Streaming groups students by similar ability levels, allowing for targeted instruction but potentially limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Mixed-ability grouping fosters inclusive learning environments where students can collaborate and learn from each other's strengths, promoting social development and adaptable problem-solving skills. Choosing between streaming and mixed-ability grouping impacts both academic outcomes and classroom dynamics.
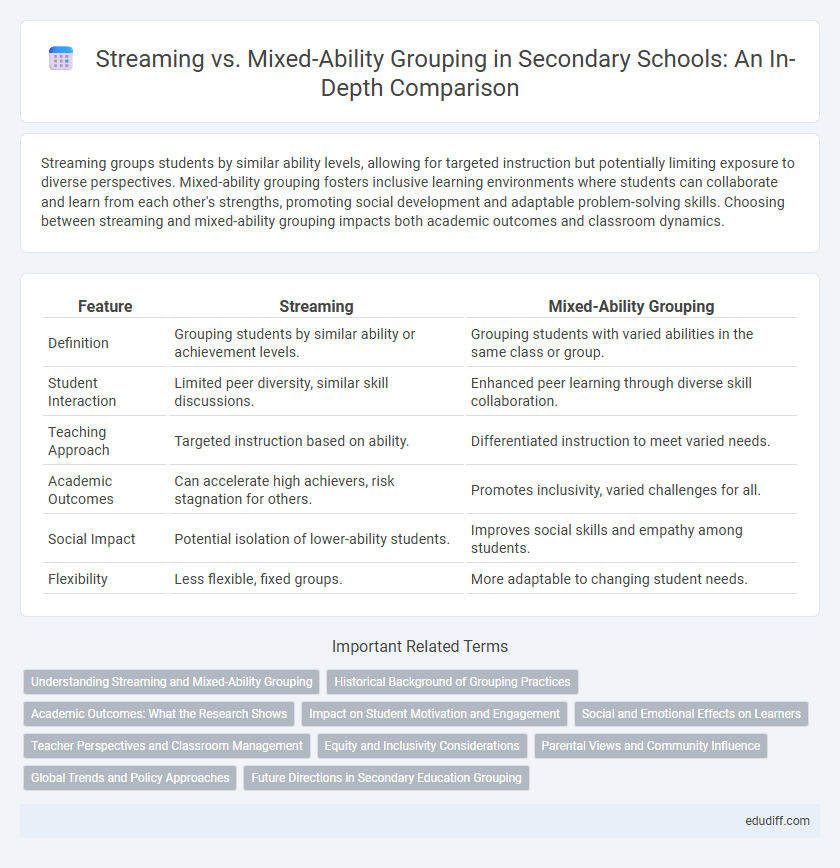
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Streaming | Mixed-Ability Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grouping students by similar ability or achievement levels. | Grouping students with varied abilities in the same class or group. |
| Student Interaction | Limited peer diversity, similar skill discussions. | Enhanced peer learning through diverse skill collaboration. |
| Teaching Approach | Targeted instruction based on ability. | Differentiated instruction to meet varied needs. |
| Academic Outcomes | Can accelerate high achievers, risk stagnation for others. | Promotes inclusivity, varied challenges for all. |
| Social Impact | Potential isolation of lower-ability students. | Improves social skills and empathy among students. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed groups. | More adaptable to changing student needs. |
Understanding Streaming and Mixed-Ability Grouping
Streaming separates students into distinct groups based on their abilities, allowing tailored instruction that targets specific skill levels and accelerates learning for high achievers. Mixed-ability grouping combines students of varied skill levels within the same classroom, fostering peer learning, collaboration, and social development while aiming to reduce stigmatization. Effective implementation of both methods depends on careful assessment, clear objectives, and ongoing evaluation to meet diverse student needs.
Historical Background of Grouping Practices
Historically, streaming emerged in the early 20th century as a method to categorize students based on perceived ability levels to streamline instruction and resource allocation. Mixed-ability grouping gained prominence in the mid-20th century as educators sought to promote equity and collaborative learning by integrating students of diverse skill levels. Both practices reflect evolving educational philosophies influenced by social, political, and pedagogical trends across decades.
Academic Outcomes: What the Research Shows
Research consistently reveals that mixed-ability grouping fosters higher overall academic achievement compared to streaming, especially in literacy and numeracy. Students in mixed-ability classrooms benefit from peer-assisted learning, which enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills across diverse ability levels. Conversely, streaming often leads to widened achievement gaps and lowered self-esteem for lower-track students, negatively impacting long-term academic outcomes.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Streaming often leads to fixed academic groups that can diminish motivation for students placed in lower tiers by fostering a sense of inadequacy. Mixed-ability grouping enhances engagement by providing diverse peer interactions and differentiated instruction tailored to varied skill levels. Research shows that inclusive classrooms with mixed-ability groups increase student confidence and participation, leading to improved academic outcomes.
Social and Emotional Effects on Learners
Streaming often leads to social segmentation, where students may experience diminished self-esteem and increased anxiety due to perceived ability differences. Mixed-ability grouping fosters inclusive peer interactions and promotes emotional resilience by encouraging collaboration and mutual support among diverse learners. Research indicates that learners in mixed groups exhibit enhanced social skills and greater emotional well-being compared to their streamed counterparts.
Teacher Perspectives and Classroom Management
Teachers observe that streaming allows for targeted instruction but often limits peer interaction, while mixed-ability grouping fosters collaborative learning despite diverse skill levels. Classroom management challenges intensify in mixed-ability settings due to varied pacing, requiring adaptive strategies to maintain engagement. Effective teacher perspectives emphasize balancing curriculum demands with differentiated support to optimize student outcomes in both models.
Equity and Inclusivity Considerations
Streaming often reinforces educational inequities by segregating students based on perceived ability, limiting access to diverse perspectives and resources. Mixed-ability grouping promotes inclusivity by fostering collaborative learning environments where students of varying skill levels support each other's growth. Equity in education improves when schools implement mixed-ability strategies that challenge stereotypes and provide tailored support for all learners.
Parental Views and Community Influence
Parental views on streaming often highlight concerns about stigmatization and limited social interaction, whereas many favor mixed-ability grouping for its inclusivity and peer learning benefits. Community influence plays a pivotal role, with culturally diverse communities advocating for mixed-ability classrooms to foster equity and reduce educational disparities. Research indicates that parental support correlates strongly with community norms, shaping school policies toward either streaming or mixed-ability placements.
Global Trends and Policy Approaches
Global trends in education reveal a shift from streaming, which separates students by ability, toward mixed-ability grouping that promotes diversity and inclusion. Policy approaches in countries like Finland and Canada emphasize inclusive classroom practices and differentiation strategies to accommodate varied learning needs. Research indicates mixed-ability grouping enhances social cohesion and reduces educational inequities on a global scale.
Future Directions in Secondary Education Grouping
Future directions in secondary education grouping emphasize personalized learning through adaptive technologies that cater to individual student needs within both streaming and mixed-ability frameworks. Research highlights the potential of data-driven assessments to dynamically adjust group placements, enhancing academic outcomes and social development. Integrating collaborative digital platforms fosters inclusive environments, bridging gaps between diverse student abilities and promoting equity in secondary classrooms.
Streaming vs Mixed-Ability Grouping Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com