Technical schools offer comprehensive programs that combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on training in fields such as engineering, IT, and healthcare, preparing students for a range of technical professions. Trade schools focus specifically on skill-based training for skilled trades like plumbing, electrical work, and welding, emphasizing practical experience and industry certification. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, with technical schools providing broader education and trade schools concentrating on specialized manual skills.
Table of Comparison
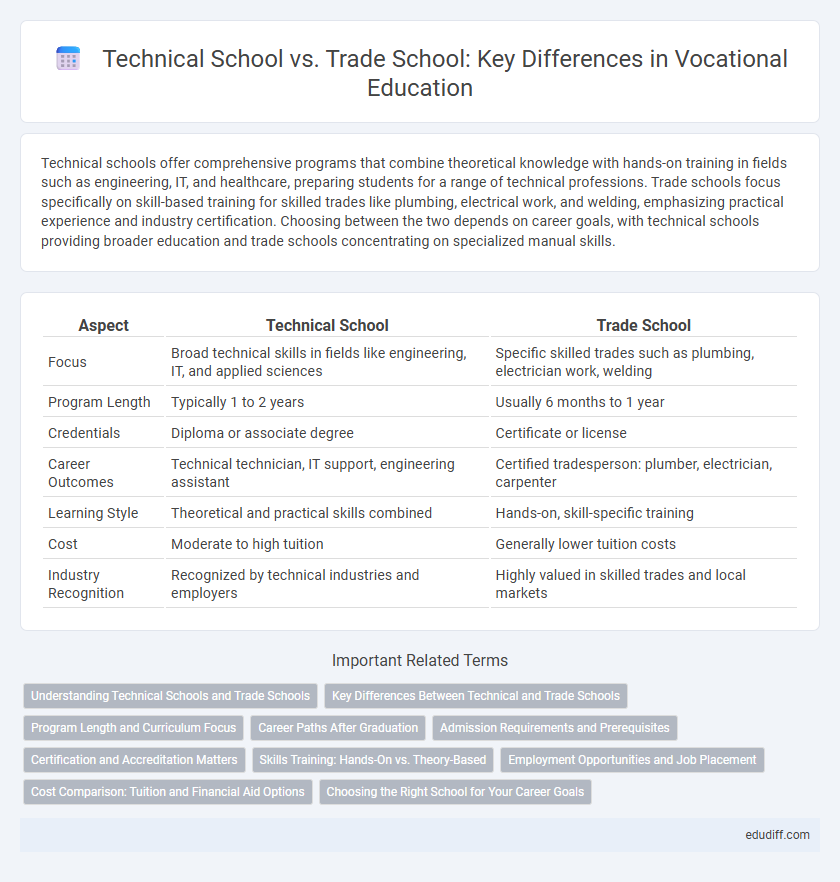
| Aspect | Technical School | Trade School |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Broad technical skills in fields like engineering, IT, and applied sciences | Specific skilled trades such as plumbing, electrician work, welding |
| Program Length | Typically 1 to 2 years | Usually 6 months to 1 year |
| Credentials | Diploma or associate degree | Certificate or license |
| Career Outcomes | Technical technician, IT support, engineering assistant | Certified tradesperson: plumber, electrician, carpenter |
| Learning Style | Theoretical and practical skills combined | Hands-on, skill-specific training |
| Cost | Moderate to high tuition | Generally lower tuition costs |
| Industry Recognition | Recognized by technical industries and employers | Highly valued in skilled trades and local markets |
Understanding Technical Schools and Trade Schools
Technical schools provide specialized education in fields such as information technology, engineering technology, and healthcare, emphasizing both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Trade schools focus primarily on hands-on training for specific trades like welding, plumbing, or automotive repair, preparing students for immediate entry into the workforce. Both institutions offer accelerated programs designed to meet industry demands, but technical schools often include broader academic components alongside skill development.
Key Differences Between Technical and Trade Schools
Technical schools emphasize theoretical knowledge and advanced technical skills in fields like engineering technology, computer science, and healthcare, preparing students for specialized professions. Trade schools focus on hands-on training for specific skilled trades such as welding, plumbing, electrician work, and automotive repair, enabling faster entry into the workforce. Curriculums at technical schools are often broader and longer, while trade schools offer shorter, practical programs centered on specific job competencies.
Program Length and Curriculum Focus
Technical schools typically offer programs ranging from one to four years, emphasizing comprehensive theoretical knowledge combined with practical skills across fields like engineering, IT, and healthcare. Trade schools usually provide shorter, more focused programs lasting a few months to two years, concentrating on hands-on training for specific trades such as welding, plumbing, or electrical work. Program length and curriculum focus distinguish technical schools' broader educational approach from trade schools' specialized skill development.
Career Paths After Graduation
Technical schools provide specialized training in fields like engineering technology, computer science, and healthcare, preparing graduates for careers that often require technical certifications or associate degrees. Trade schools focus on hands-on skills in trades such as plumbing, electrical work, welding, and automotive repair, enabling students to enter the workforce quickly as skilled tradespeople. Career paths from technical schools typically lead to positions like technician, technologist, or developer, while trade school graduates often become licensed tradespersons, contractors, or service specialists.
Admission Requirements and Prerequisites
Technical schools typically require a high school diploma or GED and may ask for standardized test scores or specific coursework in math and science as prerequisites for admission. Trade schools often have more flexible admission requirements, focusing primarily on a basic educational credential without demanding extensive prerequisite courses. Both institutions may require entrance exams or interviews, but technical schools generally have more rigorous academic standards reflecting their emphasis on advanced technical training.
Certification and Accreditation Matters
Technical schools often offer comprehensive programs that lead to industry-recognized certifications and hold regional or national accreditation, ensuring the quality and transferability of credits. Trade schools focus primarily on hands-on training for specific trades and typically provide certifications that validate practical skills essential for immediate employment. Understanding the differences in certification types and accreditation bodies is crucial for students to choose an institution that aligns with their career goals and meets industry standards.
Skills Training: Hands-On vs. Theory-Based
Technical schools emphasize a blend of hands-on skills training and theoretical knowledge, preparing students for complex technical roles in industries like engineering, IT, and healthcare. Trade schools focus predominantly on hands-on skills training specific to skilled trades such as plumbing, electrical work, and welding, enabling students to enter the workforce quickly with practical expertise. The choice between technical and trade schools depends on the desired balance between theory and applied skills for career objectives.
Employment Opportunities and Job Placement
Technical schools offer specialized training in advanced technologies and engineering fields, enhancing employment opportunities in industries such as IT, healthcare, and manufacturing. Trade schools focus on hands-on skills for specific trades like plumbing, electrician work, and HVAC, providing direct pathways to jobs with apprenticeship options. Both institutions emphasize job placement services, but technical schools often partner with larger corporations while trade schools connect students with local employers and unions.
Cost Comparison: Tuition and Financial Aid Options
Technical schools generally have higher tuition fees compared to trade schools due to their broader curriculum and advanced facilities. Trade schools often offer more affordable tuition and specialized financial aid options such as apprenticeships, grants, and employer partnerships. Evaluating cost savings alongside aid availability is essential for students deciding between these vocational education paths.
Choosing the Right School for Your Career Goals
Choosing the right educational path between a technical school and a trade school depends on your specific career goals and industry preferences. Technical schools offer comprehensive programs in fields like information technology, healthcare, and engineering technology, emphasizing theory alongside practical skills. Trade schools focus on hands-on training for specialized trades such as plumbing, welding, and electrical work, prioritizing direct job readiness and certification.
Technical school vs Trade school Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com