Resident Assistants (RAs) primarily oversee student living environments, ensuring safety and fostering community engagement in dormitories. Teaching Assistants (TAs) support academic instruction by grading assignments, leading discussion sections, and assisting professors with course management. Both roles develop leadership and communication skills but differ in focus--RAs emphasize residential life, while TAs concentrate on academic support.
Table of Comparison
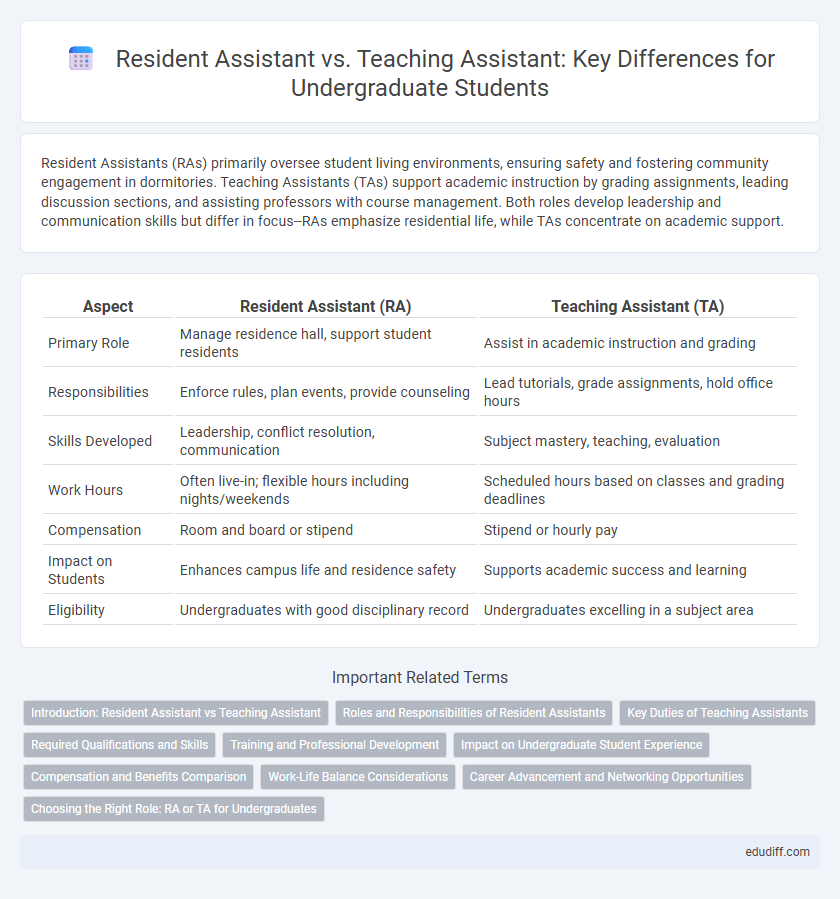
| Aspect | Resident Assistant (RA) | Teaching Assistant (TA) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage residence hall, support student residents | Assist in academic instruction and grading |
| Responsibilities | Enforce rules, plan events, provide counseling | Lead tutorials, grade assignments, hold office hours |
| Skills Developed | Leadership, conflict resolution, communication | Subject mastery, teaching, evaluation |
| Work Hours | Often live-in; flexible hours including nights/weekends | Scheduled hours based on classes and grading deadlines |
| Compensation | Room and board or stipend | Stipend or hourly pay |
| Impact on Students | Enhances campus life and residence safety | Supports academic success and learning |
| Eligibility | Undergraduates with good disciplinary record | Undergraduates excelling in a subject area |
Introduction: Resident Assistant vs Teaching Assistant
Resident Assistants (RAs) manage residential communities by providing peer support, enforcing policies, and organizing events to foster engagement. Teaching Assistants (TAs) assist faculty by grading assignments, leading discussion sections, and offering academic support to students. Both roles enhance the undergraduate experience through leadership and mentorship in different campus environments.
Roles and Responsibilities of Resident Assistants
Resident Assistants (RAs) primarily focus on creating a safe, inclusive living environment by enforcing residence hall policies and facilitating community-building activities. They provide peer support, mediate conflicts, and organize educational programs to enhance residents' personal and academic development. Unlike Teaching Assistants who support academic instruction, RAs serve as leaders and resources within campus housing, promoting student well-being and engagement.
Key Duties of Teaching Assistants
Teaching Assistants (TAs) primarily support professors by grading assignments, leading discussion sections, and conducting review sessions to enhance undergraduate learning. They manage course logistics such as maintaining attendance records and facilitating communication between students and faculty. Unlike Resident Assistants, TAs focus on academic responsibilities rather than residential life management.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Resident Assistants require strong interpersonal skills, conflict resolution abilities, and a commitment to community building, often necessitating prior experience in leadership or peer counseling. Teaching Assistants must possess subject-matter expertise, effective communication skills, and proficiency in instructional techniques, typically demonstrated through academic achievement in the relevant discipline. Both roles demand responsibility and teamwork, but RAs emphasize resident welfare while TAs focus on supporting academic instruction.
Training and Professional Development
Resident Assistant training emphasizes conflict resolution, emergency procedures, and community building to prepare students for on-campus leadership roles. Teaching Assistant development focuses on pedagogical skills, subject mastery, grading techniques, and effective communication for academic support. Both roles offer specialized workshops and continuous mentorship to enhance professional competencies relevant to their unique responsibilities.
Impact on Undergraduate Student Experience
Resident Assistants (RAs) foster community engagement and provide peer support within residence halls, directly enhancing students' social integration and personal development. Teaching Assistants (TAs) contribute to academic success by facilitating understanding of course material, offering personalized feedback, and supporting classroom management. Together, RAs and TAs play distinct but complementary roles in shaping a holistic and supportive undergraduate experience.
Compensation and Benefits Comparison
Resident Assistants (RAs) often receive compensation in the form of free or discounted on-campus housing and meal plans, which substantially reduces living expenses. Teaching Assistants (TAs) typically earn a stipend or hourly wage based on instructional responsibilities, providing direct financial compensation. While RAs benefit from tangible housing perks and community-building allowances, TAs gain monetary payment that supplements their academic expenses and professional development.
Work-Life Balance Considerations
Resident Assistants (RAs) often face irregular hours due to on-call duties and residential event planning, which can impact personal time and social activities. Teaching Assistants (TAs) usually have more structured schedules centered around class times, grading, and office hours, allowing for better predictability in balancing academics and personal life. Both roles require strong time management skills, but TAs typically experience a more consistent work-life balance compared to RAs.
Career Advancement and Networking Opportunities
Resident Assistants gain leadership experience by managing residential communities, enhancing interpersonal skills crucial for roles in student affairs or counseling fields. Teaching Assistants develop expertise in subject matter and communication through direct academic support, preparing them for careers in education or research. Both positions offer unique networking opportunities: Resident Assistants connect with campus administration and diverse student groups, while Teaching Assistants build relationships with faculty and academic professionals.
Choosing the Right Role: RA or TA for Undergraduates
Choosing between a Resident Assistant (RA) and a Teaching Assistant (TA) depends on your strengths and interests as an undergraduate. An RA role emphasizes leadership, community building, and conflict resolution within residence halls, offering valuable interpersonal and organizational skills. A TA position focuses on academic support, grading, and assisting professors, ideal for those seeking experience in teaching and subject mastery.
Resident Assistant vs Teaching Assistant Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com