Full-time status typically requires enrolling in 12 or more credit hours per semester, allowing students to graduate sooner and access financial aid benefits. Part-time status involves fewer credit hours, offering greater flexibility for those balancing work or personal commitments but often extends the time needed to complete a degree. Understanding the differences helps undergraduates make informed decisions about their academic workload and career planning.
Table of Comparison
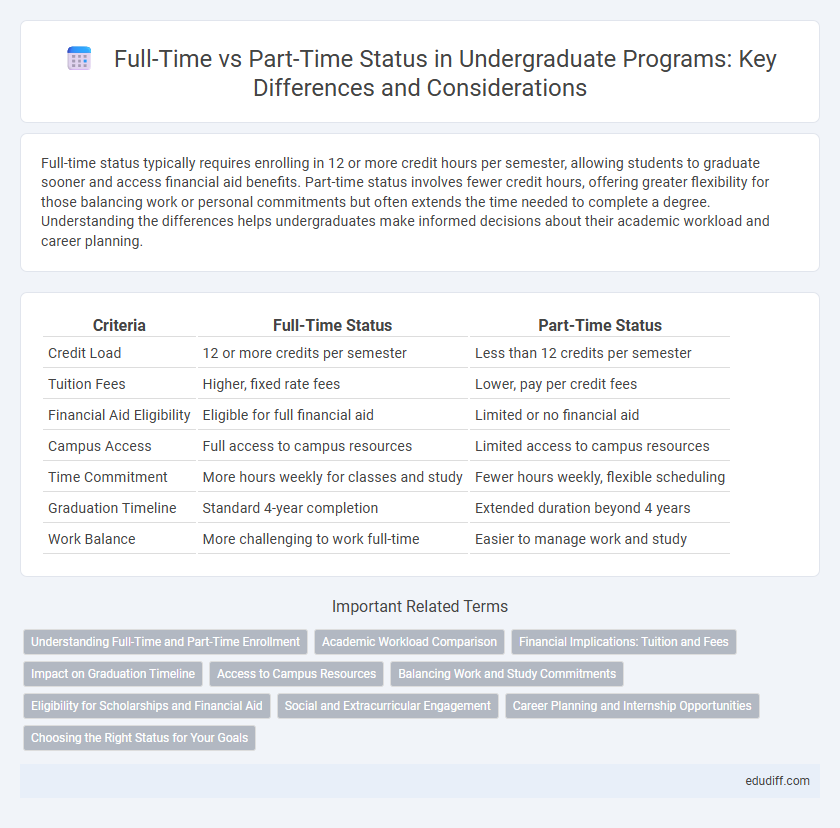
| Criteria | Full-Time Status | Part-Time Status |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Load | 12 or more credits per semester | Less than 12 credits per semester |
| Tuition Fees | Higher, fixed rate fees | Lower, pay per credit fees |
| Financial Aid Eligibility | Eligible for full financial aid | Limited or no financial aid |
| Campus Access | Full access to campus resources | Limited access to campus resources |
| Time Commitment | More hours weekly for classes and study | Fewer hours weekly, flexible scheduling |
| Graduation Timeline | Standard 4-year completion | Extended duration beyond 4 years |
| Work Balance | More challenging to work full-time | Easier to manage work and study |
Understanding Full-Time and Part-Time Enrollment
Full-time enrollment typically requires students to register for at least 12 credit hours per semester, enabling access to more financial aid options and campus resources. Part-time status applies to those taking fewer than 12 credit hours, offering greater schedule flexibility but often limiting eligibility for scholarships and on-campus benefits. Understanding these distinctions helps undergraduates balance academic workload, financial planning, and personal commitments effectively.
Academic Workload Comparison
Full-time undergraduate students typically enroll in 12 to 18 credit hours per semester, allowing for a balanced academic workload that supports steady progress toward degree completion. Part-time students usually take fewer than 12 credit hours, resulting in a reduced course load but extended time to graduate. This difference in credit hours directly impacts academic expectations, time management, and financial aid eligibility.
Financial Implications: Tuition and Fees
Full-time undergraduate students typically incur higher tuition costs due to a greater number of enrolled credit hours, while part-time students pay tuition based on individual course credits, potentially reducing immediate financial burden. However, full-time status often maintains eligibility for financial aid packages such as scholarships, grants, and federal student loans that may be limited or unavailable for part-time enrollment. Universities may also charge fees differently for both statuses, impacting overall expenses related to registration, campus facilities, and student services.
Impact on Graduation Timeline
Full-time undergraduate students typically complete their degrees faster, often graduating within four years due to a heavier course load per semester. Part-time students, taking fewer credits, may extend their graduation timeline beyond the standard duration, sometimes by several years. The difference in enrollment status directly influences academic progress, financial aid eligibility, and time-to-degree completion.
Access to Campus Resources
Full-time undergraduate students typically gain comprehensive access to campus resources such as academic advising, libraries, fitness centers, and career services, enhancing their overall educational experience. Part-time students may face limitations or reduced access to these facilities, impacting their ability to fully engage with campus life and support systems. Universities often prioritize resource allocation for full-time enrollees, making status a critical factor in resource availability.
Balancing Work and Study Commitments
Maintaining full-time status typically requires enrollment in 12 or more credit hours, demanding significant time management to balance academic responsibilities with work commitments. Part-time status, usually fewer than 12 credit hours, provides greater flexibility for students who work extensive hours or have other personal obligations. Effective scheduling and prioritization are essential strategies for undergraduates to successfully manage both work and study while meeting their educational goals.
Eligibility for Scholarships and Financial Aid
Full-time status typically requires enrollment in at least 12 credit hours per semester, making students eligible for most scholarships and financial aid programs that mandate full-time enrollment. Part-time students, enrolled in fewer than 12 credits, often face limited access to financial aid, as many grant and scholarship opportunities are restricted to full-time status. Eligibility criteria for federal financial aid, including Pell Grants and subsidized loans, generally prioritize full-time students, affecting the amount and type of aid available to part-time undergraduates.
Social and Extracurricular Engagement
Full-time undergraduate students typically experience higher levels of social and extracurricular engagement due to their increased on-campus presence and access to diverse student organizations, events, and networking opportunities. Part-time students often face challenges balancing academic responsibilities with work and personal commitments, which can limit their participation in campus activities. Research indicates that full-time enrollment correlates with greater peer interaction, leadership roles, and a stronger sense of community involvement.
Career Planning and Internship Opportunities
Full-time undergraduate students often have greater access to career planning resources and internship opportunities due to their continuous enrollment and university engagement. Part-time students may face challenges balancing work and study, which can limit availability for internships but can also provide valuable real-world experience that enhances career readiness. Understanding the impact of enrollment status on career services and internship eligibility is crucial for effective career planning.
Choosing the Right Status for Your Goals
Selecting the right enrollment status as an undergraduate depends on balancing credit load with academic and personal goals. Full-time status, typically defined as taking 12 or more credits per semester, supports faster degree completion and eligibility for many scholarships and financial aid programs. Part-time enrollment offers flexibility for students managing work or family commitments but may extend the time required to graduate and affect financial aid eligibility.
Full-Time Status vs Part-Time Status Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com