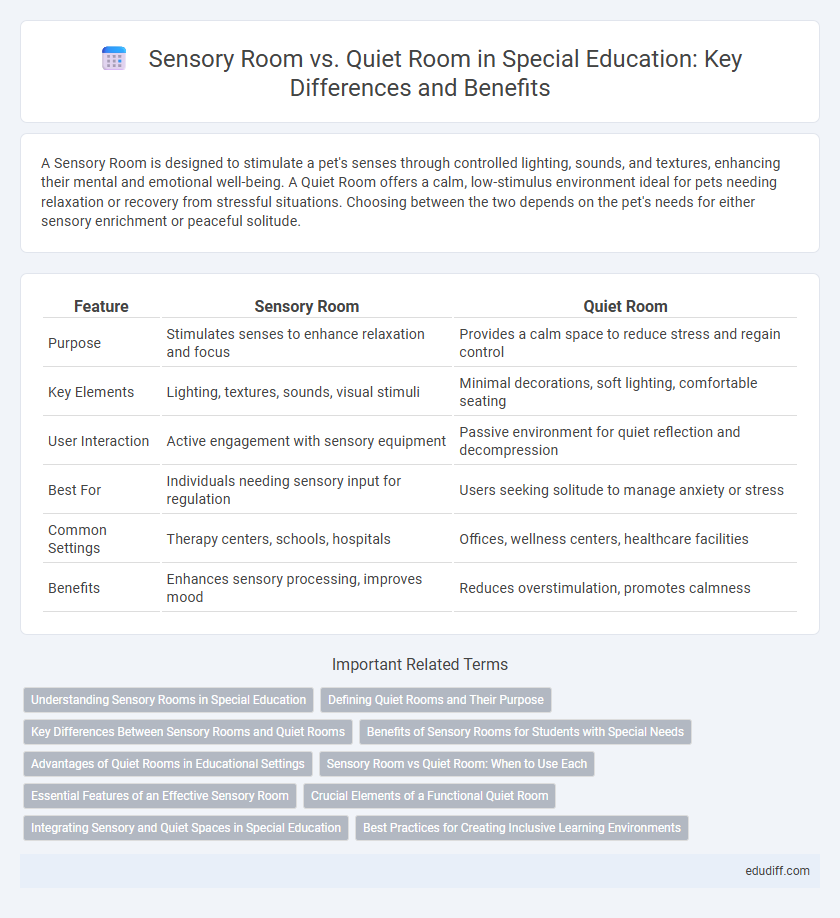
A Sensory Room is designed to stimulate a pet's senses through controlled lighting, sounds, and textures, enhancing their mental and emotional well-being. A Quiet Room offers a calm, low-stimulus environment ideal for pets needing relaxation or recovery from stressful situations. Choosing between the two depends on the pet's needs for either sensory enrichment or peaceful solitude.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sensory Room | Quiet Room |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stimulates senses to enhance relaxation and focus | Provides a calm space to reduce stress and regain control |
| Key Elements | Lighting, textures, sounds, visual stimuli | Minimal decorations, soft lighting, comfortable seating |
| User Interaction | Active engagement with sensory equipment | Passive environment for quiet reflection and decompression |
| Best For | Individuals needing sensory input for regulation | Users seeking solitude to manage anxiety or stress |
| Common Settings | Therapy centers, schools, hospitals | Offices, wellness centers, healthcare facilities |
| Benefits | Enhances sensory processing, improves mood | Reduces overstimulation, promotes calmness |
Understanding Sensory Rooms in Special Education
Sensory rooms provide controlled environments equipped with specialized tools such as weighted blankets, tactile panels, and calming light projections to support sensory integration and emotional regulation for students with autism and sensory processing disorders. Quiet rooms, often minimalistic spaces, focus on reducing external stimuli to offer a retreat for students needing immediate calmness or stress relief during overwhelming moments. Implementing sensory rooms in special education enhances multi-sensory learning and self-regulation strategies, improving focus and reducing behavioral challenges compared to traditional quiet rooms.
