General Education provides a broad foundation across multiple disciplines, fostering critical thinking and communication skills essential for diverse career paths. Core Curriculum emphasizes a set of required courses that ensure all students gain essential knowledge in key academic areas, promoting academic consistency within a specific institution. Both approaches aim to equip undergraduates with foundational skills, but Core Curriculum typically offers more structured and standardized requirements.
Table of Comparison
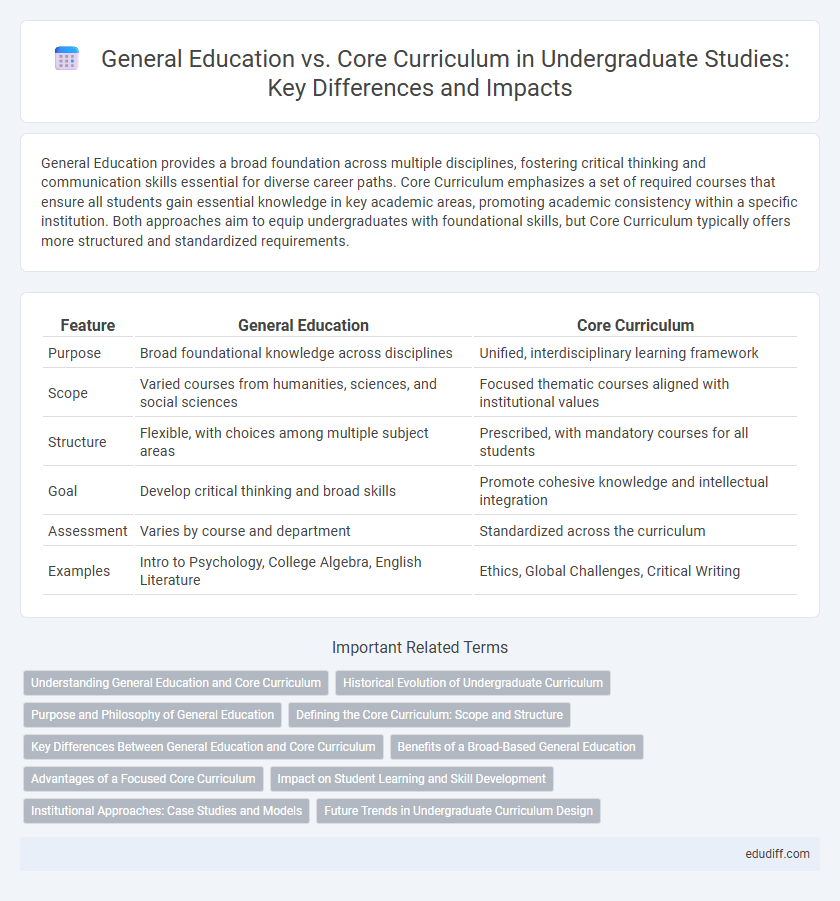
| Feature | General Education | Core Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Broad foundational knowledge across disciplines | Unified, interdisciplinary learning framework |
| Scope | Varied courses from humanities, sciences, and social sciences | Focused thematic courses aligned with institutional values |
| Structure | Flexible, with choices among multiple subject areas | Prescribed, with mandatory courses for all students |
| Goal | Develop critical thinking and broad skills | Promote cohesive knowledge and intellectual integration |
| Assessment | Varies by course and department | Standardized across the curriculum |
| Examples | Intro to Psychology, College Algebra, English Literature | Ethics, Global Challenges, Critical Writing |
Understanding General Education and Core Curriculum
General Education provides a broad foundation of knowledge and essential skills across multiple disciplines, emphasizing critical thinking, communication, and quantitative reasoning. Core Curriculum focuses on a structured set of courses required for all undergraduates within a specific institution, designed to ensure mastery of fundamental academic areas and promote intellectual engagement. Both frameworks aim to develop well-rounded students but differ in scope and institutional implementation.
