Trade schools provide specialized, hands-on training for specific careers, enabling students to enter the workforce quickly with practical skills. Community colleges offer a broader range of academic courses alongside vocational programs, allowing for more flexibility and opportunities to transfer credits to four-year institutions. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, desired learning style, and time commitment.
Table of Comparison
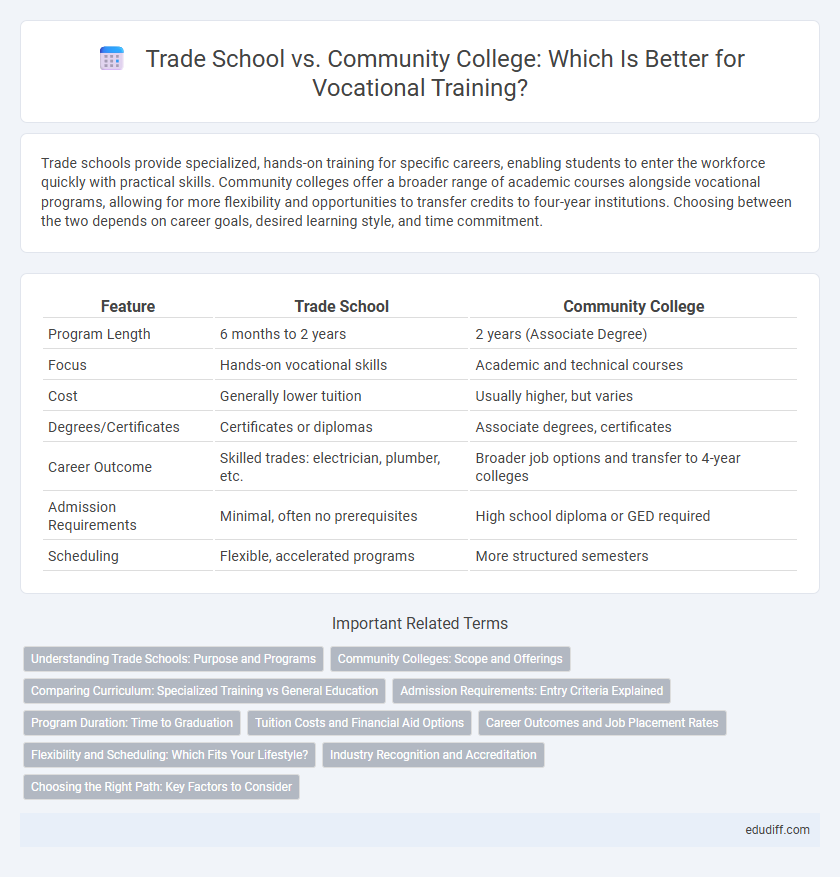
| Feature | Trade School | Community College |
|---|---|---|
| Program Length | 6 months to 2 years | 2 years (Associate Degree) |
| Focus | Hands-on vocational skills | Academic and technical courses |
| Cost | Generally lower tuition | Usually higher, but varies |
| Degrees/Certificates | Certificates or diplomas | Associate degrees, certificates |
| Career Outcome | Skilled trades: electrician, plumber, etc. | Broader job options and transfer to 4-year colleges |
| Admission Requirements | Minimal, often no prerequisites | High school diploma or GED required |
| Scheduling | Flexible, accelerated programs | More structured semesters |
Understanding Trade Schools: Purpose and Programs
Trade schools specialize in hands-on training for specific vocations such as electrician, plumbing, or automotive technology, providing targeted skills that lead directly to industry certifications and licensure. These programs typically last from a few months to two years, emphasizing practical experience over academic theory found in community colleges. Trade schools cater to students seeking rapid entry into the workforce with a concentrated curriculum designed to meet employer demands in trades and technical fields.
Community Colleges: Scope and Offerings
Community colleges provide a broad spectrum of vocational programs tailored to diverse industries such as healthcare, information technology, and skilled trades. These institutions offer flexible scheduling, including part-time and evening classes, supporting non-traditional students and working adults. With strong ties to local employers and workforce development initiatives, community colleges often facilitate internships and job placement services enhancing career readiness.
Comparing Curriculum: Specialized Training vs General Education
Trade schools emphasize specialized training with hands-on skills tailored to specific careers such as welding, HVAC, or cosmetology, enabling faster entry into the workforce. Community colleges offer a broader curriculum featuring general education courses alongside technical programs, providing a foundation for transfer to four-year universities or diverse career pathways. Comparing curriculum, trade schools prioritize direct occupational skills, while community colleges balance vocational training with academic development.
Admission Requirements: Entry Criteria Explained
Trade schools usually require a high school diploma or GED, emphasizing practical skills and relevant experience for admission, whereas community colleges often have open admissions with minimal requirements like a high school diploma or equivalent. Community colleges may also require placement tests or prerequisite courses for certain programs, while trade schools focus on direct entry into specialized vocational training. Understanding these entry criteria helps prospective students choose the pathway that best suits their educational background and career goals.
Program Duration: Time to Graduation
Trade school programs typically range from 6 months to 2 years, offering accelerated paths to workforce entry. Community college programs usually require 2 years to complete an associate degree, providing broader academic foundations. Shorter time to graduation at trade schools enables quicker skill acquisition tailored to specific vocational careers.
Tuition Costs and Financial Aid Options
Trade schools typically offer lower tuition costs compared to community colleges, making them an affordable option for hands-on vocational training. Financial aid options for trade schools often include scholarships, grants, and federal student aid, though availability varies widely by program and location. Community colleges provide broader access to financial aid opportunities, including state grants and work-study programs, which can help offset higher tuition fees.
Career Outcomes and Job Placement Rates
Trade schools offer specialized training with a direct focus on specific careers, resulting in higher job placement rates within skilled trades such as HVAC, welding, and electrical work. Community colleges provide broader academic programs with transferable credits that often lead to careers requiring associate degrees or further education, supporting diverse career outcomes in healthcare, business, and technology fields. Data shows trade schools generally have faster employment timelines due to intensive, hands-on curricula tailored to industry demands.
Flexibility and Scheduling: Which Fits Your Lifestyle?
Trade schools offer focused, hands-on training with flexible scheduling options such as evening and weekend classes, ideal for individuals seeking to quickly enter the workforce or balance work and study. Community colleges provide a broader range of courses with varied schedules, including part-time and online classes, catering to students who desire more academic flexibility and the option to transfer credits to a four-year institution. Evaluating your personal commitments and career goals helps determine whether the structured programs of trade schools or the adaptable offerings of community colleges best fit your lifestyle.
Industry Recognition and Accreditation
Trade schools often provide specialized industry-recognized certifications that align directly with specific vocational careers, enhancing employment opportunities in fields like welding, electrical work, or cosmetology. Community colleges, accredited by regional or national agencies, offer a broader educational scope with associate degrees and transferable credits, which can be valuable for evolving career paths and further academic pursuits. Industry recognition for trade schools tends to be more focused and immediate, whereas community colleges balance accreditation with diverse program offerings and pathways.
Choosing the Right Path: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing between trade school and community college depends on career goals, program duration, and cost-effectiveness; trade schools offer specialized, faster training for skilled trades like electrician or HVAC technician, while community colleges provide broader academic options with potential for transfer to four-year universities. Accreditation, hands-on experience, job placement rates, and local industry demand are critical factors influencing the decision. Evaluating these elements ensures alignment with long-term vocational objectives and financial considerations.
Trade School vs Community College Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com