Pursuing a double major allows undergraduate students to specialize in two academic disciplines within a single degree, fostering interdisciplinary skills and broadening career opportunities without extending the time required to graduate. In contrast, a dual degree involves earning two separate degrees, often requiring additional coursework and time, offering deeper expertise and credentials in distinct fields. Choosing between a double major and a dual degree depends on the student's career goals, time commitment, and desire for specialized knowledge versus a broader academic experience.
Table of Comparison
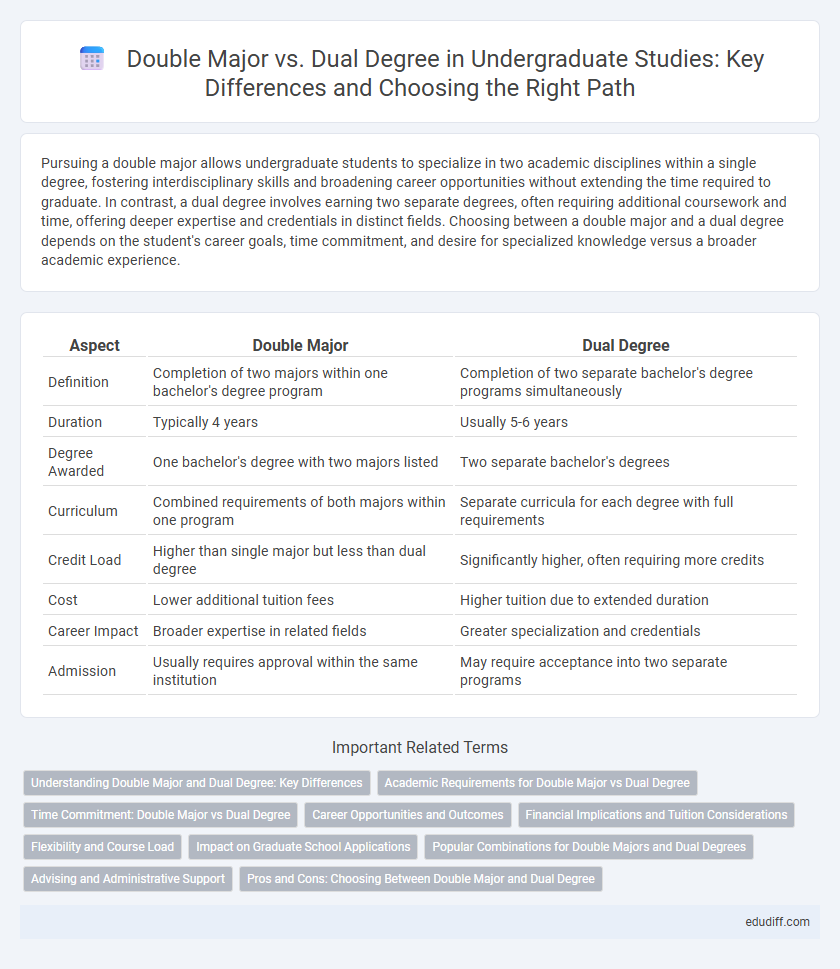
| Aspect | Double Major | Dual Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Completion of two majors within one bachelor's degree program | Completion of two separate bachelor's degree programs simultaneously |
| Duration | Typically 4 years | Usually 5-6 years |
| Degree Awarded | One bachelor's degree with two majors listed | Two separate bachelor's degrees |
| Curriculum | Combined requirements of both majors within one program | Separate curricula for each degree with full requirements |
| Credit Load | Higher than single major but less than dual degree | Significantly higher, often requiring more credits |
| Cost | Lower additional tuition fees | Higher tuition due to extended duration |
| Career Impact | Broader expertise in related fields | Greater specialization and credentials |
| Admission | Usually requires approval within the same institution | May require acceptance into two separate programs |
Understanding Double Major and Dual Degree: Key Differences
A double major allows students to earn one bachelor's degree by completing the requirements of two academic disciplines within the same institution, promoting an integrated skill set. A dual degree involves pursuing two separate bachelor's degrees, often requiring additional coursework and time, which results in two distinct diplomas. Understanding these key differences helps students align their academic goals with their career aspirations and manage their workload effectively.
