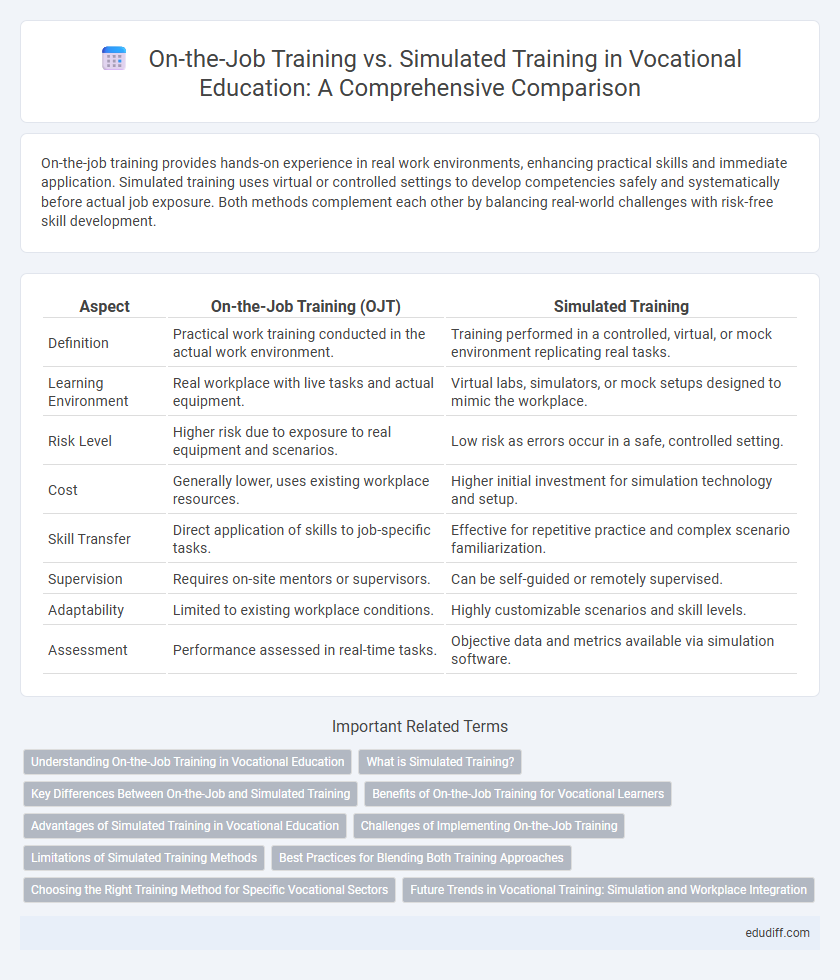
On-the-job training provides hands-on experience in real work environments, enhancing practical skills and immediate application. Simulated training uses virtual or controlled settings to develop competencies safely and systematically before actual job exposure. Both methods complement each other by balancing real-world challenges with risk-free skill development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | On-the-Job Training (OJT) | Simulated Training |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practical work training conducted in the actual work environment. | Training performed in a controlled, virtual, or mock environment replicating real tasks. |
| Learning Environment | Real workplace with live tasks and actual equipment. | Virtual labs, simulators, or mock setups designed to mimic the workplace. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to exposure to real equipment and scenarios. | Low risk as errors occur in a safe, controlled setting. |
| Cost | Generally lower, uses existing workplace resources. | Higher initial investment for simulation technology and setup. |
| Skill Transfer | Direct application of skills to job-specific tasks. | Effective for repetitive practice and complex scenario familiarization. |
| Supervision | Requires on-site mentors or supervisors. | Can be self-guided or remotely supervised. |
| Adaptability | Limited to existing workplace conditions. | Highly customizable scenarios and skill levels. |
| Assessment | Performance assessed in real-time tasks. | Objective data and metrics available via simulation software. |
Understanding On-the-Job Training in Vocational Education
On-the-Job Training (OJT) in vocational education provides hands-on experience by immersing learners directly in real work environments, enhancing skill acquisition through practical application. This method fosters immediate problem-solving abilities, workplace adaptability, and exposure to actual industry standards. Compared to simulated training, OJT ensures trainees develop job-specific competencies essential for effective performance and career readiness.
