Open source tools offer flexibility and customization through accessible source code, enabling developers to adapt software to specific project requirements without licensing restrictions. Proprietary tools provide dedicated support and streamlined integration, often featuring specialized functionalities optimized for particular industries or workflows. Evaluating project needs and budget constraints is essential for choosing between open source and proprietary solutions to maximize efficiency and return on investment.
Table of Comparison
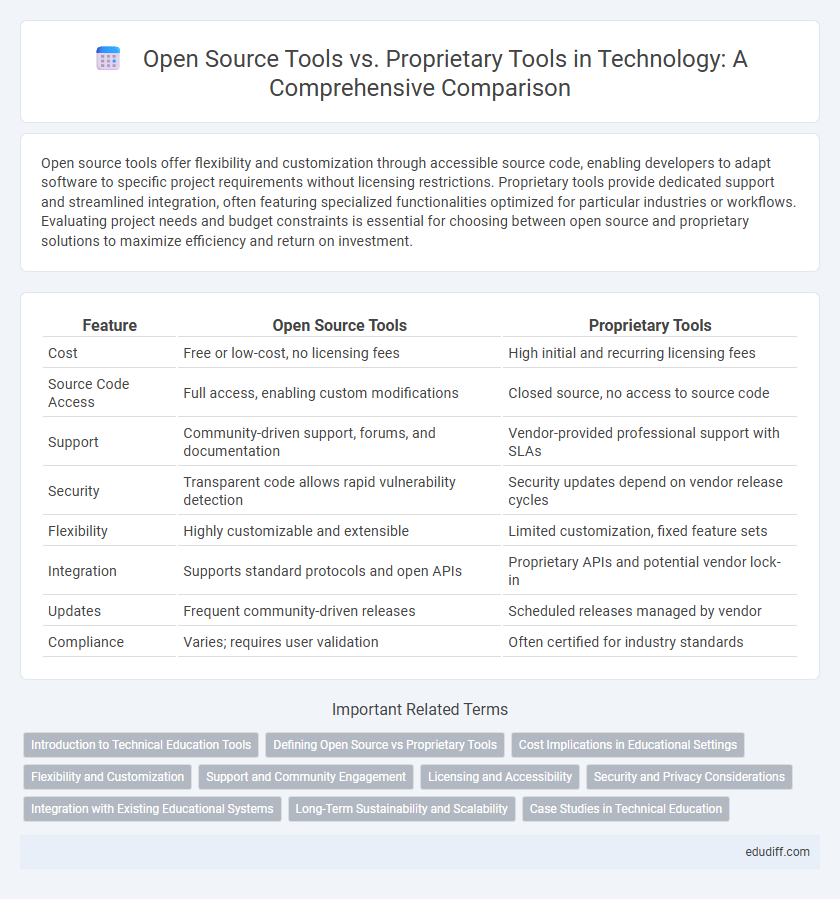
| Feature | Open Source Tools | Proprietary Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or low-cost, no licensing fees | High initial and recurring licensing fees |
| Source Code Access | Full access, enabling custom modifications | Closed source, no access to source code |
| Support | Community-driven support, forums, and documentation | Vendor-provided professional support with SLAs |
| Security | Transparent code allows rapid vulnerability detection | Security updates depend on vendor release cycles |
| Flexibility | Highly customizable and extensible | Limited customization, fixed feature sets |
| Integration | Supports standard protocols and open APIs | Proprietary APIs and potential vendor lock-in |
| Updates | Frequent community-driven releases | Scheduled releases managed by vendor |
| Compliance | Varies; requires user validation | Often certified for industry standards |
Introduction to Technical Education Tools
Open source tools offer flexible, cost-effective solutions for technical education, enabling customization and community-driven improvements. Proprietary tools provide polished, user-friendly interfaces and dedicated support, often guaranteeing reliability and robust feature sets. Selecting the right educational tool depends on specific curriculum needs, budget constraints, and the desired level of control over software customization.
Defining Open Source vs Proprietary Tools
Open source tools provide publicly accessible source code, enabling users to modify, distribute, and collaborate under licenses such as GPL or MIT. Proprietary tools restrict access to source code, maintaining exclusive control over modification, usage rights, and distribution typically governed by commercial licenses. The fundamental distinction lies in transparency and user freedom, where open source fosters community-driven innovation and proprietary emphasizes vendor control and support.
Cost Implications in Educational Settings
Open source tools in educational settings offer significant cost savings by eliminating licensing fees, enabling schools to allocate budgets towards hardware upgrades and training. Proprietary tools, while often providing dedicated support and robust features, require substantial upfront costs and recurring subscription fees, which can strain limited educational budgets. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and scalability, is essential for institutions aiming to maximize the impact of their technology investments.
Flexibility and Customization
Open source tools offer unparalleled flexibility and customization through accessible source code, enabling developers to tailor software to specific technical requirements. Proprietary tools often have fixed features and limited customization options, restricting adaptability to unique workflows. Organizations seeking high configurability and control typically prefer open source solutions for their ability to evolve with project needs.
Support and Community Engagement
Open source tools offer robust community engagement with extensive forums, user-contributed documentation, and frequent updates from a global developer base, ensuring rapid troubleshooting and continuous improvement. Proprietary tools provide dedicated, professional support teams with service-level agreements (SLAs) and structured training resources, delivering predictable response times and tailored assistance. Evaluating specific support requirements and community activity levels is essential for selecting between open source flexibility and proprietary reliability.
Licensing and Accessibility
Open source tools offer licenses such as GPL, MIT, and Apache, providing users with the freedom to modify, distribute, and access source code without cost, enhancing transparency and flexibility in development. Proprietary tools operate under restrictive licenses that limit usage, modification, and redistribution, often requiring expensive subscriptions or one-time purchases, which can constrain accessibility and customization. Licensing terms directly impact software adoption, collaborative potential, and total cost of ownership in both enterprise and individual use scenarios.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Open source tools often provide greater transparency and community-driven security audits, enabling quicker identification and resolution of vulnerabilities compared to proprietary tools. Proprietary tools may offer specialized security features and dedicated support but can lack transparency, posing potential privacy risks due to closed-source code and undisclosed data handling practices. Evaluating the threat model, compliance requirements, and incident response capabilities is crucial when choosing between open source and proprietary security solutions.
Integration with Existing Educational Systems
Open source tools often provide greater flexibility for integration with existing educational systems due to their customizable codebase and extensive community-driven plugin support. Proprietary tools may offer streamlined installation and dedicated vendor support but frequently face limitations in interoperability and require costly APIs or middleware for seamless integration. Educational institutions benefit from evaluating the compatibility of open source platforms like Moodle or Sakai with legacy systems compared to proprietary solutions such as Blackboard or Canvas.
Long-Term Sustainability and Scalability
Open source tools offer long-term sustainability by enabling continuous community-driven updates and scalable customization without licensing restrictions. Proprietary tools, while often providing dedicated support and integrated solutions, may face limitations in scalability due to vendor lock-in and evolving licensing costs. Choosing the right tool depends on balancing the need for flexible, cost-effective growth with reliable vendor-backed stability.
Case Studies in Technical Education
Case studies in technical education reveal that open source tools enhance student engagement through hands-on experience with real-world software, promoting collaboration and innovation in coding projects. Proprietary tools provide structured support and comprehensive documentation, ensuring streamlined learning and integration within professional environments. Data indicates institutions leveraging open source platforms report higher adaptability and cost-efficiency in curricula development compared to those reliant on proprietary solutions.
Open Source Tools vs Proprietary Tools Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com