Defining Quiet Rooms and Their Purpose
Quiet rooms serve as calming environments specifically designed to provide sensory relief and reduce overstimulation for individuals with sensory processing challenges. These spaces typically feature minimal visual and auditory distractions to promote relaxation and emotional regulation. Unlike sensory rooms, which often include interactive sensory equipment, quiet rooms prioritize simplicity and tranquility to facilitate mental rest and focus.
Key Differences Between Sensory Rooms and Quiet Rooms
Sensory rooms are designed to stimulate or calm the senses through controlled lighting, sounds, and tactile experiences, aiding sensory processing and regulation. Quiet rooms provide a minimalist, distraction-free environment for relaxation and mental decompression, focusing on reducing sensory input to promote calmness. The key difference lies in sensory rooms actively engaging sensory pathways, while quiet rooms emphasize sensory reduction and peaceful solitude.
Benefits of Sensory Rooms for Students with Special Needs
Sensory rooms provide a controlled environment designed to stimulate or calm the sensory systems of students with special needs, enhancing focus and emotional regulation. These rooms offer tailored sensory inputs such as soft lighting, textured objects, and soothing sounds that support cognitive development and reduce anxiety. Compared to quiet rooms, sensory rooms actively engage multiple senses, promoting skill development and improving behavior in educational settings.
Advantages of Quiet Rooms in Educational Settings
Quiet rooms in educational settings provide a controlled environment that minimizes sensory input, helping students with anxiety or sensory processing disorders to focus and regulate emotions effectively. These spaces offer a dedicated area for mental restoration, improving concentration and reducing behavioral incidents. Unlike sensory rooms, quiet rooms emphasize calmness and minimal stimulation, supporting cognitive function and stress relief.
Sensory Room vs Quiet Room: When to Use Each
Sensory rooms are designed to provide controlled multisensory stimulation, ideal for individuals needing sensory integration therapy or calming sensory input, while quiet rooms offer a distraction-free environment to support relaxation and stress reduction. Use sensory rooms when aiming to engage or regulate sensory processing through lights, sounds, and tactile elements, whereas quiet rooms are better suited for decompression in overwhelming situations. Selecting between a sensory room and a quiet room depends on the individual's specific sensory needs and the desired therapeutic outcome.
Essential Features of an Effective Sensory Room
An effective sensory room includes customizable lighting, tactile objects, and calming sounds to engage multiple senses, promoting relaxation and focus. Essential features also encompass adjustable seating and soundproofing to create a safe, controlled environment that reduces sensory overload. These elements collectively support sensory processing needs and emotional regulation for individuals with special requirements.
Crucial Elements of a Functional Quiet Room
A functional quiet room prioritizes soundproofing, comfortable seating, and controlled lighting to create a calming environment that reduces sensory overstimulation. Unlike sensory rooms equipped with multisensory stimuli, quiet rooms emphasize minimal sensory input, providing a safe space for rest and emotional regulation. Essential elements include acoustic panels, soft textures, and adjustable ambient light to promote relaxation and mental clarity.
Integrating Sensory and Quiet Spaces in Special Education
Integrating sensory rooms and quiet rooms in special education enhances individualized learning by addressing both overstimulation and the need for calming environments. Sensory rooms provide controlled sensory input to support regulation and focus, while quiet rooms offer a retreat for emotional decompression. Combining these spaces fosters emotional self-regulation, reduces behavioral challenges, and promotes inclusive classroom engagement for students with sensory processing differences.
Best Practices for Creating Inclusive Learning Environments
Sensory rooms and quiet rooms both play crucial roles in creating inclusive learning environments by addressing diverse sensory and emotional needs. Sensory rooms incorporate multi-sensory equipment like tactile panels, soft lighting, and sound modules to stimulate or calm students, while quiet rooms offer a minimalistic, distraction-free space for emotional regulation and focused reflection. Effective implementation includes considering individual sensory profiles, integrating flexible access, and ensuring staff training to support purposeful use tailored to each learner's requirements.
Sensory Room vs Quiet Room Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com