Modification involves changing the pet's environment or care routines to better suit its specific needs without altering the pet itself, while accommodation entails adjusting human behavior or expectations to accept and support the pet's unique traits. Understanding the differences ensures that pet owners provide appropriate support, enhancing the pet's quality of life and promoting a harmonious relationship. Effective management blends both strategies to prioritize the pet's well-being and foster mutual understanding.
Table of Comparison
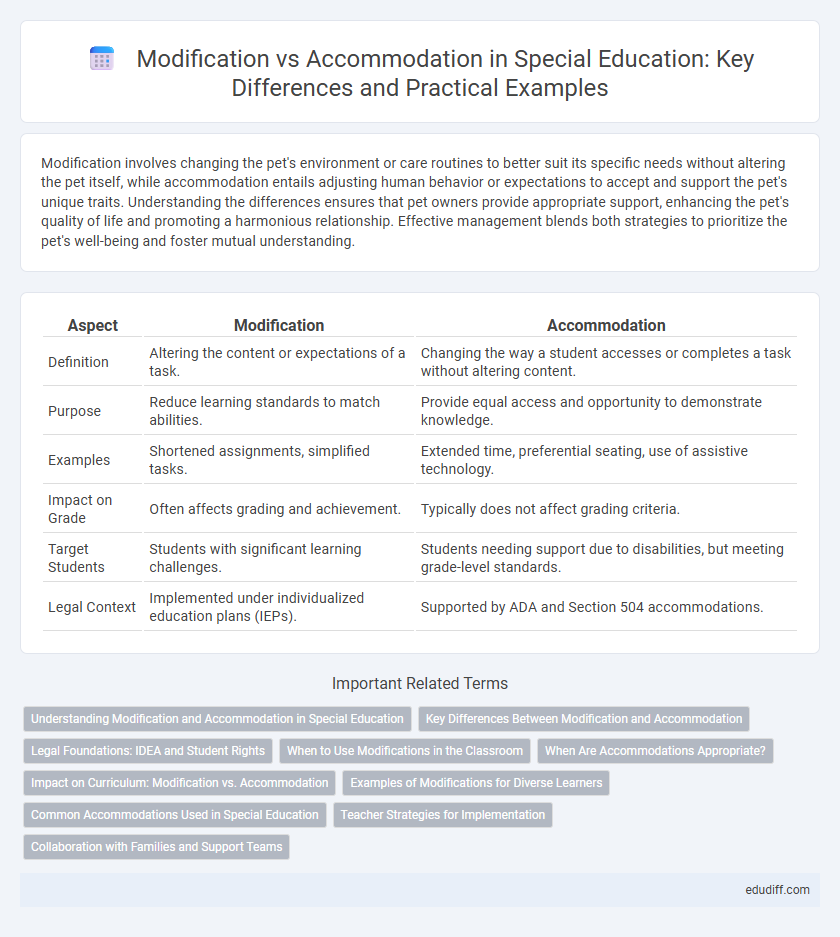
| Aspect | Modification | Accommodation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Altering the content or expectations of a task. | Changing the way a student accesses or completes a task without altering content. |
| Purpose | Reduce learning standards to match abilities. | Provide equal access and opportunity to demonstrate knowledge. |
| Examples | Shortened assignments, simplified tasks. | Extended time, preferential seating, use of assistive technology. |
| Impact on Grade | Often affects grading and achievement. | Typically does not affect grading criteria. |
| Target Students | Students with significant learning challenges. | Students needing support due to disabilities, but meeting grade-level standards. |
| Legal Context | Implemented under individualized education plans (IEPs). | Supported by ADA and Section 504 accommodations. |
Understanding Modification and Accommodation in Special Education
Modification in special education involves altering the content, standards, or expectations of a curriculum to meet the unique needs of students with disabilities, often changing what students are expected to learn. Accommodation refers to adjustments in the way students access or demonstrate learning without changing the instructional level or content, such as extended time or preferential seating. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing effective individualized education programs (IEPs) that support diverse learning needs while maintaining appropriate academic goals.
Key Differences Between Modification and Accommodation
Modification involves altering the academic expectations or standards, such as simplifying tasks or reducing the complexity of assignments for students with disabilities. Accommodation refers to changes in how a student accesses information or demonstrates learning, like extended time or preferential seating, without changing the curriculum's level of difficulty. Key differences lie in the scope: modifications change what is taught or expected, while accommodations change how the learning is delivered or assessed.
Legal Foundations: IDEA and Student Rights
Modification and accommodation in special education are grounded in the legal framework established by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), which safeguards student rights and mandates appropriate educational support. Modifications alter the curriculum expectations, while accommodations provide access without changing learning outcomes, both essential for compliance with IDEA's free appropriate public education (FAPE) requirements. Student rights under IDEA ensure individualized education programs (IEPs) address specific needs through legally enforceable modifications and accommodations.
When to Use Modifications in the Classroom
Modifications should be used in the classroom when students have significant cognitive, developmental, or physical disabilities that prevent them from accessing grade-level content at expected levels. They involve altering the curriculum expectations, such as reducing the complexity or length of assignments, to provide meaningful access to learning. Employing modifications ensures students can succeed by tailoring educational goals to their individual capabilities and needs.
When Are Accommodations Appropriate?
Accommodations are appropriate when a student with a disability requires changes in how they access learning without altering the curriculum expectations or learning standards. These adjustments include extended time, preferential seating, or assistive technology to provide equal access to instruction and assessment. The goal is to remove barriers and enable the student to demonstrate their knowledge fairly and effectively.
Impact on Curriculum: Modification vs. Accommodation
Modifications involve altering the curriculum's content, objectives, or performance expectations to meet a student's unique needs, often resulting in simplified assignments or reduced learning goals. Accommodations maintain the same curriculum standards but provide supports such as extended time, preferential seating, or assistive technology to enable access and participation. The impact on curriculum is significant, as modifications change what is taught or assessed, while accommodations change how students learn without lowering academic expectations.
Examples of Modifications for Diverse Learners
Examples of modifications for diverse learners include simplifying assignments by reducing the number of questions or changing the complexity of the tasks to match individual learning levels. Adjusted grading criteria, such as accepting shorter or partially correct answers, help ensure fair assessment of students with unique needs. Providing alternative formats, like oral reports instead of written essays, supports diverse learners in demonstrating their understanding effectively.
Common Accommodations Used in Special Education
Common accommodations used in special education include extended time on tests, preferential seating, and the use of assistive technology such as speech-to-text software. These modifications help address individual learning needs without altering the core curriculum. Providing visual aids and breaking down tasks into manageable steps also supports students with disabilities in accessing the same educational content as their peers.
Teacher Strategies for Implementation
Teachers implement modifications by altering the curriculum's complexity or expectations to meet diverse learner needs, such as simplifying assignments or adjusting grading criteria. Accommodations focus on providing supports that enable students to access the same curriculum without changing learning goals, including extended time, preferential seating, or assistive technology. Effective teacher strategies involve clear communication with students and collaboration with special education professionals to tailor instruction methods and materials for individual learning profiles.
Collaboration with Families and Support Teams
Effective collaboration with families and support teams ensures that modifications tailor educational content to individual student needs while accommodations adjust the learning environment or delivery methods. Open communication and shared decision-making foster a holistic approach, maximizing student engagement and success. Involving families in regular feedback loops strengthens consistency between home and school supports.
Modification vs Accommodation Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com