Historical Evolution of Undergraduate Curriculum
The historical evolution of undergraduate curriculum reveals that General Education programs emerged to provide broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, fostering critical thinking and civic responsibility. In contrast, Core Curriculum systems developed to ensure mastery of foundational subjects deemed essential for academic rigor and intellectual unity. This shift reflects differing educational philosophies prioritizing interdisciplinary exposure versus concentrated disciplinary depth within undergraduate studies.
Purpose and Philosophy of General Education
General Education aims to cultivate critical thinking, communication skills, and ethical reasoning across diverse disciplines, fostering well-rounded individuals prepared for societal participation. Its philosophy emphasizes broad intellectual foundations to promote lifelong learning and adaptability in a rapidly changing world. In contrast, Core Curriculum often centers on a prescribed set of fundamental courses designed to ensure mastery of essential knowledge and skills within a specific academic framework.
Defining the Core Curriculum: Scope and Structure
The Core Curriculum encompasses a fixed set of interdisciplinary courses designed to ensure foundational knowledge across multiple academic domains such as humanities, sciences, and social sciences. It establishes a cohesive educational framework aimed at developing critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills essential for undergraduate success. The scope of the Core Curriculum mandates a balanced distribution of credits, typically ranging from 30 to 45 credit hours, structured to provide depth and breadth in general education while aligning with institutional learning outcomes.
Key Differences Between General Education and Core Curriculum
General Education programs offer a broad range of courses across multiple disciplines to ensure well-rounded knowledge, while Core Curriculum focuses on a specific set of required courses designed to establish foundational skills and knowledge in a particular field or institution. General Education emphasizes exposure to diverse subjects such as humanities, sciences, and social sciences, whereas Core Curriculum prioritizes depth and consistency in essential academic areas mandated by the institution. Students benefit from General Education's interdisciplinary approach contrasted with Core Curriculum's structured pathway tailored to academic and professional requirements.
Benefits of a Broad-Based General Education
A broad-based general education offers undergraduates a diverse foundation in critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills applicable across various disciplines. Exposure to multiple fields fosters intellectual flexibility and cultural awareness, preparing students for a dynamic job market and lifelong learning. This versatility enhances adaptability and encourages interdisciplinary collaboration, essential for success in rapidly evolving professional environments.
Advantages of a Focused Core Curriculum
A focused core curriculum provides undergraduate students with a cohesive, interdisciplinary foundation that promotes critical thinking and deeper subject mastery. It ensures consistent learning outcomes across diverse academic majors, fostering essential skills such as analytical reasoning and effective communication. Concentrating on a well-defined curriculum helps streamline academic progress, reducing course overlap and enabling timely degree completion.
Impact on Student Learning and Skill Development
General Education programs provide a broad foundation of knowledge across multiple disciplines, promoting critical thinking and adaptability, which are essential for holistic student learning. Core Curriculum, often more structured and focused on specific competency areas, ensures mastery of fundamental skills such as quantitative reasoning, communication, and ethical reasoning. Both frameworks significantly enhance skill development, with General Education encouraging interdisciplinary understanding and Core Curriculum fostering depth in essential academic proficiencies.
Institutional Approaches: Case Studies and Models
Institutional approaches to General Education versus Core Curriculum vary significantly, reflecting diverse academic goals and student needs across universities. Case studies reveal models where General Education emphasizes broad, interdisciplinary exposure, while Core Curriculum enforces a prescribed set of foundational courses for all undergraduates. Successful frameworks balance flexibility with structure, fostering critical thinking and comprehensive knowledge essential for bachelor's degree completion.
Future Trends in Undergraduate Curriculum Design
Future trends in undergraduate curriculum design emphasize integrating flexible general education frameworks with core curriculum components to foster interdisciplinary skills and adaptability. Institutions increasingly prioritize experiential learning, digital literacy, and global competencies within both structures to meet workforce demands. Data shows that modular curricula combining general education breadth and core curriculum depth enhance student engagement and lifelong learning outcomes.
General Education vs Core Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com