Universal Design for Learning (UDL) offers a proactive framework that provides multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to support diverse learners, including special pets with unique needs. Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies and materials to meet individual pet capabilities and learning styles, ensuring personalized support. Both approaches emphasize inclusivity but UDL focuses on flexible curriculum design, while differentiated instruction adapts delivery and assessment.
Table of Comparison
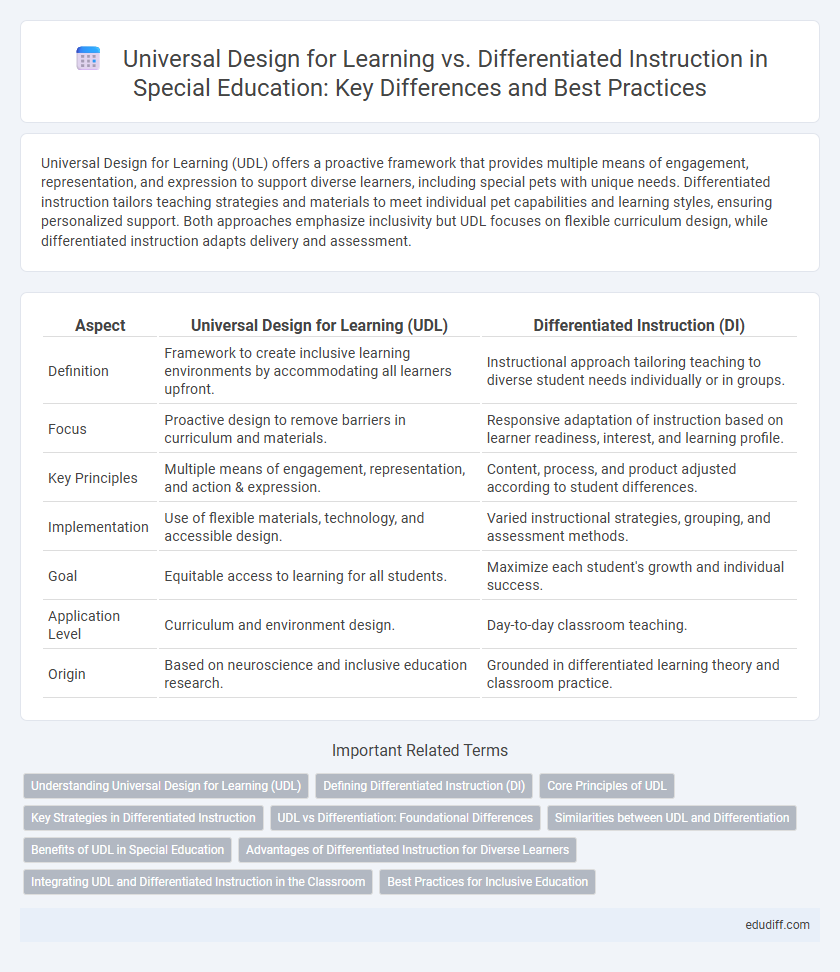
| Aspect | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) | Differentiated Instruction (DI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework to create inclusive learning environments by accommodating all learners upfront. | Instructional approach tailoring teaching to diverse student needs individually or in groups. |
| Focus | Proactive design to remove barriers in curriculum and materials. | Responsive adaptation of instruction based on learner readiness, interest, and learning profile. |
| Key Principles | Multiple means of engagement, representation, and action & expression. | Content, process, and product adjusted according to student differences. |
| Implementation | Use of flexible materials, technology, and accessible design. | Varied instructional strategies, grouping, and assessment methods. |
| Goal | Equitable access to learning for all students. | Maximize each student's growth and individual success. |
| Application Level | Curriculum and environment design. | Day-to-day classroom teaching. |
| Origin | Based on neuroscience and inclusive education research. | Grounded in differentiated learning theory and classroom practice. |
Understanding Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a research-based educational framework aimed at improving and optimizing teaching and learning for all students by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. UDL emphasizes proactive curriculum design that anticipates learner variability, ensuring accessibility and inclusivity without the need for modifications after instruction begins. Unlike Differentiated Instruction, which adapts teaching based on individual needs, UDL designs flexible learning environments from the outset to accommodate diverse learners universally.
