Work-based learning offers hands-on experience in real work environments, allowing students to develop practical skills and professional networks directly relevant to their careers. Simulated learning uses controlled, virtual scenarios to replicate workplace challenges, enhancing problem-solving abilities and technical knowledge without the risks of actual job settings. Both approaches complement each other by combining real-world exposure with safe, guided practice to improve vocational competence.
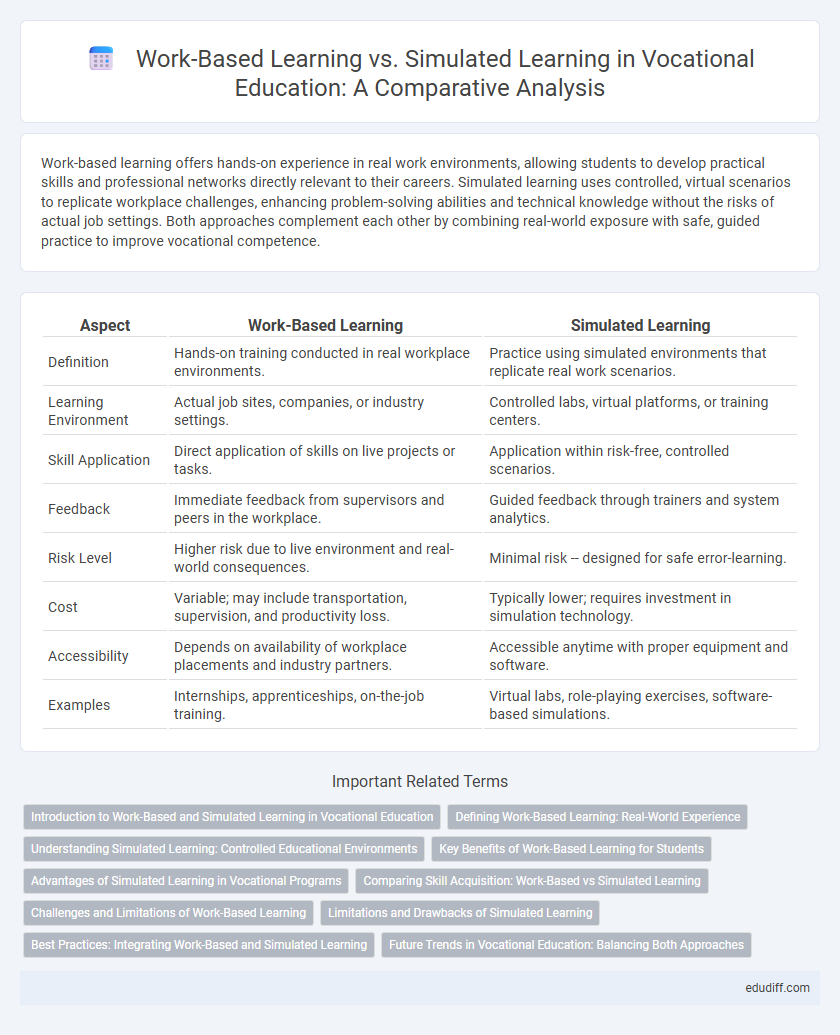
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Work-Based Learning | Simulated Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on training conducted in real workplace environments. | Practice using simulated environments that replicate real work scenarios. |
| Learning Environment | Actual job sites, companies, or industry settings. | Controlled labs, virtual platforms, or training centers. |
| Skill Application | Direct application of skills on live projects or tasks. | Application within risk-free, controlled scenarios. |
| Feedback | Immediate feedback from supervisors and peers in the workplace. | Guided feedback through trainers and system analytics. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to live environment and real-world consequences. | Minimal risk -- designed for safe error-learning. |
| Cost | Variable; may include transportation, supervision, and productivity loss. | Typically lower; requires investment in simulation technology. |
| Accessibility | Depends on availability of workplace placements and industry partners. | Accessible anytime with proper equipment and software. |
| Examples | Internships, apprenticeships, on-the-job training. | Virtual labs, role-playing exercises, software-based simulations. |
Introduction to Work-Based and Simulated Learning in Vocational Education
Work-based learning integrates real-world job experience within vocational education, enhancing practical skills and industry readiness through direct exposure to workplace environments. Simulated learning uses realistic scenarios and virtual technologies to replicate job tasks, allowing learners to practice skills in a controlled, risk-free setting. Both approaches complement vocational training by bridging theoretical knowledge with hands-on application, improving competency and employability.
