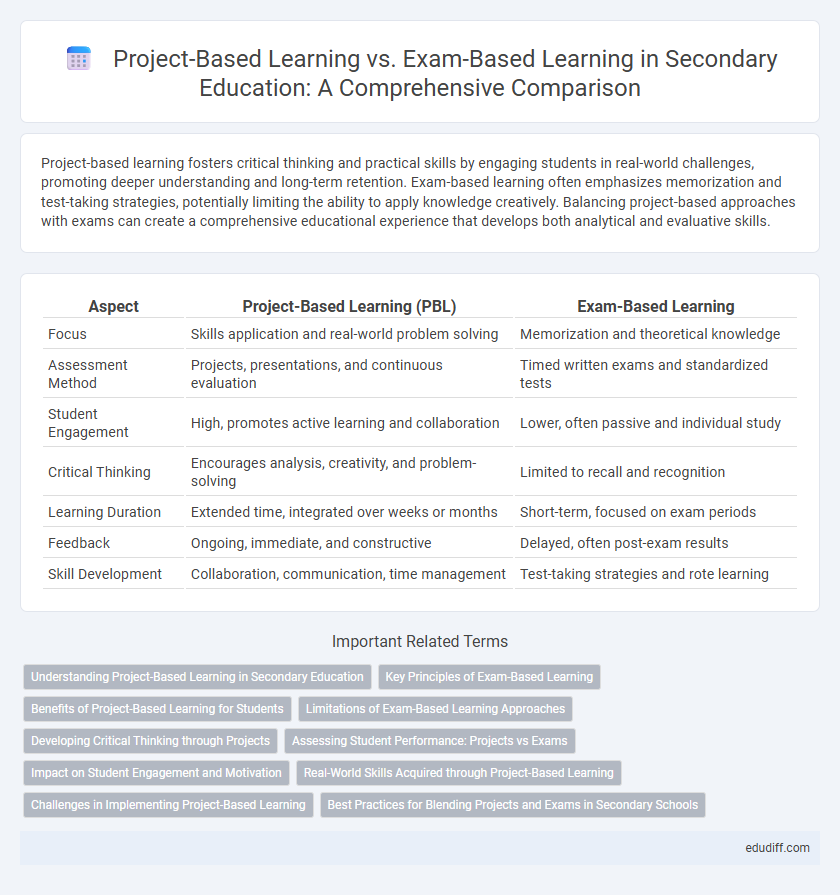
Project-based learning fosters critical thinking and practical skills by engaging students in real-world challenges, promoting deeper understanding and long-term retention. Exam-based learning often emphasizes memorization and test-taking strategies, potentially limiting the ability to apply knowledge creatively. Balancing project-based approaches with exams can create a comprehensive educational experience that develops both analytical and evaluative skills.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Exam-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Skills application and real-world problem solving | Memorization and theoretical knowledge |
| Assessment Method | Projects, presentations, and continuous evaluation | Timed written exams and standardized tests |
| Student Engagement | High, promotes active learning and collaboration | Lower, often passive and individual study |
| Critical Thinking | Encourages analysis, creativity, and problem-solving | Limited to recall and recognition |
| Learning Duration | Extended time, integrated over weeks or months | Short-term, focused on exam periods |
| Feedback | Ongoing, immediate, and constructive | Delayed, often post-exam results |
| Skill Development | Collaboration, communication, time management | Test-taking strategies and rote learning |
Understanding Project-Based Learning in Secondary Education
Project-Based Learning (PBL) in secondary education emphasizes active student engagement through real-world projects, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Unlike traditional exam-based learning, PBL allows students to apply knowledge practically, enhancing retention and deeper understanding of subject matter. Research indicates that PBL improves learner motivation and prepares students for future academic and career challenges by developing essential 21st-century skills.
Key Principles of Exam-Based Learning
Exam-Based Learning emphasizes mastery of subject content through standardized assessments, promoting recall and application under timed conditions. This approach prioritizes clear learning objectives aligned with curriculum standards, ensuring measurable outcomes for student performance. Regular testing reinforces retention and identifies areas needing improvement, driving focused instructional strategies.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning for Students
Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on projects relevant to their lives. This approach promotes deeper understanding and retention of knowledge compared to traditional exam-based learning, which often emphasizes memorization. Students develop communication and time-management skills essential for future academic and career success.
Limitations of Exam-Based Learning Approaches
Exam-based learning often promotes rote memorization over critical thinking, limiting students' ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. This approach can increase anxiety and reduce motivation, impacting overall academic performance. Additionally, exams tend to assess narrow skill sets, neglecting creativity, problem-solving, and collaboration essential for secondary education success.
Developing Critical Thinking through Projects
Project-based learning enhances critical thinking by engaging secondary students in real-world problem-solving and collaborative investigations, fostering analytical skills beyond rote memorization. Unlike exam-based learning, which emphasizes standardized testing, project-based approaches require synthesis, evaluation, and creative application of knowledge. Evidence shows students involved in project-based activities develop stronger decision-making and reasoning abilities vital for academic and career success.
Assessing Student Performance: Projects vs Exams
Project-based learning assesses student performance through practical application of knowledge, encouraging critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, which provides a holistic evaluation of skills. Exam-based learning primarily measures students' ability to recall and apply information under timed conditions, emphasizing memorization and standardized testing metrics. Combining both methods can offer a more comprehensive understanding of student competencies and learning outcomes.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-Based Learning significantly enhances student engagement and motivation by fostering hands-on, collaborative experiences that promote active problem-solving and real-world application. Exam-Based Learning often limits motivation by emphasizing rote memorization and high-stakes testing, which can induce anxiety and reduce intrinsic interest. Research shows students in project-based environments demonstrate higher persistence, creativity, and a deeper connection to the subject matter compared to those in exam-focused settings.
Real-World Skills Acquired through Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) equips secondary students with critical real-world skills such as problem-solving, collaboration, and effective communication by engaging them in hands-on, interdisciplinary projects. Unlike Exam-Based Learning, which primarily tests rote memorization, PBL fosters adaptability and creative thinking essential for modern workplaces. This approach enhances students' ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, preparing them for success beyond the classroom.
Challenges in Implementing Project-Based Learning
Implementing Project-Based Learning (PBL) in secondary education faces challenges such as the demand for extensive teacher training and the need for significant classroom resources. Assessment complexities arise because PBL requires evaluating skills like collaboration and critical thinking, which are not easily measured by traditional exams. Time constraints and curriculum coverage pressure also hinder the seamless integration of PBL within standardized academic schedules.
Best Practices for Blending Projects and Exams in Secondary Schools
Effective integration of project-based learning and exam-based assessment in secondary schools enhances critical thinking and content mastery by balancing practical application with standardized evaluation. Incorporating project milestones aligned with exam objectives ensures consistent knowledge reinforcement and skill development throughout the term. Utilizing rubrics that assess both project creativity and exam readiness fosters comprehensive learning outcomes and student engagement.
Project-Based Learning vs Exam-Based Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com