A Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) identifies the reasons behind a pet's challenging behaviors by analyzing environmental triggers and consequences, forming the foundation for effective intervention. A Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) builds on the FBA by outlining specific strategies and interventions tailored to modify or replace undesirable behaviors with positive alternatives. Understanding the distinction between FBA and BIP is crucial for developing targeted behavioral support that addresses the root causes and promotes lasting change in special pets.
Table of Comparison
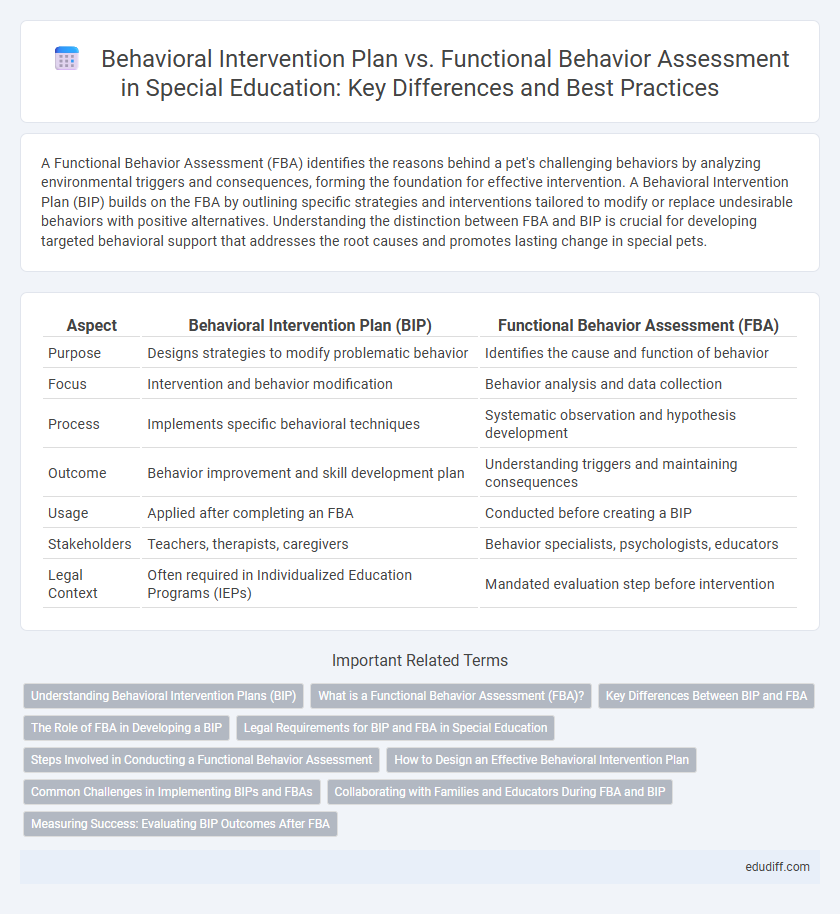
| Aspect | Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) | Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designs strategies to modify problematic behavior | Identifies the cause and function of behavior |
| Focus | Intervention and behavior modification | Behavior analysis and data collection |
| Process | Implements specific behavioral techniques | Systematic observation and hypothesis development |
| Outcome | Behavior improvement and skill development plan | Understanding triggers and maintaining consequences |
| Usage | Applied after completing an FBA | Conducted before creating a BIP |
| Stakeholders | Teachers, therapists, caregivers | Behavior specialists, psychologists, educators |
| Legal Context | Often required in Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) | Mandated evaluation step before intervention |
Understanding Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIP)
A Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) is a strategic document developed from the insights gained through a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) to address specific behavioral challenges. A well-constructed BIP includes clear interventions, teaching strategies, and support mechanisms tailored to reduce problematic behaviors and promote positive alternatives. Effective BIPs incorporate data-driven goals and continuous progress monitoring to ensure adaptive behavior improvements in educational or clinical settings.
What is a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA)?
A Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) is a systematic process used to identify the underlying causes and functions of challenging behaviors in individuals with special needs. By collecting data through observations, interviews, and record reviews, the FBA helps determine the triggers, consequences, and purpose of specific behaviors. This assessment informs the development of effective Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIPs) tailored to address and modify problematic behaviors.
Key Differences Between BIP and FBA
A Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) is a detailed, actionable strategy designed to address specific challenging behaviors identified through assessment, outlining intervention techniques and support mechanisms. In contrast, a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) is a data-driven process used to identify the underlying causes and functions of these behaviors through observation and analysis. Key differences include the FBA's focus on understanding behavior origins, while the BIP emphasizes implementing targeted interventions based on FBA findings to promote positive behavior change.
The Role of FBA in Developing a BIP
A Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) plays a critical role in developing an effective Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) by identifying the underlying causes and functions of challenging behaviors. The FBA collects detailed data on antecedents, behaviors, and consequences to inform tailored strategies within the BIP that address specific behavioral triggers. This data-driven approach ensures the BIP is personalized and targets the root of the behavior for sustainable intervention outcomes.
Legal Requirements for BIP and FBA in Special Education
Legal requirements mandate that a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) be conducted before developing a Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) for students eligible under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). The FBA identifies the underlying causes of challenging behaviors, ensuring that the BIP includes evidence-based strategies tailored to the student's specific needs. Compliance with IDEA requires documented FBA results and a BIP that outlines measurable goals, interventions, and progress monitoring to protect students' rights and support their educational success.
Steps Involved in Conducting a Functional Behavior Assessment
Conducting a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) involves clearly identifying the specific behavior, gathering comprehensive data through observations and interviews, and analyzing antecedents, behaviors, and consequences to determine the function of the behavior. Data collection methods include direct observation, ABC charts, and input from educators or caregivers to establish patterns and triggers. The assessment concludes with hypothesis formulation about the behavior's purpose, guiding the development of an effective Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP).
How to Design an Effective Behavioral Intervention Plan
Designing an effective Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) begins with a thorough Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) to accurately identify the antecedents, behaviors, and consequences influencing the student's actions. Key elements of a successful BIP include setting clear, measurable goals, incorporating evidence-based strategies tailored to the individual's needs, and involving educators, caregivers, and specialists for consistent implementation. Regular progress monitoring and data-driven modifications ensure the intervention remains responsive and effective in promoting positive behavioral outcomes.
Common Challenges in Implementing BIPs and FBAs
Common challenges in implementing Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIPs) and Functional Behavior Assessments (FBAs) include inconsistent data collection, limited staff training, and insufficient collaboration among educators and caregivers. These obstacles hinder accurate assessment and effective intervention, reducing the overall success of behavior management strategies. Addressing these barriers requires ongoing professional development and a cohesive communication framework to ensure fidelity in implementing BIPs and FBAs.
Collaborating with Families and Educators During FBA and BIP
Collaborating with families and educators during Functional Behavior Assessments (FBAs) and Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIPs) ensures tailored strategies addressing students' unique behavioral needs. Effective communication fosters shared understanding of behavioral functions, enabling consensus on intervention goals and consistent implementation across home and school environments. Integrating family insights with educators' observations enhances data accuracy and promotes successful, sustainable behavioral improvements.
Measuring Success: Evaluating BIP Outcomes After FBA
Measuring success in a Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) begins with data collected during the Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA), which identifies the function of challenging behaviors. Key metrics include reductions in target behaviors, increases in replacement behaviors, and consistency in implementing intervention strategies across settings. Regular progress monitoring and data analysis ensure the BIP remains effective and responsive to the student's evolving needs.
Behavioral Intervention Plan vs Functional Behavior Assessment Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com