Apprenticeships provide hands-on training in a specific trade or profession, combining paid work with structured learning over a longer period. Internships offer shorter-term experiences focused on gaining industry exposure and developing skills, often within a broader range of fields. Both pathways help build practical expertise, but apprenticeships typically lead to certification or direct employment opportunities.
Table of Comparison
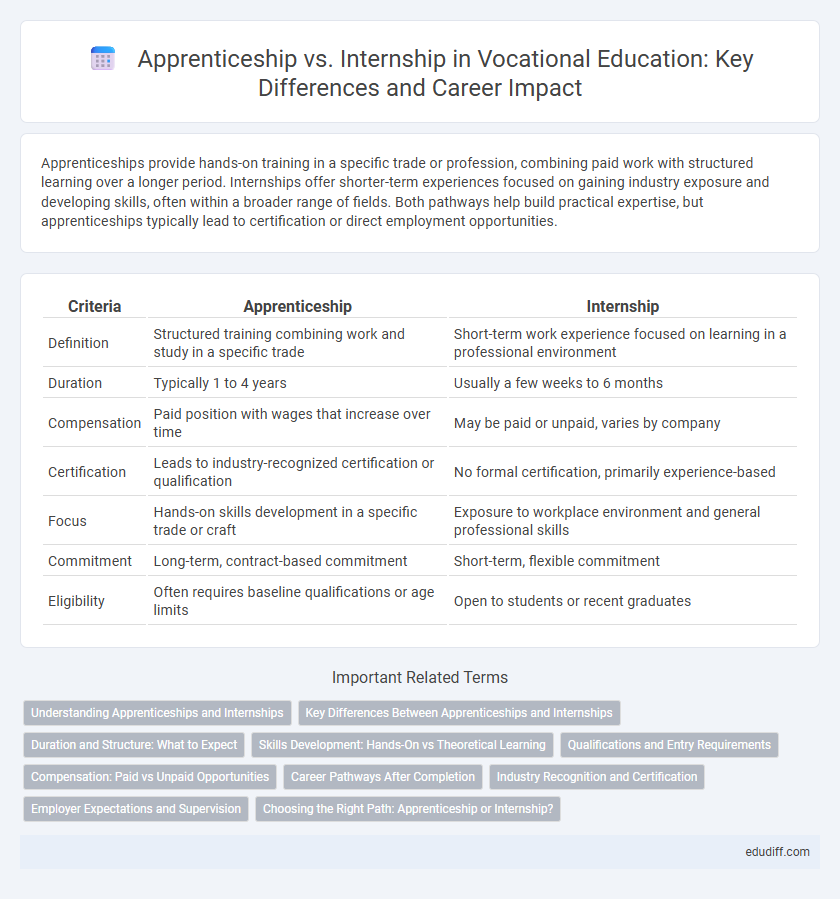
| Criteria | Apprenticeship | Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured training combining work and study in a specific trade | Short-term work experience focused on learning in a professional environment |
| Duration | Typically 1 to 4 years | Usually a few weeks to 6 months |
| Compensation | Paid position with wages that increase over time | May be paid or unpaid, varies by company |
| Certification | Leads to industry-recognized certification or qualification | No formal certification, primarily experience-based |
| Focus | Hands-on skills development in a specific trade or craft | Exposure to workplace environment and general professional skills |
| Commitment | Long-term, contract-based commitment | Short-term, flexible commitment |
| Eligibility | Often requires baseline qualifications or age limits | Open to students or recent graduates |
Understanding Apprenticeships and Internships
Apprenticeships offer structured, paid training programs combining on-the-job experience with classroom instruction, designed to develop specific trade skills over an extended period. Internships typically provide shorter-term, often unpaid opportunities for students or recent graduates to gain practical exposure and industry insight in various fields. Understanding these distinctions helps individuals choose between immersive skill-building and exploratory professional experience in vocational careers.
Key Differences Between Apprenticeships and Internships
Apprenticeships provide structured, long-term training programs combining paid work experience with classroom education, specifically linked to skilled trades, while internships typically offer shorter, project-based work experience focused on career exploration. Apprenticeships often result in professional certification or licensure, whereas internships rarely provide formal qualifications. Key differences include duration, compensation, training depth, and credential outcomes, with apprenticeships emphasizing hands-on mastery and internships prioritizing exposure and networking opportunities.
Duration and Structure: What to Expect
Apprenticeships typically span one to six years, offering a structured combination of paid on-the-job training and classroom instruction tailored to specific trades or industries. Internships tend to be shorter, ranging from a few weeks to six months, often emphasizing observational and project-based experiences without formal coursework. The extended duration and comprehensive curriculum of apprenticeships provide deeper skill development, while internships offer flexibility and exposure to professional environments.
Skills Development: Hands-On vs Theoretical Learning
Apprenticeships emphasize hands-on skills development through practical work experience in real job settings, fostering mastery of trade-specific techniques and tools. Internships typically focus on theoretical learning complemented by project-based tasks, providing broader industry exposure and foundational knowledge. Both pathways enhance career readiness but differ in the balance between experiential training and academic understanding.
Qualifications and Entry Requirements
Apprenticeships typically require candidates to meet specific vocational qualifications or possess a basic education level, often tailored to the trade, such as a high school diploma or equivalent. Internships generally have more flexible entry requirements, accepting college students or recent graduates looking to gain practical experience without mandatory prior qualifications. Both pathways emphasize skill development, but apprenticeships usually mandate formal enrollment in a registered training program, while internships prioritize relevant academic background or interest.
Compensation: Paid vs Unpaid Opportunities
Apprenticeships typically offer paid opportunities, providing trainees with a wage that reflects their growing skill level and on-the-job training. In contrast, internships can be either paid or unpaid, depending on the industry, company policy, and legal regulations surrounding labor laws. Paid apprenticeships often lead to higher retention rates and financial stability for learners compared to many unpaid internship programs.
Career Pathways After Completion
Apprenticeships offer hands-on training with a direct path to skilled trade careers, often leading to certification and permanent employment within industries like construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. Internships provide broader exposure to various professional settings, enhancing resumes and networking opportunities that facilitate entry into fields such as marketing, finance, and technology. Career pathways after apprenticeships typically involve advancement in specific trades, while internships often lead to diverse roles in corporate or creative sectors.
Industry Recognition and Certification
Apprenticeships offer industry-recognized certifications that validate specific skills and enhance employability in trades such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare. Internships provide practical experience but often lack formal certification, limiting direct industry recognition across sectors like marketing and finance. Certification obtained through apprenticeships ensures compliance with industry standards and increases credibility with employers.
Employer Expectations and Supervision
Employers expect apprenticeships to provide hands-on, skill-specific training under close supervision, ensuring the apprentice gains practical expertise directly related to the trade. Internships typically involve broader exposure to workplace culture and general tasks with more indirect supervision, focusing on professional development and networking opportunities. Supervision in apprenticeships is often more structured and consistent, whereas internships may offer more autonomy, depending on the employer's goals.
Choosing the Right Path: Apprenticeship or Internship?
Choosing between an apprenticeship and an internship depends on career goals and industry requirements, as apprenticeships offer hands-on training with a focus on skill mastery and certification, while internships provide broader exposure and professional networking opportunities. Apprenticeships typically involve longer commitments and are common in trades like construction and manufacturing, delivering structured learning and wage progression. Internships, often shorter and available in corporate or creative sectors, emphasize gaining workplace experience and building a resume for future employment.
Apprenticeship vs Internship Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com