Linear curriculum follows a sequential progression where students complete subjects in a fixed order, ensuring foundational knowledge is built before advancing. Modular curriculum divides content into independent modules, allowing flexibility in learning pace and topic selection based on student needs. The choice between linear and modular approaches impacts curriculum design, student engagement, and mastery of subject matter.
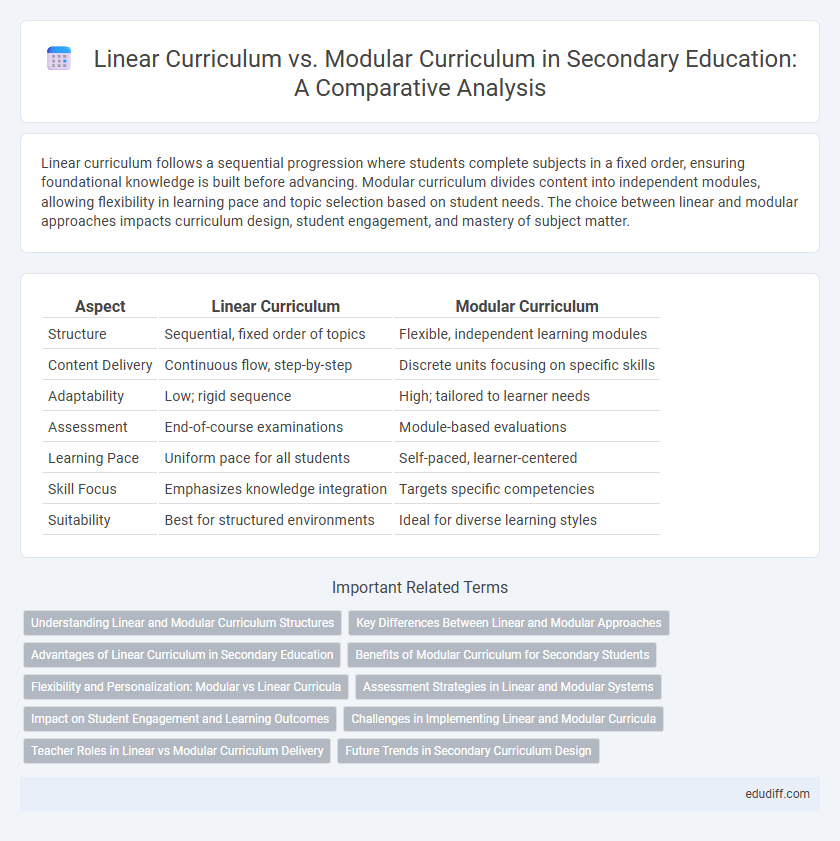
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Linear Curriculum | Modular Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Sequential, fixed order of topics | Flexible, independent learning modules |
| Content Delivery | Continuous flow, step-by-step | Discrete units focusing on specific skills |
| Adaptability | Low; rigid sequence | High; tailored to learner needs |
| Assessment | End-of-course examinations | Module-based evaluations |
| Learning Pace | Uniform pace for all students | Self-paced, learner-centered |
| Skill Focus | Emphasizes knowledge integration | Targets specific competencies |
| Suitability | Best for structured environments | Ideal for diverse learning styles |
Understanding Linear and Modular Curriculum Structures
Linear curriculum structures progress sequentially, with each topic building directly on the previous one, promoting cumulative knowledge acquisition and skill development. In contrast, modular curriculum structures consist of independent units or modules that students can study in any order, allowing for flexible learning paths tailored to individual needs. This modular approach emphasizes mastery of discrete topics, enabling targeted assessments and personalized education strategies.
Key Differences Between Linear and Modular Approaches
Linear curriculum follows a sequential, fixed progression where students master one topic before advancing, emphasizing cumulative knowledge building. Modular curriculum offers flexible, self-contained units allowing learners to access and complete modules independently, promoting personalized pacing and interdisciplinary connections. Key differences include structure rigidity, adaptability to diverse learning needs, and the emphasis on integrated versus compartmentalized content delivery.
Advantages of Linear Curriculum in Secondary Education
Linear curriculum in secondary education offers a structured progression that builds foundational knowledge systematically, enhancing student comprehension and retention. Its sequential design simplifies assessment by allowing educators to measure mastery of specific skills step-by-step. Consistent pacing in a linear curriculum also supports uniform academic readiness across diverse student groups, promoting equity in learning outcomes.
Benefits of Modular Curriculum for Secondary Students
Modular curriculum offers secondary students personalized learning by allowing them to progress at their own pace and focus on specific skill sets, which enhances knowledge retention and engagement. Its flexible structure facilitates targeted mastery of subjects, promoting independent learning and critical thinking essential for academic success. This approach also supports diverse learning styles and provides timely feedback, ultimately improving student motivation and performance.
Flexibility and Personalization: Modular vs Linear Curricula
Modular curriculum offers greater flexibility and personalization compared to linear curriculum by allowing students to select and sequence units based on individual interests and learning paces. Linear curriculum follows a fixed, sequential structure, limiting opportunities for customization and adaptive learning experiences. This flexibility in modular curriculum supports diverse learning styles and promotes student engagement through tailored educational pathways.
Assessment Strategies in Linear and Modular Systems
Assessment strategies in linear curriculum systems typically emphasize cumulative testing and sequential evaluation, ensuring mastery of each topic before progressing. In contrast, modular curriculum systems prioritize formative assessments and flexible evaluation methods tailored to individual modules, allowing for targeted feedback and skill development. This approach in modular systems facilitates adaptive learning and continuous improvement throughout the course.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Linear curriculum structures provide a continuous progression of topics, enhancing student comprehension through logical sequencing, which often leads to improved retention and mastery of subjects. Modular curriculum, emphasizing flexible, self-contained units, encourages active student engagement by allowing learners to focus on specific areas of interest or weakness, fostering personalized learning experiences. Comparative studies indicate modular curricula can boost motivation and adaptability, while linear curricula support consistent knowledge building essential for cumulative subjects like mathematics and sciences.
Challenges in Implementing Linear and Modular Curricula
Challenges in implementing linear curricula include limited flexibility and difficulty addressing diverse student needs due to rigid progression paths. Modular curricula face issues with integration and coherence, as fragmented modules may disrupt knowledge continuity and learning flow. Both approaches require significant teacher training and resource allocation to effectively manage curriculum design and assessment aligned with educational goals.
Teacher Roles in Linear vs Modular Curriculum Delivery
In a linear curriculum, teachers primarily act as the central authority, delivering content sequentially and maintaining a structured learning path that ensures consistent progression through predetermined topics. In contrast, modular curriculum delivery positions teachers as facilitators who support student autonomy by guiding learners through independent or self-paced modules, fostering personalized learning experiences. This shift demands educators adapt their roles from content deliverers to mentors who provide feedback, encourage critical thinking, and accommodate diverse learning needs.
Future Trends in Secondary Curriculum Design
Future trends in secondary curriculum design emphasize personalized learning pathways, integrating adaptive technologies to tailor content to individual student needs. Modular curriculum frameworks enable flexibility and interdisciplinary connections, promoting skills like critical thinking and problem-solving essential for evolving job markets. Linear curriculums face challenges in responsiveness and customization, pushing educational institutions to adopt modular approaches that support lifelong learning and competency-based assessments.
Linear Curriculum vs Modular Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com