounds and ethnicities. Independent schools typically have selective admissions, which can limit the range of cultural and economic diversity within their student body. Inclusive practices in state schools foster a more representative educational environment that reflects societal diversity and promotes equal opportunities.
Parental Involvement and Community Engagement
Parental involvement in state schools often includes active participation in school councils and volunteering for events, enhancing community ties and student support systems. Independent schools frequently encourage personalized parent-teacher communication and exclusive activities, fostering a close-knit community with tailored educational experiences. Both sectors benefit from strong community engagement, yet state schools emphasize broader accessibility while independent schools prioritize individualized parental contributions.
University and Career Pathways
State schools often provide broad access to diverse university pathways and vocational programs aligned with local employment opportunities, supported by government funding. Independent schools tend to offer specialized academic curricula, extracurricular activities, and extensive university counseling services, enhancing students' chances for admission to prestigious universities and competitive career fields. Both school types contribute uniquely to career readiness, with state schools focusing on inclusive access and independent schools emphasizing tailored academic excellence.
State schools vs Independent schools Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com