Positive Behavioral Interventions emphasize understanding and addressing the root causes of challenging behaviors in special pets, promoting tailored strategies that reinforce desirable actions and improve emotional well-being. Traditional discipline often relies on punishment and may not consider the unique needs or communication styles of special pets, which can lead to increased stress and behavioral issues. Implementing positive interventions fosters trust, reduces anxiety, and supports long-term behavioral improvements in special pets.
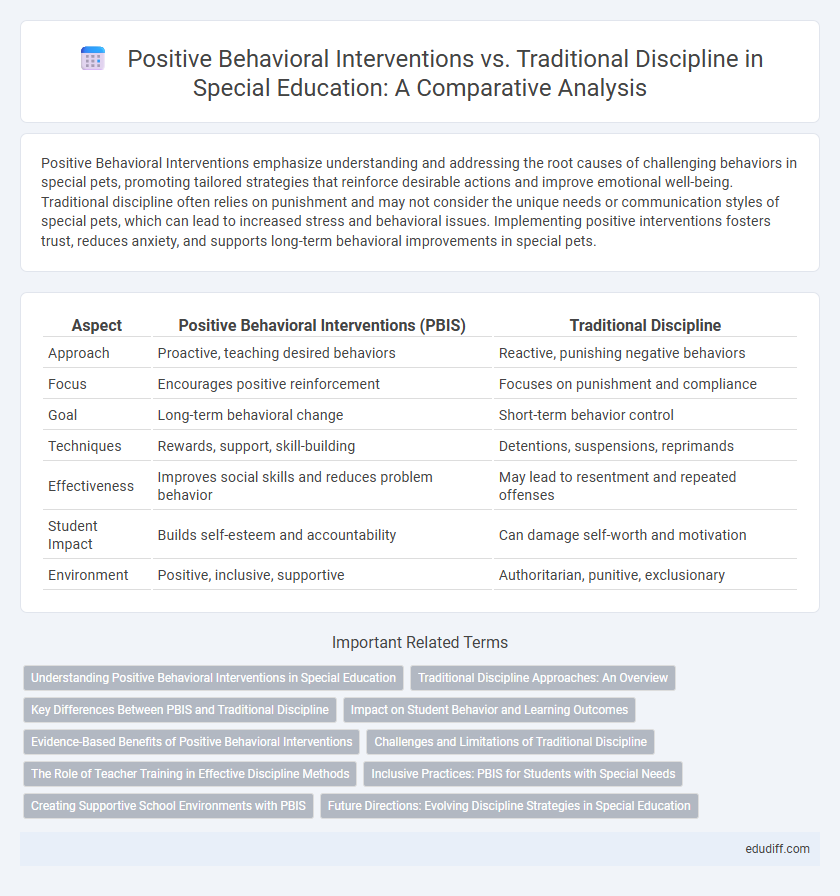
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Positive Behavioral Interventions (PBIS) | Traditional Discipline |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Proactive, teaching desired behaviors | Reactive, punishing negative behaviors |
| Focus | Encourages positive reinforcement | Focuses on punishment and compliance |
| Goal | Long-term behavioral change | Short-term behavior control |
| Techniques | Rewards, support, skill-building | Detentions, suspensions, reprimands |
| Effectiveness | Improves social skills and reduces problem behavior | May lead to resentment and repeated offenses |
| Student Impact | Builds self-esteem and accountability | Can damage self-worth and motivation |
| Environment | Positive, inclusive, supportive | Authoritarian, punitive, exclusionary |
Understanding Positive Behavioral Interventions in Special Education
Positive Behavioral Interventions (PBIs) in special education emphasize proactive strategies that promote desirable behaviors and prevent challenging ones through tailored supports and reinforcement. PBIs focus on understanding underlying causes of behavior, using data-driven approaches to create individualized behavior plans that improve student outcomes. Unlike traditional discipline, which often relies on punishment, PBIs foster a supportive environment conducive to learning and emotional growth.
