Extended School Year (ESY) services provide individualized support for students with special needs to prevent skill regression during long breaks, often based on specific IEP goals. Summer school programs typically offer broader academic enrichment and credit recovery opportunities for all students, including those with disabilities. Parents and educators should evaluate which option best addresses the child's unique learning requirements and legal entitlements under IDEA.
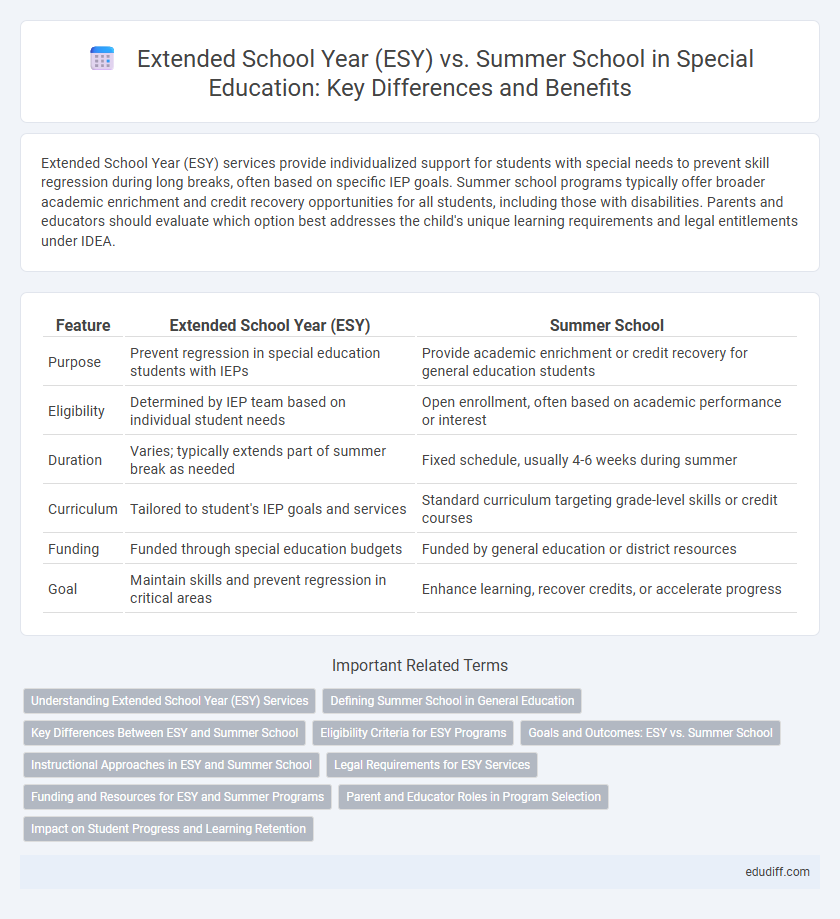
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Extended School Year (ESY) | Summer School |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent regression in special education students with IEPs | Provide academic enrichment or credit recovery for general education students |
| Eligibility | Determined by IEP team based on individual student needs | Open enrollment, often based on academic performance or interest |
| Duration | Varies; typically extends part of summer break as needed | Fixed schedule, usually 4-6 weeks during summer |
| Curriculum | Tailored to student's IEP goals and services | Standard curriculum targeting grade-level skills or credit courses |
| Funding | Funded through special education budgets | Funded by general education or district resources |
| Goal | Maintain skills and prevent regression in critical areas | Enhance learning, recover credits, or accelerate progress |
Understanding Extended School Year (ESY) Services
Extended School Year (ESY) services provide specially designed instruction beyond the traditional school calendar for students with disabilities to prevent significant regression in critical skills. Unlike typical summer school programs, ESY is individualized based on a student's unique needs as determined by their Individualized Education Program (IEP) team. These services focus on maintaining progress rather than introducing new curriculum content, ensuring continuity in learning and development during extended breaks.
