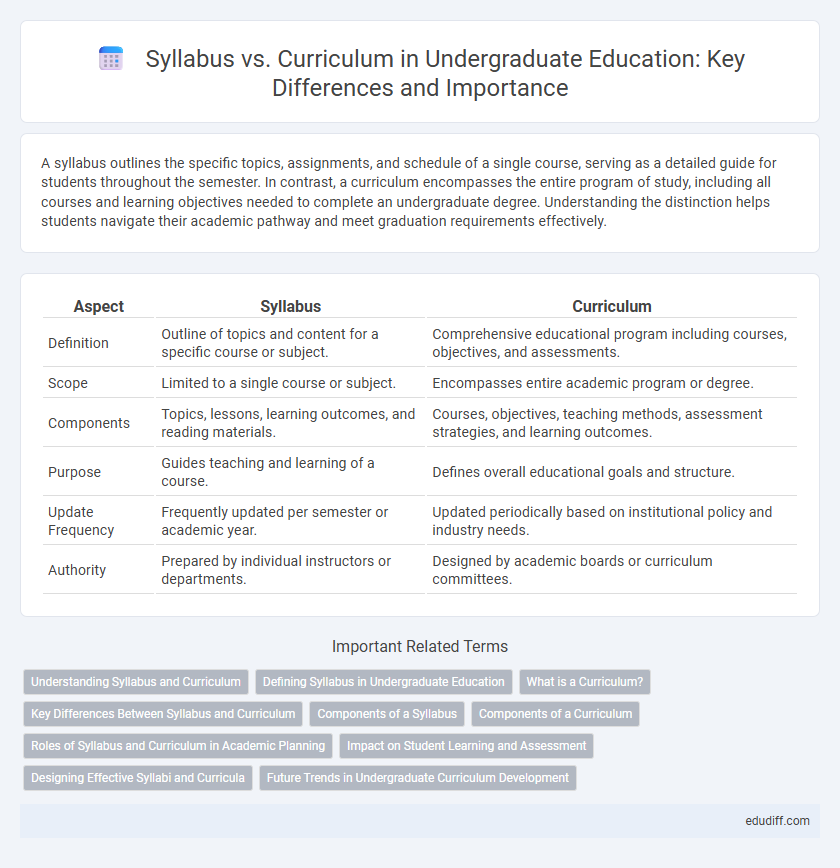
A syllabus outlines the specific topics, assignments, and schedule of a single course, serving as a detailed guide for students throughout the semester. In contrast, a curriculum encompasses the entire program of study, including all courses and learning objectives needed to complete an undergraduate degree. Understanding the distinction helps students navigate their academic pathway and meet graduation requirements effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Syllabus | Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outline of topics and content for a specific course or subject. | Comprehensive educational program including courses, objectives, and assessments. |
| Scope | Limited to a single course or subject. | Encompasses entire academic program or degree. |
| Components | Topics, lessons, learning outcomes, and reading materials. | Courses, objectives, teaching methods, assessment strategies, and learning outcomes. |
| Purpose | Guides teaching and learning of a course. | Defines overall educational goals and structure. |
| Update Frequency | Frequently updated per semester or academic year. | Updated periodically based on institutional policy and industry needs. |
| Authority | Prepared by individual instructors or departments. | Designed by academic boards or curriculum committees. |
Understanding Syllabus and Curriculum
The syllabus outlines specific topics, objectives, and assessment methods for a single course, providing a detailed roadmap for what students will learn and how they will be evaluated. The curriculum encompasses the broader academic program, integrating multiple syllabi to achieve comprehensive educational goals across semesters or years. Understanding the distinction helps undergraduate students navigate their studies effectively by aligning course-level learning with program-level outcomes.
Defining Syllabus in Undergraduate Education
A syllabus in undergraduate education outlines the detailed plan for a specific course, including learning objectives, topics, assignments, and assessment methods. It serves as a contract between instructors and students, providing clear expectations and a structured timeline for course content delivery. Unlike the broader curriculum, which encompasses all courses in a degree program, the syllabus targets the instructional framework for individual classes.
What is a Curriculum?
A curriculum is a comprehensive educational framework outlining the entire scope of courses, learning objectives, and academic content designed for an undergraduate program. It integrates various syllabi, teaching methods, assessment strategies, and skill development goals to provide a structured pathway for student learning and progression. Curriculum planning ensures alignment with institutional standards, industry requirements, and academic outcomes to equip undergraduates with relevant knowledge and competencies.
Key Differences Between Syllabus and Curriculum
The syllabus refers to the specific content, topics, and materials covered in a particular course or subject, outlining what students are expected to learn. The curriculum encompasses the overall educational plan, including multiple courses, objectives, teaching methods, and assessment strategies designed to achieve broader academic goals. Key differences include the syllabus being course-specific and detailed, while the curriculum provides a comprehensive framework for an entire program or degree.
Components of a Syllabus
A syllabus outlines the specific components of an undergraduate course, including learning objectives, assessment methods, reading materials, and lesson schedules. It serves as a detailed roadmap for students, facilitating clear expectations and structured content delivery. Unlike the broader curriculum, which encompasses the overall program's goals and sequence of courses, a syllabus focuses on the granular elements that guide individual class instruction.
Components of a Curriculum
A curriculum comprises multiple components, including objectives, content, learning experiences, instructional materials, and assessment methods, all designed to ensure comprehensive education. Unlike a syllabus that outlines specific course topics and timelines, the curriculum provides a broader framework encompassing educational philosophy, course sequences, and skill development goals. Effective curriculum design integrates these elements to align academic standards with student learning outcomes across the undergraduate program.
Roles of Syllabus and Curriculum in Academic Planning
The syllabus serves as a detailed guide outlining specific topics, learning objectives, assessment methods, and schedule for individual courses within an undergraduate program, ensuring focused knowledge delivery. The curriculum encompasses the entire academic program structure, integrating various syllabi to define the scope, sequence, and educational goals crucial for holistic student development and competency building. Together, the syllabus and curriculum align course content with institutional learning outcomes, facilitating effective academic planning and consistent quality assurance across undergraduate studies.
Impact on Student Learning and Assessment
Syllabus defines specific course content, learning objectives, and assessment methods, directly shaping student learning experiences and performance evaluations. Curriculum encompasses the broader educational framework, integrating multiple syllabi to ensure comprehensive skill development and knowledge acquisition across an academic program. Effective alignment between syllabus and curriculum enhances consistency in assessment standards and promotes cohesive student learning outcomes.
Designing Effective Syllabi and Curricula
Designing effective syllabi requires clear learning objectives, detailed course content, and assessment methods tailored to align with overarching curriculum goals. Curriculum design emphasizes a coherent sequence of courses ensuring comprehensive coverage of subject areas and progressive skill development for undergraduates. Integrating well-structured syllabi within a thoughtfully planned curriculum enhances student engagement and academic success.
Future Trends in Undergraduate Curriculum Development
Emerging future trends in undergraduate curriculum development emphasize interdisciplinary studies and integration of technology-enhanced learning to prepare students for dynamic career landscapes. Syllabus design is evolving to include flexible modules and competency-based assessments that align with rapidly changing industry standards. Incorporating real-world problem-solving projects within curricula fosters critical thinking and adaptability essential for future workforce demands.
Syllabus vs Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com