Community colleges offer affordable, flexible pathways with smaller class sizes and a focus on practical skills, making them ideal for students seeking accessible education or planning to transfer to a university later. Universities provide a broader range of academic programs, research opportunities, and campus resources, fostering a more immersive college experience geared toward advanced degrees and specialized careers. Choosing between a community college and a university depends on individual goals, financial considerations, and desired learning environments.
Table of Comparison
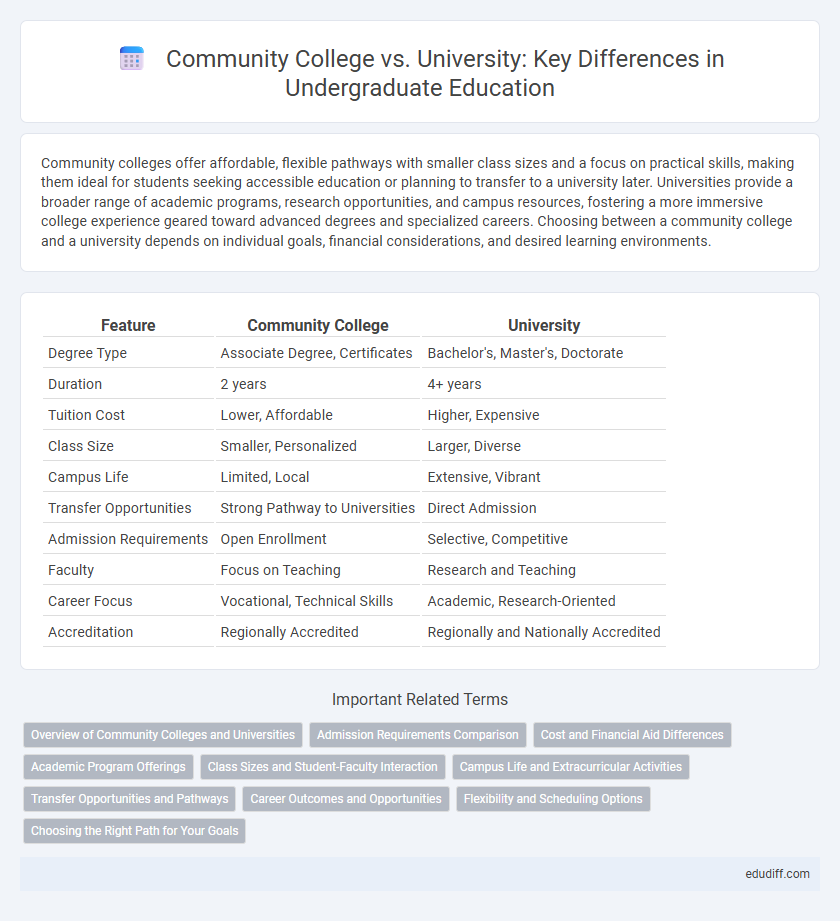
| Feature | Community College | University |
|---|---|---|
| Degree Type | Associate Degree, Certificates | Bachelor's, Master's, Doctorate |
| Duration | 2 years | 4+ years |
| Tuition Cost | Lower, Affordable | Higher, Expensive |
| Class Size | Smaller, Personalized | Larger, Diverse |
| Campus Life | Limited, Local | Extensive, Vibrant |
| Transfer Opportunities | Strong Pathway to Universities | Direct Admission |
| Admission Requirements | Open Enrollment | Selective, Competitive |
| Faculty | Focus on Teaching | Research and Teaching |
| Career Focus | Vocational, Technical Skills | Academic, Research-Oriented |
| Accreditation | Regionally Accredited | Regionally and Nationally Accredited |
Overview of Community Colleges and Universities
Community colleges primarily offer two-year associate degrees, certificates, and transfer programs designed to provide affordable, accessible education and workforce training. Universities provide comprehensive undergraduate and graduate programs with a focus on research, diverse academic disciplines, and campus facilities supporting a broader student experience. Community colleges typically have smaller class sizes and lower tuition costs, while universities offer a wider range of majors, extracurricular activities, and advanced resources.
Admission Requirements Comparison
Community colleges typically offer open admission policies requiring only a high school diploma or GED, making them more accessible to a broader range of students. Universities often demand higher academic standards, including minimum GPA thresholds, standardized test scores like the SAT or ACT, and prerequisites such as specific coursework. These rigorous admission criteria at universities aim to ensure readiness for more specialized and intensive academic programs compared to community colleges.
Cost and Financial Aid Differences
Community colleges typically offer significantly lower tuition rates compared to universities, making them a cost-effective option for many undergraduate students. Financial aid at community colleges often covers tuition and fees through federal grants, state aid, and scholarships tailored to local students, while universities provide a broader range of financial aid packages, including merit-based scholarships and work-study programs. Students seeking to minimize debt frequently choose community colleges for the first two years before transferring to universities to complete their degrees.
Academic Program Offerings
Community colleges provide a wide range of associate degrees and certificate programs tailored to technical skills and workforce readiness, often emphasizing practical, career-oriented education. Universities typically offer a broader spectrum of academic programs, including bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees across diverse disciplines with extensive research opportunities. The academic depth and specialization available at universities support advanced study and professional development beyond the foundational coursework common at community colleges.
Class Sizes and Student-Faculty Interaction
Community colleges typically offer smaller class sizes, averaging 15 to 20 students, which fosters personalized student-faculty interaction and enhances academic support. Universities often have larger lecture halls with 100+ students, limiting direct engagement but supplemented by discussion sections and office hours. Smaller classes at community colleges promote active participation and tailored feedback, leading to stronger mentorship opportunities.
Campus Life and Extracurricular Activities
Community colleges often provide a more intimate campus environment with smaller class sizes, fostering closer interactions and accessible faculty support. Universities offer a diverse range of extracurricular activities, including extensive clubs, sports teams, and cultural organizations, enriching the overall student experience. Participation in these activities at universities often leads to broader networking opportunities and enhanced personal development.
Transfer Opportunities and Pathways
Community colleges offer structured transfer pathways that enable students to complete general education requirements at a lower cost before transferring to a university. Universities often have articulation agreements with community colleges, ensuring credit transferability and smoother transitions into bachelor's degree programs. These opportunities make community colleges a strategic starting point for students aiming to pursue a four-year degree with financial and academic flexibility.
Career Outcomes and Opportunities
Community colleges offer affordable, flexible programs focused on practical skills and workforce readiness, leading to higher employment rates in technical fields. Universities provide broader academic training, access to research opportunities, and stronger alumni networks, which often result in higher earning potential and leadership positions. Career outcomes vary significantly based on chosen majors, with universities more likely to offer pathways to professional degrees and advanced careers.
Flexibility and Scheduling Options
Community colleges offer greater flexibility and diverse scheduling options with many evening, weekend, and online courses tailored for working students and those with family commitments. Universities generally have more rigid class schedules, often structured around traditional daytime hours, limiting adaptability for non-traditional students. This flexibility in community colleges enables easier balancing of education, work, and personal life, which is a significant advantage for many undergraduate students.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Goals
Community colleges offer affordable tuition and flexible schedules ideal for students seeking vocational training or a seamless transfer to a four-year university. Universities provide comprehensive programs, research opportunities, and a wider range of degrees suited for career-focused or academic aspirations. Evaluating personal career goals, financial resources, and preferred learning environments is crucial when deciding between community college and university pathways.
Community College vs University Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com