Defining Summer School in General Education
Summer school in general education typically offers focused academic instruction during the summer break to help students maintain skills, recover credits, or advance in coursework. It is designed for a broad student population and emphasizes core subjects like math, reading, and science, aligning with grade-level standards. Unlike Extended School Year (ESY) services, summer school does not necessarily address individualized special education goals or prevent substantial regression.
Key Differences Between ESY and Summer School
Extended School Year (ESY) programs provide specially designed instruction for students with disabilities to prevent substantial regression of skills during extended breaks, unlike summer school which is typically open to all students and focuses on academic enrichment or credit recovery. ESY services are individualized, mandated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), and emphasize maintaining critical skills, whereas summer school generally offers standardized curriculum enhancements without legal requirements for eligibility. Eligibility for ESY is determined through IEP team decisions based on data showing the risk of regression and recoupment needs, contrasting with summer school enrollment based on student choice or academic performance.
Eligibility Criteria for ESY Programs
Eligibility criteria for Extended School Year (ESY) programs require documentation of a student's significant regression or lack of recoupment of skills during extended breaks, primarily affecting students with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs). ESY determination involves a multidisciplinary team assessing factors such as the severity of disability, critical life skills, and the student's need to prevent substantial loss of progress. Unlike general summer school enrollment, ESY eligibility centers on maintaining educational gains critical for students with disabilities rather than academic advancement for all students.
Goals and Outcomes: ESY vs. Summer School
Extended School Year (ESY) services focus on maintaining critical skills and preventing regression for students with disabilities, ensuring continuity in Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals. Summer school programs primarily emphasize academic enrichment and grade-level advancement for the general student population. ESY addresses specialized needs to support functional progress, while summer school targets broad curriculum review and skill-building.
Instructional Approaches in ESY and Summer School
Extended School Year (ESY) programs provide individualized, intensive instruction tailored to students with disabilities to prevent significant regression, emphasizing specialized teaching methods aligned with each student's IEP goals. Summer school typically offers broader academic enrichment and remediation using general education curricula designed to support grade-level skills and credit recovery. Instructional approaches in ESY prioritize consistency and continuity of specially designed services, while summer school focuses on reinforcing standard content through group-based, grade-level instruction.
Legal Requirements for ESY Services
Extended School Year (ESY) services are legally mandated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to provide special education and related services beyond the regular school year for students with disabilities who require such support to prevent significant regression. ESY eligibility is determined through an individualized evaluation process, considering the student's unique needs and potential for skill loss during breaks. Unlike summer school programs which typically focus on general education enrichment or credit recovery, ESY services ensure compliance with federal law to maintain a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) for qualifying students.
Funding and Resources for ESY and Summer Programs
Extended School Year (ESY) programs receive specialized funding through Individualized Education Program (IEP) allocations, ensuring resources target students with significant regression risks, unlike general summer school funded by district budgets for broader student populations. ESY funding covers specialized staff, tailored materials, and assistive technologies aligned with students' unique needs, while summer school typically utilizes standard educational materials and generalized staffing. This targeted resource allocation in ESY supports sustained skill retention for students with disabilities, contrasting with the more generalized academic enrichment objectives of summer school programs.
Parent and Educator Roles in Program Selection
Parents and educators play a critical role in selecting between Extended School Year (ESY) services and traditional summer school programs by assessing a student's unique educational needs and goals. Collaboration ensures that decisions are based on individualized education program (IEP) requirements, with ESY designed to prevent significant regression for students with disabilities, while summer school typically offers credit recovery or enrichment. Effective communication and shared understanding of state guidelines and student progress data empower families and teachers to advocate for the most appropriate summer learning option.
Impact on Student Progress and Learning Retention
Extended School Year (ESY) programs provide targeted support tailored to students with disabilities, preventing significant regression in critical skills during breaks, unlike general summer school which primarily addresses grade-level content for all students. ESY emphasizes continuity in individualized education plan (IEP) objectives, ensuring sustained academic and functional progress, whereas summer school often serves a broader purpose of remediation or advancement. The focused nature of ESY leads to better learning retention and bridges gaps that summer school may not effectively address for special education students.
Extended School Year (ESY) vs Summer School Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com