Traditional Discipline Approaches: An Overview
Traditional discipline approaches often emphasize punitive measures such as detention, suspension, and expulsion to manage student behavior. These methods rely on punishment to discourage negative actions but may fail to address underlying causes or promote long-term behavioral change. Research indicates that traditional discipline can contribute to increased dropout rates and does not support the development of positive social skills.
Key Differences Between PBIS and Traditional Discipline
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) emphasize proactive strategies to promote positive behavior through reinforcement, whereas traditional discipline often relies on punitive measures that address misbehavior after it occurs. PBIS integrates data-driven decision-making and individualized support plans to meet diverse student needs, contrasting with the one-size-fits-all approach typical of traditional discipline models. This shift results in decreased office referrals and suspensions, fostering a more inclusive and supportive learning environment.
Impact on Student Behavior and Learning Outcomes
Positive Behavioral Interventions (PBIS) significantly improve student behavior by fostering a supportive and inclusive classroom environment, reducing disciplinary incidents by up to 40%. Traditional discipline methods often rely on punitive measures, which can increase dropout rates and negatively affect academic performance. Data shows that schools implementing PBIS see enhanced student engagement and higher standardized test scores compared to those using traditional discipline approaches.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Positive Behavioral Interventions
Positive Behavioral Interventions (PBIs) significantly reduce suspension rates and improve student academic performance by fostering supportive learning environments. Research demonstrates that PBIs enhance social-emotional skills and increase student engagement more effectively than traditional discipline methods. Data from the Office of Special Education Programs indicates schools implementing PBIs report higher attendance and lower office discipline referrals, validating their evidence-based benefits.
Challenges and Limitations of Traditional Discipline
Traditional discipline methods often rely on punitive measures that fail to address the root causes of challenging behaviors, resulting in limited long-term effectiveness. These approaches frequently contribute to increased student disengagement, higher suspension rates, and negative impacts on mental health. The lack of individualized support and focus on behavioral development exacerbates disparities, particularly among students with special needs.
The Role of Teacher Training in Effective Discipline Methods
Teacher training plays a critical role in implementing Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) effectively, equipping educators with strategies that promote student engagement and reduce disruptive behaviors. Unlike traditional discipline, which often relies on punitive measures, PBIS-trained teachers use data-driven approaches to foster a positive classroom environment and support social-emotional learning. Research shows that schools with comprehensive teacher training in PBIS experience lower suspension rates and improved student outcomes, highlighting the importance of professional development in discipline methods.
Inclusive Practices: PBIS for Students with Special Needs
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) provide an inclusive framework tailored to meet the diverse needs of students with special needs, emphasizing proactive strategies rather than punitive measures common in traditional discipline. PBIS fosters a positive school climate by teaching social-emotional skills, reinforcing desired behaviors, and using data-driven techniques to customize interventions, which enhances engagement and reduces exclusionary discipline such as suspensions. Research indicates that schools implementing PBIS see improved academic outcomes and behavioral compliance among students with disabilities, promoting equity and access within educational environments.
Creating Supportive School Environments with PBIS
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) emphasize proactive strategies to create supportive school environments that reduce disciplinary issues and promote positive behaviors. Data from multiple studies show schools implementing PBIS report decreased suspension rates, improved student engagement, and enhanced overall climate compared to traditional discipline methods focused on punishment. PBIS frameworks utilize tiered interventions, data-driven decision-making, and consistent reinforcement to foster inclusivity and academic success.
Future Directions: Evolving Discipline Strategies in Special Education
Future directions in special education discipline emphasize the integration of Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) to create individualized, proactive strategies that reduce reliance on punitive measures. Data-driven decision-making and technology-enhanced behavioral assessments facilitate tailored interventions, promoting inclusive environments that support neurodiverse learners. Research highlights ongoing shifts toward trauma-informed practices and restorative justice, fostering adaptive skills and emotional regulation over exclusionary discipline.
Positive Behavioral Interventions vs Traditional Discipline Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com