Academic Requirements for Double Major vs Dual Degree
Double major programs require students to fulfill core curriculum and major-specific credits for two disciplines within a single undergraduate degree, typically totaling around 120-150 credit hours. Dual degree programs mandate completion of two separate degrees, often extending total credits to 150-180 or more, with distinct graduation requirements for each degree. Academic requirements for dual degrees usually involve meeting separate residency, thesis, and internship standards, making them more demanding than double majors.
Time Commitment: Double Major vs Dual Degree
Pursuing a double major typically requires completing two sets of major requirements within the timeframe of a single undergraduate degree, often extending studies by a semester to a year. A dual degree demands fulfilling the full credit requirements for two separate degrees, generally resulting in an extended time commitment of two or more years beyond a traditional bachelor's program. Students should consider the increased course load and longer duration when choosing between a double major and a dual degree.
Career Opportunities and Outcomes
Double majors offer students expertise in two academic disciplines, enhancing versatility and problem-solving skills highly sought by employers in competitive job markets. Dual degrees provide distinct qualifications from two separate programs, often leading to specialized career paths with increased earning potential and professional recognition. Graduates with dual degrees typically benefit from expanded networking opportunities and access to diverse industries, boosting long-term career advancement.
Financial Implications and Tuition Considerations
Double major programs typically involve completing two fields of study within a single undergraduate degree, often without significantly extending the time or cost of education, making them a more cost-effective option. Dual degree programs require separate degrees, usually necessitating additional semesters and, consequently, higher tuition and related expenses. Financial implications vary by institution, but students should carefully evaluate the increased tuition costs, potential eligibility for financial aid, and overall return on investment when considering dual degrees versus double majors.
Flexibility and Course Load
Double majors offer greater flexibility by allowing students to pursue two related fields within a single degree program, often sharing core courses and reducing the overall course load. Dual degrees require completing two separate degree programs, which typically increases the total credit hours and extends the time needed for graduation. Students seeking a manageable balance between diverse academic interests and workload often prefer double majors, while those aiming for distinct qualifications may choose dual degrees despite the heavier course demands.
Impact on Graduate School Applications
Choosing a double major or dual degree can significantly influence graduate school applications, with dual degrees often demonstrating broader interdisciplinary expertise due to earning two separate diplomas. Graduate programs may view dual degrees as a stronger indicator of academic rigor and time management, which can enhance an applicant's competitiveness. However, a double major provides depth within a single institution and field, allowing focused research experience that is highly valued in specialized graduate programs.
Popular Combinations for Double Majors and Dual Degrees
Popular combinations for double majors often include Business and Economics, Psychology and Sociology, or Computer Science and Mathematics, enabling students to deepen expertise in closely related fields. Dual degree programs frequently pair complementary disciplines such as Engineering and Business Administration or Law and Public Policy, allowing students to earn two distinct degrees with broader professional qualifications. These combinations align with market demands, enhancing employability and interdisciplinary skills critical in competitive job markets.
Advising and Administrative Support
Double major students often receive streamlined advising through a single college's academic office, allowing coordinated course planning and consistent guidance on degree requirements. Dual degree candidates typically navigate separate advising teams and administrative systems for each program, which can complicate scheduling and require more proactive communication. Universities with dedicated support services for dual degree students tend to provide smoother administrative assistance, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and enhancing the overall academic experience.
Pros and Cons: Choosing Between Double Major and Dual Degree
Choosing between a double major and a dual degree impacts academic workload and career opportunities; a double major allows students to complete two concentrations within one degree, often saving time and tuition costs but may limit specialization depth. A dual degree requires fulfilling requirements for two separate degrees, offering broader expertise and increased employability but demands more time and financial investment. Students must weigh factors like program flexibility, graduation timeline, and long-term professional goals to make an informed decision.
Double Major vs Dual Degree Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com