General education courses provide a broad foundation of knowledge across various disciplines, fostering critical thinking and communication skills essential for academic success. Major requirements concentrate on specialized subjects that develop expertise and technical skills directly related to a student's chosen field. Balancing both ensures a well-rounded education that prepares students for diverse career opportunities and lifelong learning.
Table of Comparison
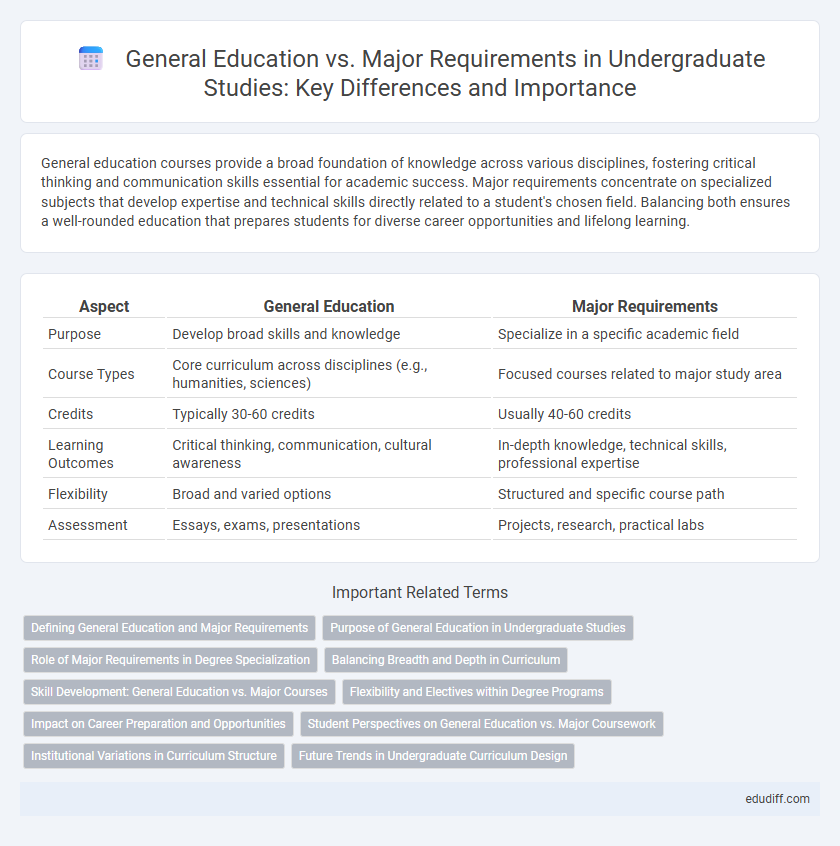
| Aspect | General Education | Major Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Develop broad skills and knowledge | Specialize in a specific academic field |
| Course Types | Core curriculum across disciplines (e.g., humanities, sciences) | Focused courses related to major study area |
| Credits | Typically 30-60 credits | Usually 40-60 credits |
| Learning Outcomes | Critical thinking, communication, cultural awareness | In-depth knowledge, technical skills, professional expertise |
| Flexibility | Broad and varied options | Structured and specific course path |
| Assessment | Essays, exams, presentations | Projects, research, practical labs |
Defining General Education and Major Requirements
General education requirements encompass foundational courses designed to develop broad skills and knowledge across disciplines such as humanities, sciences, and social sciences. Major requirements consist of specialized courses focusing on a student's chosen field of study, aimed at building expertise and comprehensive understanding within that discipline. Completing both ensures a balanced undergraduate education, integrating critical thinking and specialized skills.
Purpose of General Education in Undergraduate Studies
General Education courses provide undergraduates with a broad foundation of essential skills and knowledge across multiple disciplines, promoting critical thinking, communication, and cultural awareness. These requirements ensure students develop a well-rounded intellectual base that supports professional and personal growth beyond their specialized Major studies. By fostering interdisciplinary understanding, General Education prepares students for adaptable problem-solving and informed citizenship in diverse real-world contexts.
Role of Major Requirements in Degree Specialization
Major requirements play a critical role in degree specialization by providing in-depth knowledge and technical skills specific to a student's chosen field, ensuring expertise beyond the foundational concepts covered in general education. These specialized courses equip students with practical competencies and advanced theoretical understanding necessary for professional success and graduate study readiness. Fulfilling major requirements differentiates students within their discipline, aligning academic training with career objectives and industry standards.
Balancing Breadth and Depth in Curriculum
Balancing breadth and depth in undergraduate curricula involves integrating general education courses that develop critical thinking, communication, and interdisciplinary knowledge alongside major requirements that provide specialized expertise in a specific field. General education fosters a well-rounded foundation by exposing students to diverse disciplines such as humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, while major requirements ensure mastery of core concepts and advanced skills necessary for professional competency and research. Effective curriculum design harmonizes these components to cultivate adaptable graduates equipped for complex problem-solving and lifelong learning.
Skill Development: General Education vs. Major Courses
General education courses develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills through a broad curriculum, enhancing adaptability across various fields. Major courses provide specialized, in-depth knowledge and technical skills essential for expertise in a specific discipline. Combining both builds a well-rounded skill set that prepares undergraduates for complex professional challenges and lifelong learning.
Flexibility and Electives within Degree Programs
General Education requirements provide foundational knowledge across diverse disciplines, offering flexibility in course selection to broaden intellectual perspectives. Major requirements focus on specialized skills and advanced knowledge within a specific field, typically offering fewer elective options to ensure depth of expertise. Balancing both allows undergraduate students to customize their academic experience while meeting core degree standards.
Impact on Career Preparation and Opportunities
General education courses develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills essential for adaptability in diverse career fields. Major requirements provide specialized knowledge and technical expertise that directly align with industry standards and professional competencies. Balancing both enhances employability by offering a well-rounded skill set and in-depth subject mastery necessary for career advancement.
Student Perspectives on General Education vs. Major Coursework
Students often perceive general education courses as essential for developing critical thinking and broad knowledge, yet they may prioritize major coursework for its direct relevance to their career goals and specialization. The balance between the two can influence students' academic engagement and satisfaction, as general education provides interdisciplinary skills while major requirements deepen expertise. Perspectives vary widely, with some students valuing the diversity of general education and others focusing on efficiency and depth within their chosen field.
Institutional Variations in Curriculum Structure
Institutional variations in curriculum structure significantly impact the balance between General Education and Major Requirements at the undergraduate level. Some universities emphasize a broad-based curriculum with extensive General Education courses, promoting interdisciplinary knowledge and critical thinking skills. In contrast, other institutions prioritize specialized Major Requirements, tailoring coursework to deepen expertise and professional readiness within a specific discipline.
Future Trends in Undergraduate Curriculum Design
Future trends in undergraduate curriculum design emphasize integrating flexible general education pathways with specialized major requirements to foster interdisciplinary skills and adaptability. Data suggests a shift towards modular learning units that allow personalized combinations of general education and major courses, enhancing employability and lifelong learning potential. Institutions adopting technology-driven platforms enable real-time curriculum adjustments to meet evolving industry demands and global competencies.
General Education vs Major Requirements Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com