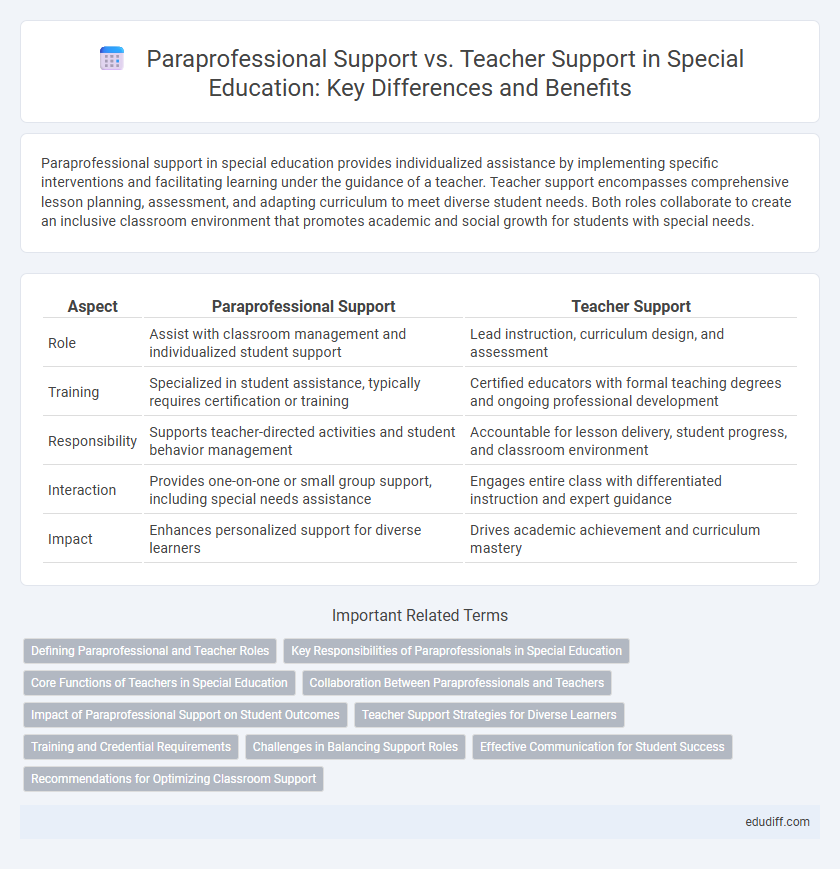
Paraprofessional support in special education provides individualized assistance by implementing specific interventions and facilitating learning under the guidance of a teacher. Teacher support encompasses comprehensive lesson planning, assessment, and adapting curriculum to meet diverse student needs. Both roles collaborate to create an inclusive classroom environment that promotes academic and social growth for students with special needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Paraprofessional Support | Teacher Support |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Assist with classroom management and individualized student support | Lead instruction, curriculum design, and assessment |
| Training | Specialized in student assistance, typically requires certification or training | Certified educators with formal teaching degrees and ongoing professional development |
| Responsibility | Supports teacher-directed activities and student behavior management | Accountable for lesson delivery, student progress, and classroom environment |
| Interaction | Provides one-on-one or small group support, including special needs assistance | Engages entire class with differentiated instruction and expert guidance |
| Impact | Enhances personalized support for diverse learners | Drives academic achievement and curriculum mastery |
Defining Paraprofessional and Teacher Roles
Paraprofessional roles in special education primarily involve providing direct instructional assistance and behavioral support under the supervision of licensed teachers, facilitating individualized student learning needs. Teachers hold the responsibility for designing curriculum, delivering formal instruction, assessing student progress, and making instructional decisions aligned with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs). Clearly defined boundaries between paraprofessional and teacher duties ensure effective collaboration and compliance with educational policies, optimizing support for students with disabilities.
Key Responsibilities of Paraprofessionals in Special Education
Paraprofessionals in special education provide essential instructional support, assist with the implementation of individualized education programs (IEPs), and facilitate communication between students, teachers, and families. Their key responsibilities include adapting learning materials, monitoring student behavior, and supporting social skills development for students with disabilities. Paraprofessionals also ensure a safe and inclusive classroom environment while collaborating closely with teachers to meet diverse learner needs.
Core Functions of Teachers in Special Education
Paraprofessional support in special education primarily involves assisting with behavioral management and implementing individualized instruction plans under teacher supervision. Teachers, however, retain core functions such as assessment, curriculum adaptation, individualized education program (IEP) development, and direct specialized instruction delivery. Effective collaboration ensures paraprofessionals supplement these teacher-led responsibilities, optimizing student outcomes in special education settings.
Collaboration Between Paraprofessionals and Teachers
Effective collaboration between paraprofessionals and teachers enhances special education outcomes by combining instructional expertise with personalized student support. Structured communication and shared goal-setting foster a cohesive learning environment that addresses diverse student needs efficiently. Regular professional development and team planning sessions strengthen this partnership, ensuring consistent and adaptive instructional strategies.
Impact of Paraprofessional Support on Student Outcomes
Paraprofessional support significantly enhances student outcomes by providing targeted, individualized assistance that complements teacher instruction, especially for students with special needs. Research shows that effective collaboration between paraprofessionals and teachers leads to improved academic performance, increased engagement, and better behavioral management. The strategic deployment of paraprofessionals in classrooms contributes to a more inclusive learning environment, fostering student confidence and skill development.
Teacher Support Strategies for Diverse Learners
Teacher support strategies for diverse learners include differentiated instruction tailored to individual learning styles and needs, promoting higher engagement and comprehension. Incorporating multimodal teaching methods, such as visual aids, hands-on activities, and collaborative projects, enhances understanding for students with varied abilities. Regular formative assessments allow teachers to adjust their approaches, ensuring personalized learning pathways and fostering academic growth in inclusive classrooms.
Training and Credential Requirements
Paraprofessional support typically requires a high school diploma and specialized training or certification in assisting students with special needs, while teacher support demands a bachelor's degree and state licensure with ongoing professional development. Paraprofessionals often complete targeted workshops on behavior management and instructional strategies, whereas teachers undergo rigorous coursework in pedagogy, special education law, and assessment techniques. Credential requirements for teachers include passing standardized exams and fulfilling continuing education credits to maintain certification, ensuring comprehensive training for effective classroom management and student support.
Challenges in Balancing Support Roles
Balancing paraprofessional support and teacher support presents challenges in maintaining consistent communication and clearly defining roles to avoid overlap or gaps in student assistance. Lack of coordination can lead to fragmented support, affecting individualized education plans and overall student progress. Effective collaboration and ongoing training are essential to address these challenges and ensure seamless support for diverse learner needs.
Effective Communication for Student Success
Effective communication between paraprofessional support staff and teachers is crucial for fostering student success, ensuring that instructional goals and behavioral strategies are consistently reinforced. Collaborative planning and regular feedback enable paraprofessionals to align their support with teachers' expectations, enhancing personalized learning experiences for students with diverse needs. Clear communication channels reduce misunderstandings and promote a cohesive educational environment that maximizes student achievement.
Recommendations for Optimizing Classroom Support
Maximizing classroom support requires integrating paraprofessional assistance with teacher guidance to enhance student engagement and tailored instruction. Clearly defined roles and ongoing collaboration between teachers and paraprofessionals ensure consistent support aligned with individualized education program (IEP) goals. Regular professional development focused on communication strategies and instructional techniques further optimizes the effectiveness of both paraprofessional and teacher contributions.
Paraprofessional Support vs Teacher Support Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com