In-person classes provide direct interaction with instructors and peers, fostering immediate feedback and hands-on learning experiences crucial for practical subjects. Online classes offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace and balance education with other commitments. Choosing between the two depends on individual learning preferences, course requirements, and the need for face-to-face engagement.
Table of Comparison
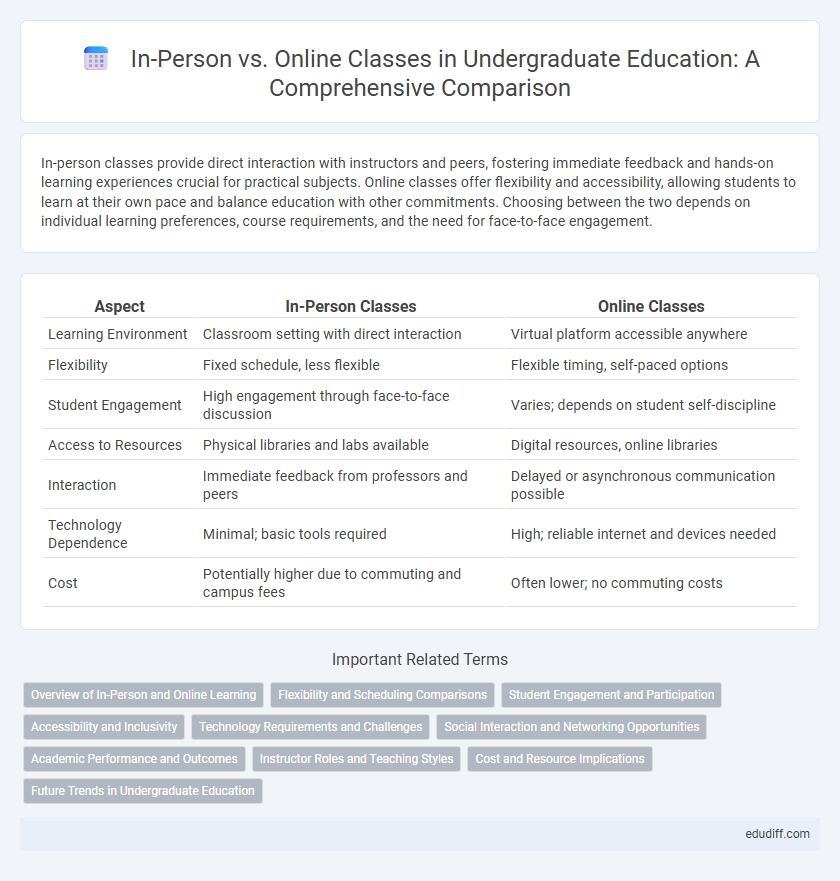
| Aspect | In-Person Classes | Online Classes |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Environment | Classroom setting with direct interaction | Virtual platform accessible anywhere |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule, less flexible | Flexible timing, self-paced options |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through face-to-face discussion | Varies; depends on student self-discipline |
| Access to Resources | Physical libraries and labs available | Digital resources, online libraries |
| Interaction | Immediate feedback from professors and peers | Delayed or asynchronous communication possible |
| Technology Dependence | Minimal; basic tools required | High; reliable internet and devices needed |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to commuting and campus fees | Often lower; no commuting costs |
Overview of In-Person and Online Learning
In-person classes offer direct interaction with instructors and peers, fostering immediate feedback and collaborative learning environments essential for hands-on subjects. Online classes provide flexible access to educational resources and accommodate varied schedules, utilizing digital platforms for lectures, assignments, and discussions. Both formats incorporate multimedia tools and assessment methods tailored to enhance comprehension and engagement based on instructional design principles.
Flexibility and Scheduling Comparisons
In-person classes offer a structured schedule with fixed times and locations, providing consistent routines but limited flexibility for students managing work or personal commitments. Online classes allow greater flexibility, enabling students to access course materials and complete assignments on their own schedules, which benefits those balancing multiple responsibilities. However, online learning demands strong time-management skills to prevent procrastination and ensure timely participation in synchronous sessions or deadlines.
Student Engagement and Participation
In-person classes foster higher student engagement through direct interaction, immediate feedback, and dynamic group discussions, which enhance comprehension and motivation. Online classes, while offering flexible participation options such as chat functions and breakout rooms, often face challenges in maintaining consistent student involvement due to distractions and technical issues. Effective strategies to boost participation in both formats include interactive activities, real-time polls, and personalized communication to sustain student interest and accountability.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
In-person classes provide tactile learning experiences and direct interaction but may limit accessibility for students with disabilities or those living in remote areas. Online classes enhance inclusivity by offering flexible scheduling and diverse digital tools, allowing a broader range of students to participate regardless of geographic or physical constraints. Hybrid models combine both, leveraging the strengths of in-person engagement and online accessibility to foster a more inclusive undergraduate learning environment.
Technology Requirements and Challenges
In-person classes require reliable campus infrastructure such as computer labs and physical access to educational technology, while online classes depend heavily on students having high-speed internet and compatible devices like laptops or tablets. Technology challenges for in-person settings often involve limited resource availability or outdated equipment, whereas online learning faces issues like connectivity disruptions and software compatibility problems. Ensuring equitable access to technology is critical for both formats to support effective undergraduate learning experiences.
Social Interaction and Networking Opportunities
In-person classes provide richer social interaction and networking opportunities through face-to-face discussions, group projects, and campus events that foster stronger personal connections. Online classes often limit spontaneous conversations and non-verbal communication, which can hinder relationship building and professional networking. However, virtual platforms try to compensate by offering discussion forums and scheduled video meetups, although these tend to be less effective for developing deep social bonds.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
In-person classes enhance academic performance by facilitating direct interaction with instructors and peers, leading to better engagement and immediate feedback. Studies show students in traditional classroom settings often achieve higher grades and retain information more effectively compared to their online counterparts. However, online classes offer flexibility and access to diverse resources, which can also promote successful academic outcomes when students maintain discipline and active participation.
Instructor Roles and Teaching Styles
In-person classes allow instructors to employ dynamic teaching styles such as spontaneous discussions and real-time feedback, enhancing student engagement through face-to-face interaction. Online classes require instructors to adapt by utilizing multimedia tools, asynchronous discussions, and structured content delivery to maintain clarity and student participation. The shift in instructor roles from traditional lecturing to digital facilitation transforms the educational experience, demanding flexibility and technological proficiency.
Cost and Resource Implications
In-person classes typically incur higher costs due to campus facility maintenance, utilities, and transportation expenses, while online classes significantly reduce these overheads by leveraging digital platforms. Resource distribution also varies; in-person instruction demands physical classrooms, labs, and printed materials, whereas online formats depend on robust internet connectivity and virtual learning tools. Budget allocation often shifts from physical infrastructure in traditional settings to technology development and student access in online education.
Future Trends in Undergraduate Education
Future trends in undergraduate education emphasize a hybrid model that integrates in-person classes with online learning platforms to enhance flexibility and accessibility. Advanced technologies such as virtual reality and AI-driven personalized learning tools are increasingly incorporated to improve engagement and accommodate diverse learning styles. Institutions are investing in digital infrastructure to support scalable, interactive remote education while maintaining the benefits of on-campus experiences.
In-Person Classes vs Online Classes Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com