SEN support provides tailored educational interventions designed to meet the unique needs of students with special educational needs, offering specialized resources and staff expertise. Mainstream provision ensures inclusive education where students with and without SEN learn alongside each other, fostering social integration and access to the general curriculum. Effective collaboration between SEN support and mainstream provision maximizes student potential by balancing individualized assistance with inclusive learning environments.
Table of Comparison
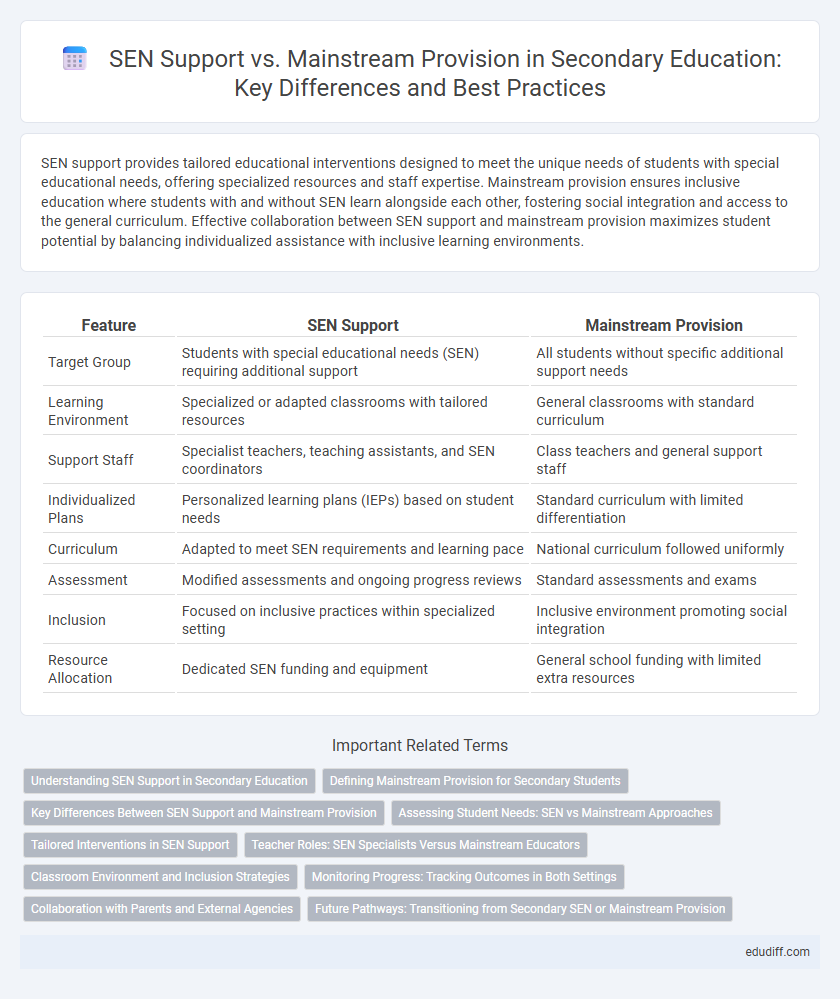
| Feature | SEN Support | Mainstream Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Target Group | Students with special educational needs (SEN) requiring additional support | All students without specific additional support needs |
| Learning Environment | Specialized or adapted classrooms with tailored resources | General classrooms with standard curriculum |
| Support Staff | Specialist teachers, teaching assistants, and SEN coordinators | Class teachers and general support staff |
| Individualized Plans | Personalized learning plans (IEPs) based on student needs | Standard curriculum with limited differentiation |
| Curriculum | Adapted to meet SEN requirements and learning pace | National curriculum followed uniformly |
| Assessment | Modified assessments and ongoing progress reviews | Standard assessments and exams |
| Inclusion | Focused on inclusive practices within specialized setting | Inclusive environment promoting social integration |
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated SEN funding and equipment | General school funding with limited extra resources |
Understanding SEN Support in Secondary Education
SEN support in secondary education involves tailored interventions designed to meet the specific learning needs of students with special educational needs, ensuring equal access to the curriculum. This support often includes individualized education plans, specialist teaching, and targeted resources to promote academic progress and social inclusion. Effective SEN provision in secondary schools relies on early identification, continuous monitoring, and close collaboration between educators, parents, and external professionals.