Defining Differentiated Instruction (DI)
Differentiated Instruction (DI) is an educational approach that customizes teaching strategies, content, and learning activities to meet diverse student needs, readiness levels, and interests. It emphasizes flexible grouping, varied instructional methods, and ongoing assessment to maximize individual student growth. Unlike Universal Design for Learning (UDL), which proactively designs lessons for all learners, DI responds dynamically to specific learner differences within the classroom.
Core Principles of UDL
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) centers on three core principles: providing multiple means of engagement to motivate learners, offering diverse methods of representation to present information, and enabling various ways of action and expression for learners to demonstrate knowledge. These principles ensure accessibility and inclusivity by addressing learner variability from the outset, contrasting with Differentiated Instruction which adapts content based on learner needs after initial delivery. UDL's proactive framework leverages neuroscientific research to design flexible learning environments that reduce barriers and support all students effectively.
Key Strategies in Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated Instruction employs key strategies such as flexible grouping, tailored content, and varied assessment methods to meet diverse student needs, enhancing engagement and comprehension. Teachers adjust instructional materials and activities based on student readiness, interests, and learning profiles to promote optimal growth. Emphasizing ongoing assessment, these strategies support personalized learning pathways within inclusive classrooms.
UDL vs Differentiation: Foundational Differences
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes designing flexible learning environments and materials from the start to accommodate all students, while Differentiated Instruction involves tailoring teaching methods and content to meet diverse learner needs after understanding their individual differences. UDL relies on proactive planning using multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression, ensuring accessibility and reducing barriers universally. Differentiation is reactive and adaptive, modifying specific aspects such as pacing, content, and process based on assessment and student response to instruction.
Similarities between UDL and Differentiation
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and Differentiated Instruction both aim to address diverse learner needs by providing flexible teaching strategies and multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Both frameworks emphasize student-centered learning environments that promote accessibility and inclusivity for students with varying abilities and learning preferences. The shared goal of UDL and Differentiated Instruction is to optimize educational outcomes by adapting content, process, and assessment to support all learners effectively.
Benefits of UDL in Special Education
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) offers significant benefits in special education by providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression to accommodate diverse learning needs. UDL promotes inclusive environments where students with disabilities can access the curriculum alongside their peers, enhancing participation and reducing barriers. This approach supports individualized learning paths, increases student motivation, and improves academic outcomes for children with special needs.
Advantages of Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Differentiated Instruction offers tailored teaching strategies that address the unique needs, readiness levels, and interests of diverse learners, enhancing engagement and comprehension. By providing multiple pathways for learning, it supports varied learning styles and promotes equity within inclusive classrooms. This approach also allows educators to adjust content, process, and product based on ongoing assessment, ensuring all students achieve academic success.
Integrating UDL and Differentiated Instruction in the Classroom
Integrating Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and Differentiated Instruction in the classroom enhances accessibility by addressing diverse learner needs through multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Utilizing UDL's flexible framework alongside differentiation strategies allows educators to customize content, process, and products, ensuring all students receive equitable opportunities to succeed. Combining these approaches fosters an inclusive learning environment that supports diverse abilities and learning styles effectively.
Best Practices for Inclusive Education
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse learner needs through multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression, fostering accessibility for all students. Differentiated Instruction (DI) tailors teaching methods, content, and assessments to individual student readiness, interests, and learning profiles, promoting personalized learning experiences. Best practices for inclusive education integrate UDL's proactive design with DI's responsive strategies, ensuring equitable access and meaningful participation for students with disabilities and varied learning styles.
Universal Design for Learning vs Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com