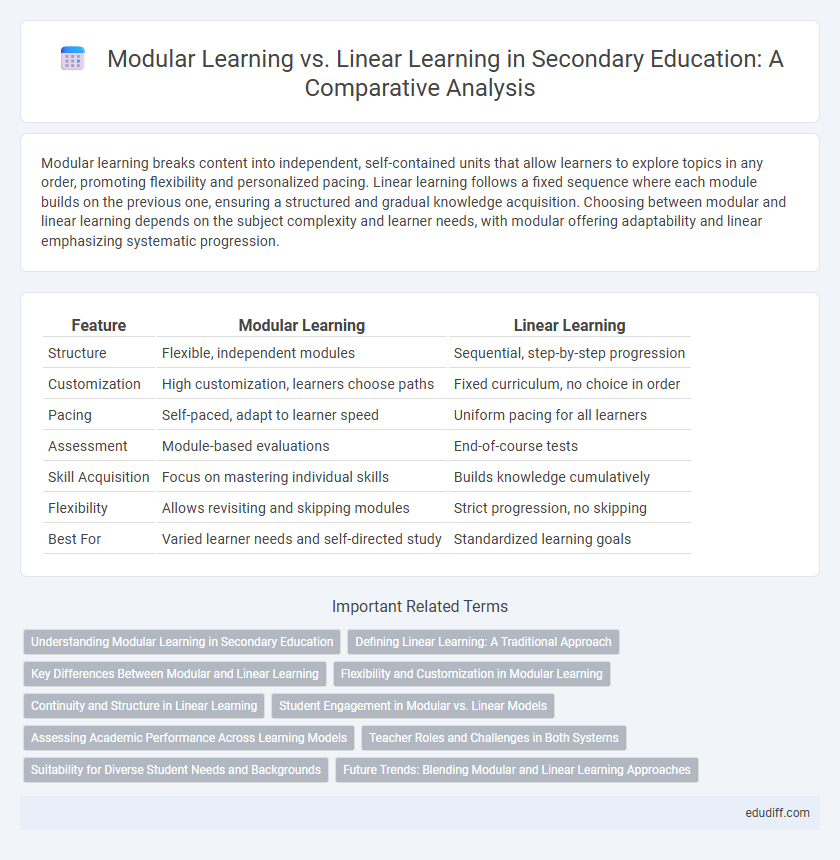
Modular learning breaks content into independent, self-contained units that allow learners to explore topics in any order, promoting flexibility and personalized pacing. Linear learning follows a fixed sequence where each module builds on the previous one, ensuring a structured and gradual knowledge acquisition. Choosing between modular and linear learning depends on the subject complexity and learner needs, with modular offering adaptability and linear emphasizing systematic progression.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modular Learning | Linear Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flexible, independent modules | Sequential, step-by-step progression |
| Customization | High customization, learners choose paths | Fixed curriculum, no choice in order |
| Pacing | Self-paced, adapt to learner speed | Uniform pacing for all learners |
| Assessment | Module-based evaluations | End-of-course tests |
| Skill Acquisition | Focus on mastering individual skills | Builds knowledge cumulatively |
| Flexibility | Allows revisiting and skipping modules | Strict progression, no skipping |
| Best For | Varied learner needs and self-directed study | Standardized learning goals |
Understanding Modular Learning in Secondary Education
Modular learning in secondary education promotes self-paced and flexible study through distinct units, enabling students to master one concept before progressing. It supports diverse learning styles and encourages autonomy, critical for adolescent development. This contrasts with linear learning, which follows a fixed sequence, potentially limiting personalized comprehension and engagement.
Defining Linear Learning: A Traditional Approach
Linear learning follows a sequential progression where concepts are taught step-by-step, ensuring mastery of foundational skills before advancing to more complex topics. This traditional approach emphasizes structured curriculum delivery and predictable learning outcomes, often prioritizing uniform pacing for all students. While effective for maintaining order, linear learning may limit flexibility and fail to address diverse learning needs within secondary education.
Key Differences Between Modular and Linear Learning
Modular learning breaks content into independent units, allowing students to master topics at their own pace and customize their learning paths, whereas linear learning follows a fixed, sequential order that builds knowledge step-by-step. Modular learning supports flexibility and personalized assessment, while linear learning emphasizes structured progression and cumulative skill development. Key differences include adaptability, student control, and the ability to revisit modules versus the predictability and systematic nature of linear curricula.
Flexibility and Customization in Modular Learning
Modular learning offers superior flexibility by allowing students to select and engage with specific modules tailored to their individual learning needs and interests, enhancing personalized education. Unlike linear learning, which follows a fixed sequence, modular learning enables customization in pacing and content depth, supporting diverse learning styles. This adaptability fosters greater student motivation and improves knowledge retention by aligning educational experiences with personal goals and strengths.
Continuity and Structure in Linear Learning
Linear learning emphasizes continuity through a structured, sequential progression of concepts that builds foundational knowledge step-by-step. This approach ensures consistent reinforcement of topics, facilitating cumulative understanding and retention over time. The clear, hierarchical structure in linear learning supports predictable content delivery, minimizing cognitive overload for secondary students.
Student Engagement in Modular vs. Linear Models
Modular learning fosters higher student engagement through interactive, self-paced modules that cater to diverse learning styles, whereas linear learning follows a fixed, sequential path that may limit personalized involvement. Studies indicate students in modular settings exhibit greater motivation and retention, benefiting from immediate application and feedback opportunities. Engagement metrics reveal modular models enhance active participation, critical thinking, and autonomy compared to traditional linear frameworks.
Assessing Academic Performance Across Learning Models
Assessing academic performance across modular learning and linear learning models reveals distinct patterns in student engagement and mastery. Modular learning allows students to progress at their own pace, often resulting in higher retention rates and improved comprehension in subjects like mathematics and science. Linear learning typically follows a fixed curriculum sequence, which may benefit learners who thrive in structured environments but can hinder those requiring more flexibility for optimal academic achievement.
Teacher Roles and Challenges in Both Systems
In modular learning, teachers act as facilitators, guiding students through self-paced modules while providing personalized support and continuous feedback. In linear learning, educators deliver structured, sequential lessons with a focus on direct instruction and pacing control. Challenges in modular learning include monitoring student progress remotely and ensuring motivation, whereas in linear learning, maintaining student engagement and addressing diverse learning speeds are primary concerns.
Suitability for Diverse Student Needs and Backgrounds
Modular learning offers flexibility by allowing students to progress at their own pace, catering to diverse learning styles and backgrounds more effectively than linear learning, which follows a fixed sequence. This adaptability supports personalized education, enabling learners to revisit modules for better comprehension and accommodate varied academic readiness. Schools embracing modular learning often see improved engagement and outcomes among students with heterogeneous abilities and experiences.
Future Trends: Blending Modular and Linear Learning Approaches
Future educational models increasingly blend modular learning's flexibility with the structured progression of linear learning to enhance personalized student engagement and knowledge retention. Adaptive digital platforms enable real-time data analysis, allowing educators to customize learning pathways that integrate modular units within a linear curriculum framework. This hybrid approach optimizes skill mastery while supporting diverse learning styles and accelerating competency development in secondary education.
Modular Learning vs Linear Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com