Defining Mainstream Provision for Secondary Students
Mainstream provision for secondary students involves placing learners with special educational needs (SEN) in general education classrooms alongside their peers, promoting inclusive education and equal access to the curriculum. This approach emphasizes differentiated instruction, tailored support, and collaboration between SEN specialists and mainstream teachers to address diverse learning needs. Effective mainstream provision also requires adaptive resources, staff training, and ongoing assessment to ensure academic progress and social integration for all secondary students.
Key Differences Between SEN Support and Mainstream Provision
SEN Support caters specifically to students with identified special educational needs, providing tailored interventions, personalized learning plans, and access to specialized staff to address individual challenges. Mainstream Provision serves the broader student population, utilizing a standard curriculum and general teaching methods, with limited modifications for inclusivity. The key differences lie in the level of individualized support, specialist resources, and targeted strategies employed to meet diverse learning requirements.
Assessing Student Needs: SEN vs Mainstream Approaches
Assessing student needs in SEN support involves detailed, individualized evaluations to identify specific learning difficulties and tailor interventions accordingly. In mainstream provision, assessments often focus on general academic progress and classroom performance, relying on standardized testing and teacher observations. SEN assessments prioritize multi-disciplinary input and ongoing review to adapt strategies, ensuring targeted support for diverse student challenges.
Tailored Interventions in SEN Support
Tailored interventions in SEN Support are designed to meet the specific learning needs of each student, providing personalized strategies and resources that address individual challenges. These interventions often include specialized teaching methods, assistive technologies, and targeted skill-building activities that enhance engagement and academic progress. In comparison to mainstream provision, SEN Support prioritizes flexibility and specificity to promote inclusion and improve outcomes for students with special educational needs.
Teacher Roles: SEN Specialists Versus Mainstream Educators
SEN specialists focus on tailored interventions and individualized learning plans to support students with special educational needs effectively. Mainstream educators integrate inclusive practices, adapting general curricula and classroom management to accommodate diverse learners. Collaboration between SEN specialists and mainstream teachers enhances comprehensive support, promoting student progress in inclusive settings.
Classroom Environment and Inclusion Strategies
SEN support within a classroom environment prioritizes tailored teaching methods and adaptive resources to meet diverse learning needs, fostering an inclusive atmosphere for students with special educational needs. Mainstream provision emphasizes universal design for learning and collaborative teaching approaches to integrate all students effectively, promoting peer interaction and participation. Inclusion strategies in both settings focus on differentiated instruction, ongoing assessment, and personalized support plans to ensure equitable access and positive educational outcomes.
Monitoring Progress: Tracking Outcomes in Both Settings
Monitoring progress in SEN support involves personalized tracking systems that measure individualized educational goals, while mainstream provision relies on standardized assessments and curriculum benchmarks. Data-driven tools such as progress monitoring software enable frequent evaluation of learning outcomes, facilitating timely adjustments in teaching strategies across both settings. Integration of qualitative and quantitative metrics ensures comprehensive analysis of student development, promoting targeted interventions and inclusive education practices.
Collaboration with Parents and External Agencies
Effective SEN support hinges on seamless collaboration with parents and external agencies, ensuring tailored interventions that meet individual student needs. Mainstream provision benefits from this partnership by fostering inclusive environments where specialized expertise and parental insights contribute to holistic educational outcomes. Coordinated communication channels between schools, families, and specialists enhance responsiveness and resource allocation, optimizing support strategies for students with special educational needs.
Future Pathways: Transitioning from Secondary SEN or Mainstream Provision
Transitioning from secondary SEN support or mainstream provision requires tailored pathways that address individual learning needs and promote independent living skills. Future pathways often include further education, vocational training, or supported employment, ensuring smoother integration into adult life. Collaboration between educators, families, and support services is essential to create personalized transition plans that maximize long-term success.
SEN Support vs Mainstream Provision Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com