What is Simulated Training?
Simulated training replicates real-world work environments using virtual reality, computer-based programs, or physical mock-ups to provide hands-on experience without the risks or costs associated with on-the-job training. This method enhances skill acquisition by allowing trainees to practice complex tasks repeatedly in a controlled setting, improving retention and performance. Industries such as aviation, healthcare, and manufacturing widely adopt simulated training to ensure safety and accuracy before actual job placement.
Key Differences Between On-the-Job and Simulated Training
On-the-job training offers hands-on experience in a real work environment, promoting immediate skill application and workflow integration. Simulated training provides a controlled, risk-free setting using virtual tools or mannequins to replicate job scenarios for focused skill development without operational disruptions. Key differences include real-time feedback and direct exposure in on-the-job training versus customizable, repeatable practice with error tolerance in simulated training.
Benefits of On-the-Job Training for Vocational Learners
On-the-job training offers vocational learners direct exposure to real work environments, allowing them to develop practical skills under authentic conditions. This hands-on experience accelerates skill acquisition and enhances job readiness by enabling immediate application of knowledge to actual tasks. Employers benefit from on-the-job training by cultivating a workforce tailored to company-specific processes and culture, promoting higher retention rates and productivity.
Advantages of Simulated Training in Vocational Education
Simulated training in vocational education offers a safe, controlled environment where learners can practice complex tasks without risk to themselves or equipment, enhancing skill retention and confidence. It provides immediate feedback and repeatability, allowing trainees to refine their techniques before real-world application. This method effectively bridges the gap between theory and practice, making it a cost-efficient alternative to traditional on-the-job training.
Challenges of Implementing On-the-Job Training
Implementing On-the-Job Training (OJT) faces challenges such as inconsistent quality due to varying skill levels among trainers and limited availability of real-time feedback for trainees. Workplace interruptions and production demands often reduce the time allocated for hands-on learning, impacting the effectiveness of OJT programs. Ensuring safety compliance and maintaining standardized training across diverse job sites further complicate the implementation process.
Limitations of Simulated Training Methods
Simulated training methods lack the unpredictability and real-time pressure of actual work environments, which limits trainees' ability to develop adaptive problem-solving skills. The absence of hands-on experience with actual equipment and materials can result in a gap between simulated scenarios and workplace realities. Furthermore, simulated environments may not fully replicate teamwork dynamics or client interactions critical for vocational competency.
Best Practices for Blending Both Training Approaches
Integrating on-the-job training with simulated training enhances skill acquisition by combining real-world experience and risk-free practice environments. Best practices include aligning simulated scenarios closely with actual job tasks to reinforce learning and systematically rotating trainees between both methods to maximize exposure and retention. Leveraging performance data from simulations and workplace assessments allows for tailored training adjustments that improve competency and confidence in vocational roles.
Choosing the Right Training Method for Specific Vocational Sectors
On-the-Job Training (OJT) offers hands-on experience tailored to real work environments, making it ideal for sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and hospitality where practical skills are crucial. Simulated Training provides a risk-free environment for complex or hazardous tasks, benefiting fields such as aviation, emergency response, and technical maintenance. Selecting the appropriate training method depends on the vocational sector's safety requirements, skill complexity, and the availability of real-world training opportunities.
Future Trends in Vocational Training: Simulation and Workplace Integration
Future trends in vocational training emphasize the integration of advanced simulation technologies with real-world workplace experiences to enhance skill acquisition. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) create immersive, risk-free environments that complement on-the-job training by providing tailored, repeatable scenarios. This hybrid approach optimizes learner engagement, accelerates competency development, and aligns training outcomes with evolving industry demands.
On-the-Job Training vs Simulated Training Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com