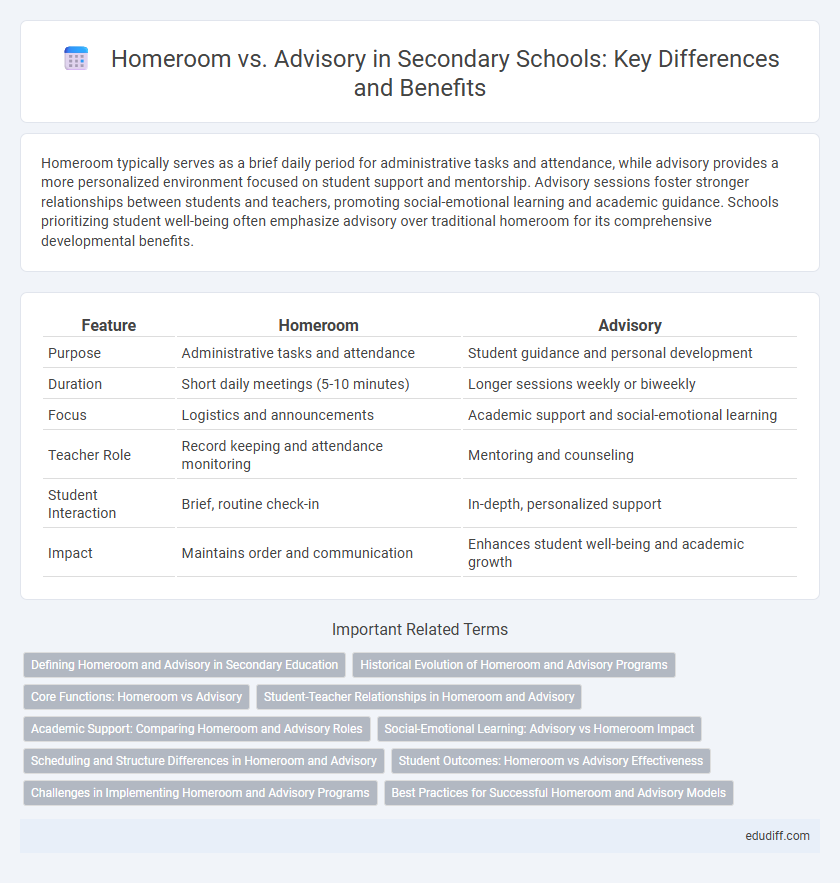
Homeroom typically serves as a brief daily period for administrative tasks and attendance, while advisory provides a more personalized environment focused on student support and mentorship. Advisory sessions foster stronger relationships between students and teachers, promoting social-emotional learning and academic guidance. Schools prioritizing student well-being often emphasize advisory over traditional homeroom for its comprehensive developmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Homeroom | Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Administrative tasks and attendance | Student guidance and personal development |
| Duration | Short daily meetings (5-10 minutes) | Longer sessions weekly or biweekly |
| Focus | Logistics and announcements | Academic support and social-emotional learning |
| Teacher Role | Record keeping and attendance monitoring | Mentoring and counseling |
| Student Interaction | Brief, routine check-in | In-depth, personalized support |
| Impact | Maintains order and communication | Enhances student well-being and academic growth |
Defining Homeroom and Advisory in Secondary Education
Homeroom in secondary education serves as a designated period where students receive daily administrative support, attendance tracking, and essential announcements from a homeroom teacher assigned to a specific group. Advisory, by contrast, focuses on fostering personal development, academic guidance, and social-emotional learning through smaller, more interactive student groups led by an advisor. Both structures aim to enhance student engagement but differ in their primary objectives and instructional approach within the secondary school environment.
Historical Evolution of Homeroom and Advisory Programs
Homeroom programs originated in the early 20th century as a method to streamline attendance taking and disseminate school announcements, serving primarily administrative functions. Advisory programs evolved later, particularly in the late 20th century, emphasizing personalized student guidance, social-emotional support, and academic mentoring. The transition reflects a broader educational shift from focusing solely on organizational tasks to fostering holistic student development.
Core Functions: Homeroom vs Advisory
Homeroom primarily functions as a daily attendance and administrative checkpoint, ensuring students receive important announcements and basic organizational support. Advisory focuses on personalized student development, offering guidance on academic progress, social-emotional well-being, and goal-setting strategies. Effective differentiation between homeroom and advisory optimizes student engagement and targeted support within school environments.
Student-Teacher Relationships in Homeroom and Advisory
Student-teacher relationships in homeroom sessions foster familiarity through daily attendance, enabling teachers to monitor academic progress and social-emotional needs consistently. Advisory periods deepen these connections by providing personalized guidance and support, promoting trust and open communication between students and advisors. Both settings enhance student engagement, but advisory's targeted support often leads to stronger mentorship and improved student outcomes.
Academic Support: Comparing Homeroom and Advisory Roles
Homeroom primarily functions as a logistical space for attendance and announcements, offering limited academic support, whereas advisory sessions provide personalized guidance tailored to students' academic progress and social-emotional needs. Advisory roles often involve small group interactions that foster goal-setting, time management skills, and direct academic mentoring, enhancing student engagement and achievement. The targeted support in advisory programs contributes to improved academic outcomes and stronger student-teacher relationships compared to the broader, administrative focus of homeroom.
Social-Emotional Learning: Advisory vs Homeroom Impact
Advisory programs provide structured social-emotional learning (SEL) by fostering relationships, self-awareness, and emotional regulation through dedicated time for reflection and discussion. Homeroom typically focuses on administrative tasks, offering limited SEL opportunities compared to advisory's targeted support. Research shows students in advisory settings demonstrate improved emotional resilience and social skills, contributing to a positive school climate.
Scheduling and Structure Differences in Homeroom and Advisory
Homeroom typically functions as a brief, daily gathering focused on attendance and announcements, with a fixed schedule early in the school day. Advisory sessions are often longer and more flexible, designed to provide personalized support, mentoring, and social-emotional learning, integrated into the weekly timetable. Schools may schedule homeroom as a consistent daily routine, whereas advisory periods vary in frequency and duration based on the institution's educational priorities.
Student Outcomes: Homeroom vs Advisory Effectiveness
Homeroom sessions primarily foster administrative efficiency and daily student check-ins, leading to moderate improvements in student organization and attendance rates. Advisory programs, designed to build deeper personal connections and social-emotional skills, have demonstrated stronger impacts on student engagement, academic motivation, and overall well-being. Schools implementing advisory models report higher student satisfaction and improvements in both academic performance and behavioral outcomes compared to traditional homeroom settings.
Challenges in Implementing Homeroom and Advisory Programs
Implementing homeroom and advisory programs presents challenges such as scheduling conflicts, limited staff training, and varying student engagement levels. Schools often struggle to allocate time within an already packed curriculum while ensuring consistent and meaningful interactions between educators and students. Overcoming these obstacles requires strategic planning, professional development, and ongoing evaluation to meet diverse student needs effectively.
Best Practices for Successful Homeroom and Advisory Models
Effective homeroom and advisory models prioritize consistent student-teacher relationships to foster trust and support academic and social-emotional growth. Incorporating personalized check-ins, goal-setting sessions, and collaborative discussions enhances engagement and helps address individual student needs. Utilizing data-driven strategies and maintaining clear communication channels between students, parents, and staff are essential best practices for maximizing the impact of these programs.
Homeroom vs Advisory Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com