Defining Work-Based Learning: Real-World Experience
Work-Based Learning (WBL) immerses students in real-world work environments, allowing them to acquire practical skills through direct interaction with industry professionals and authentic tasks. This hands-on approach enhances job readiness by fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration in actual workplace settings. Unlike Simulated Learning, WBL provides experiential learning that aligns closely with current labor market demands and employer expectations.
Understanding Simulated Learning: Controlled Educational Environments
Simulated learning offers controlled educational environments where vocational students engage in realistic tasks without the unpredictability of actual work settings. These environments use advanced technology and scenarios to replicate workplace conditions, enabling safe skill development and immediate feedback. This method enhances learner confidence and prepares them for real-world challenges more effectively than traditional classroom instruction.
Key Benefits of Work-Based Learning for Students
Work-Based Learning (WBL) offers students hands-on experience by engaging directly with real workplace environments, enhancing practical skills and job readiness. It provides opportunities for networking, mentorship, and understanding industry-specific challenges, which simulated learning often cannot fully replicate. Exposure to actual work scenarios during WBL boosts student confidence, adaptability, and employability in competitive labor markets.
Advantages of Simulated Learning in Vocational Programs
Simulated learning in vocational programs offers a safe environment for students to practice complex skills without real-world risks, enhancing confidence and competence. It allows repeated practice and immediate feedback, which accelerates skill acquisition and mastery. The controlled setting also enables instructors to tailor scenarios to specific learning objectives, improving targeted skill development.
Comparing Skill Acquisition: Work-Based vs Simulated Learning
Work-based learning enables direct skill acquisition through real-world exposure, fostering practical understanding and adaptability in actual work environments. Simulated learning offers controlled scenarios that emphasize repetitive practice and risk-free experimentation, accelerating proficiency in specific skills. While work-based learning builds contextual competence, simulated learning enhances targeted skill mastery, each complementing different aspects of vocational training.
Challenges and Limitations of Work-Based Learning
Work-Based Learning faces challenges such as limited access to diverse industry settings and inconsistent mentorship quality, which can hinder skill development and real-world experience acquisition. Time constraints and balancing work responsibilities with learning objectives often limit comprehensive understanding and reflection. Furthermore, workplace variability and safety concerns may restrict the exposure to certain tasks or technologies essential for holistic vocational training.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Simulated Learning
Simulated learning often lacks the unpredictability and complexity of real work environments, limiting the development of critical problem-solving skills essential in vocational settings. The artificial nature of simulations can result in reduced emotional engagement and motivation compared to authentic work-based experiences. Furthermore, simulated learning may not adequately prepare learners for interpersonal dynamics and real-time decision-making encountered in actual workplaces.
Best Practices: Integrating Work-Based and Simulated Learning
Integrating work-based learning with simulated learning enhances vocational training by combining real-world experience and controlled skill development environments. Best practices include aligning simulated scenarios with job-specific tasks and facilitating reflective discussions that link workplace observations to simulation outcomes. This hybrid approach improves learner engagement, competency retention, and readiness for actual job performance.
Future Trends in Vocational Education: Balancing Both Approaches
Future trends in vocational education emphasize integrating work-based learning with simulated learning to enhance skill acquisition and adaptability. Combining real-world experience from apprenticeships with advanced simulation technologies allows learners to practice complex tasks safely and repeatedly. This balanced approach maximizes employment readiness and responds to evolving industry demands by fostering both practical competence and theoretical understanding.
Work-Based Learning vs Simulated Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com