Liberal Arts education fosters critical thinking, creativity, and effective communication, preparing students for diverse career paths and lifelong learning. STEM programs emphasize technical skills, scientific inquiry, and problem-solving abilities crucial for innovation and technological advancement. Choosing between Liberal Arts and STEM depends on individual interests and career goals, as both provide valuable foundations for professional success.
Table of Comparison
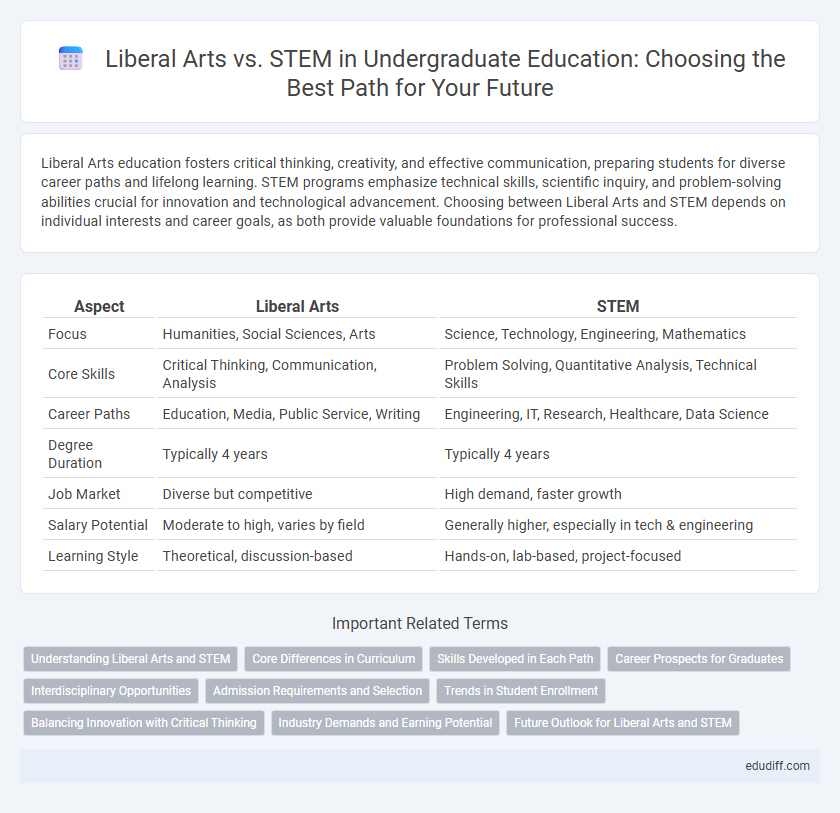
| Aspect | Liberal Arts | STEM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Humanities, Social Sciences, Arts | Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics |
| Core Skills | Critical Thinking, Communication, Analysis | Problem Solving, Quantitative Analysis, Technical Skills |
| Career Paths | Education, Media, Public Service, Writing | Engineering, IT, Research, Healthcare, Data Science |
| Degree Duration | Typically 4 years | Typically 4 years |
| Job Market | Diverse but competitive | High demand, faster growth |
| Salary Potential | Moderate to high, varies by field | Generally higher, especially in tech & engineering |
| Learning Style | Theoretical, discussion-based | Hands-on, lab-based, project-focused |
Understanding Liberal Arts and STEM
Liberal Arts education emphasizes critical thinking, communication, and a broad interdisciplinary knowledge base, fostering creativity and ethical reasoning across humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) focuses on technical skills, quantitative analysis, and practical problem-solving essential for innovation in technology and scientific research. Understanding the core methodologies and career pathways of both Liberal Arts and STEM helps students make informed decisions aligned with their academic interests and professional goals.
Core Differences in Curriculum
Liberal Arts curricula emphasize broad interdisciplinary studies including humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, promoting critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills. STEM programs concentrate on math, technology, engineering, and science subjects, focusing on hands-on experiments, quantitative analysis, and technical proficiency. Core differences in curriculum reflect the distinct goals: liberal arts develop versatile problem-solving and cultural awareness, while STEM aims at specialized technical expertise and innovation.
Skills Developed in Each Path
Liberal Arts programs emphasize critical thinking, communication, and analytical writing skills, fostering creativity and cultural awareness. STEM degrees develop technical proficiency, quantitative analysis, and problem-solving abilities essential for innovation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields. Both paths cultivate unique skill sets that prepare undergraduates for diverse career opportunities and adaptability in a rapidly changing job market.
Career Prospects for Graduates
Liberal arts graduates develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills that are highly valued in fields like education, public relations, and social services, offering diverse career paths. STEM graduates benefit from strong demand in technology, engineering, healthcare, and scientific research, leading to higher average starting salaries and rapid job growth projections. Career prospects for STEM majors often include specialized roles with opportunities for innovation, while liberal arts majors excel in adaptable, interdisciplinary positions that require creativity and analytical reasoning.
Interdisciplinary Opportunities
Liberal arts and STEM disciplines offer unique interdisciplinary opportunities that foster innovation and critical thinking across fields. Integrating liberal arts perspectives into STEM encourages creative problem-solving, ethical considerations, and communication skills essential for technological advancements. Conversely, STEM knowledge enhances liberal arts education by providing analytical tools and data-driven insights, promoting a well-rounded undergraduate experience.
Admission Requirements and Selection
Liberal Arts programs typically prioritize a broad range of high school coursework in humanities, social sciences, and communication skills, emphasizing critical thinking, creativity, and writing proficiency during admission evaluations. STEM programs require strong foundations in mathematics, science subjects, and sometimes related standardized test scores or practical assessments to demonstrate analytical and problem-solving capabilities. Selection in STEM often involves reviewing quantitative achievements and technical skills, whereas Liberal Arts admissions focus more on diverse intellectual interests and holistic essays.
Trends in Student Enrollment
Recent trends in student enrollment show a significant shift toward STEM fields, with a 25% increase in undergraduate majors over the past five years, driven by job market demand and technological advancements. In contrast, liberal arts programs have experienced a decline of approximately 10% in enrollment, as students prioritize career-oriented degrees and practical skills. Despite this, liberal arts remain essential for developing critical thinking and communication abilities, maintaining a steady interest among students seeking interdisciplinary education.
Balancing Innovation with Critical Thinking
Liberal Arts education cultivates critical thinking, creativity, and ethical reasoning, fostering well-rounded individuals who can analyze complex societal issues. STEM programs emphasize innovation, technical skills, and problem-solving abilities crucial for advancing technology and scientific discovery. Balancing both approaches equips undergraduates with the analytical rigor and innovative mindset needed to address multifaceted global challenges effectively.
Industry Demands and Earning Potential
STEM fields, including engineering, computer science, and data analytics, consistently align with high industry demands, offering graduates competitive salaries and strong job security. Liberal arts disciplines develop critical thinking, communication, and adaptability skills essential for evolving job markets, but typically exhibit slower salary growth compared to STEM careers. Employers increasingly seek interdisciplinary expertise, encouraging integration of liberal arts perspectives within STEM roles to enhance innovation and leadership capabilities.
Future Outlook for Liberal Arts and STEM
Graduates in STEM fields such as engineering, computer science, and data analytics face a rapidly growing job market driven by technological innovation and digital transformation, offering strong salary prospects and job stability. Liberal arts graduates develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills applicable to diverse industries, including education, public policy, and creative sectors, with increasing demand for adaptable professionals in an automated economy. Both paths showcase promising futures, though STEM roles tend to have higher projected employment growth rates, while liberal arts degrees provide versatile skills essential for evolving interdisciplinary careers.
Liberal Arts vs STEM Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com