The flipped classroom model enhances student engagement by allowing learners to review instructional materials at their own pace before class, promoting active participation during in-person sessions. In contrast, traditional classrooms often rely on passive lecture-based teaching, which may limit opportunities for interactive learning and immediate feedback. Research shows that flipped classrooms improve comprehension and retention by emphasizing collaborative problem-solving and personalized support.
Table of Comparison
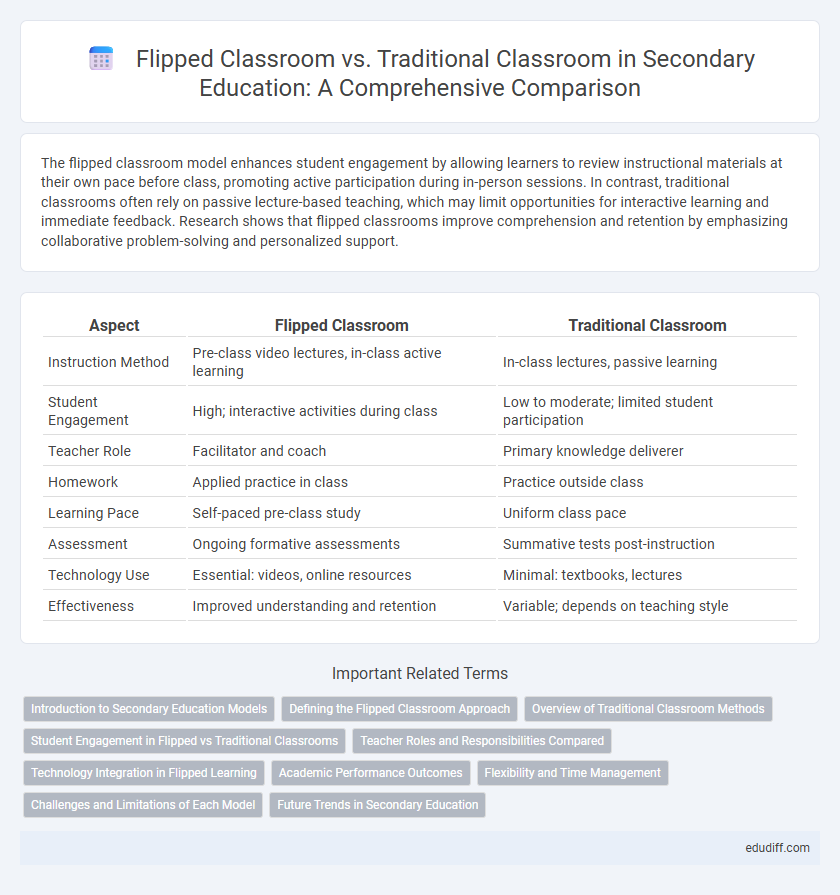
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Traditional Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Instruction Method | Pre-class video lectures, in-class active learning | In-class lectures, passive learning |
| Student Engagement | High; interactive activities during class | Low to moderate; limited student participation |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach | Primary knowledge deliverer |
| Homework | Applied practice in class | Practice outside class |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced pre-class study | Uniform class pace |
| Assessment | Ongoing formative assessments | Summative tests post-instruction |
| Technology Use | Essential: videos, online resources | Minimal: textbooks, lectures |
| Effectiveness | Improved understanding and retention | Variable; depends on teaching style |
Introduction to Secondary Education Models
Flipped classroom models transform secondary education by delivering instructional content outside of traditional class time, enabling active, collaborative learning during school hours. Traditional classrooms maintain teacher-centered lectures followed by homework, focusing on passive knowledge reception. Research shows flipped classrooms enhance student engagement and comprehension compared to conventional lecture-based methods.
Defining the Flipped Classroom Approach
The flipped classroom approach redefines traditional pedagogy by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-class time for interactive, student-centered activities. This model emphasizes active learning, where students engage in problem-solving, discussions, and collaborative projects during class, promoting deeper understanding. Unlike the traditional classroom that relies on passive lecture-based instruction, the flipped classroom fosters personalized learning and immediate feedback from educators.
Overview of Traditional Classroom Methods
Traditional classroom methods typically involve teacher-centered instruction where the educator delivers lectures and students passively receive information. This approach relies heavily on direct teaching, note-taking, and standardized assessments to evaluate understanding. Classroom interaction is generally limited to question-and-answer sessions, with less emphasis on collaborative or technology-enhanced learning strategies.
Student Engagement in Flipped vs Traditional Classrooms
Flipped classrooms significantly enhance student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class content review and in-class collaborative activities. Traditional classrooms often rely on passive lectures, leading to lower levels of student interaction and participation. Studies show that flipped models increase motivation, critical thinking, and retention by encouraging students to take ownership of their learning process.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities Compared
In a flipped classroom, teachers shift from traditional lecturers to facilitators, guiding students through interactive activities and personalized support during class time. Traditional classrooms position teachers as primary knowledge deliverers, relying heavily on lecturing and less on student engagement. This evolving role in flipped environments enhances teacher responsibilities in designing pre-class materials and monitoring individual student progress.
Technology Integration in Flipped Learning
Flipped classrooms leverage technology integration by utilizing video lectures, interactive software, and digital platforms to enhance student engagement and facilitate personalized learning outside traditional school hours. This approach contrasts with traditional classrooms where direct instruction occurs predominantly during class time, often limiting the use of technology to supplementary tools rather than core learning processes. Technology in flipped learning supports collaborative activities, real-time feedback, and access to diverse multimedia resources, fostering a more dynamic and flexible educational environment.
Academic Performance Outcomes
Flipped classrooms significantly enhance academic performance outcomes by promoting active learning and individualized instruction, resulting in higher retention rates and improved test scores compared to traditional classrooms. Students in flipped settings demonstrate increased engagement and critical thinking skills, which correlate with better problem-solving abilities and deeper understanding of the material. Research consistently shows that flipped classrooms outperform traditional lecture-based methods in secondary education by fostering collaborative learning and immediate feedback.
Flexibility and Time Management
The flipped classroom model offers increased flexibility by allowing students to access lectures and materials anytime, facilitating personalized learning paces that traditional classrooms cannot accommodate. Time management improves as in-class sessions focus on interactive activities and problem-solving, reducing passive listening and enhancing engagement. Traditional classrooms often follow rigid schedules, limiting students' ability to control their learning time and adapt to individual needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Flipped classrooms present challenges such as the need for reliable technology access and students' self-discipline to engage with pre-class materials, which can exacerbate educational inequalities. Traditional classrooms often face limitations related to passive learning and limited opportunities for personalized feedback, hindering student engagement and collaboration. Both models require educators to adapt teaching strategies to address diverse learning needs and resource availability effectively.
Future Trends in Secondary Education
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven personalized learning platforms are transforming secondary education by enabling flipped classrooms to offer tailored, interactive content that adapts to individual student needs. Traditional classrooms are increasingly integrating hybrid models, combining face-to-face instruction with digital resources to enhance engagement and facilitate collaborative learning. Data analytics and real-time feedback tools are expected to drive further evolution, empowering educators to optimize secondary education outcomes and prepare students for future digital economies.
Flipped Classroom vs Traditional Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com