Continuing education for adult pets enhances their obedience and adaptability by reinforcing learned behaviors and introducing new commands tailored to their evolving needs. Initial education lays the foundation for basic manners and socialization, crucial during the early stages of a pet's life. Emphasizing ongoing training ensures sustained mental stimulation and strengthens the human-animal bond throughout adulthood.
Table of Comparison
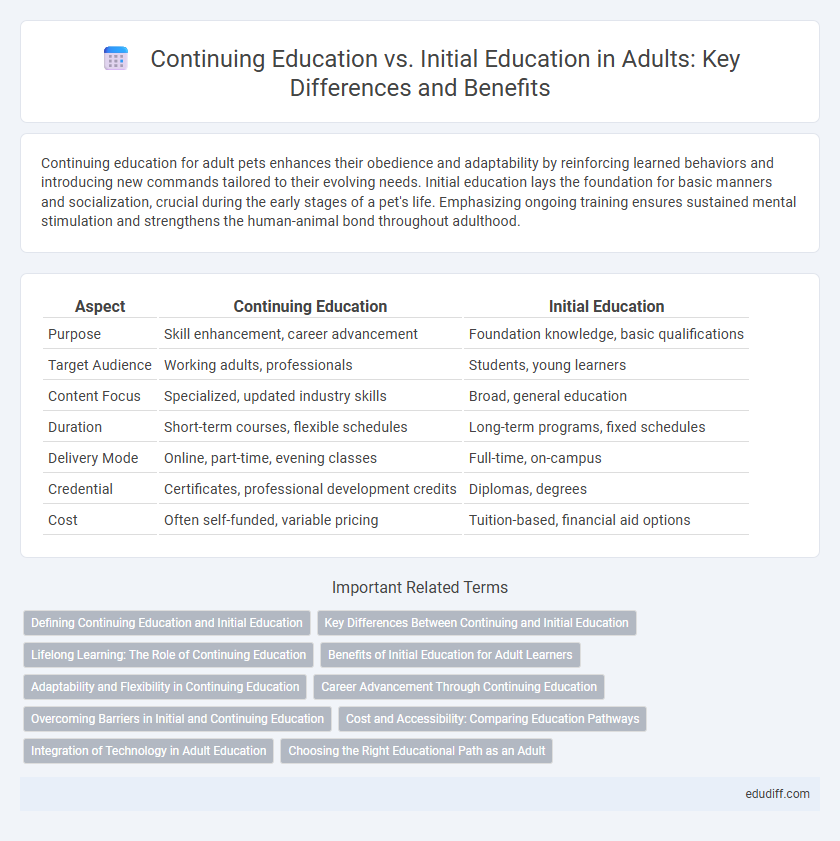
| Aspect | Continuing Education | Initial Education |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Skill enhancement, career advancement | Foundation knowledge, basic qualifications |
| Target Audience | Working adults, professionals | Students, young learners |
| Content Focus | Specialized, updated industry skills | Broad, general education |
| Duration | Short-term courses, flexible schedules | Long-term programs, fixed schedules |
| Delivery Mode | Online, part-time, evening classes | Full-time, on-campus |
| Credential | Certificates, professional development credits | Diplomas, degrees |
| Cost | Often self-funded, variable pricing | Tuition-based, financial aid options |
Defining Continuing Education and Initial Education
Continuing education refers to the ongoing learning process adults engage in after completing initial education, designed to update skills, gain new knowledge, or advance careers. Initial education typically encompasses the foundational formal schooling completed during childhood and adolescence, including primary, secondary, and higher education. These two forms of education serve distinct purposes, with initial education providing broad foundational knowledge and continuing education delivering specialized, practical learning for adult professional and personal development.
Key Differences Between Continuing and Initial Education
Continuing education focuses on skill enhancement, career advancement, and lifelong learning for adults already in the workforce, contrasting with initial education, which provides foundational knowledge and competencies primarily during youth or early adulthood. Continuing education includes professional development courses, certifications, and workshops tailored to evolving industry standards, whereas initial education encompasses primary, secondary, and tertiary schooling aimed at general intellectual development. The key differences lie in learner motivation, curriculum specificity, and the application of acquired knowledge towards immediate professional goals versus broad academic foundations.
Lifelong Learning: The Role of Continuing Education
Continuing education plays a crucial role in lifelong learning by enabling adults to update skills and knowledge in rapidly changing industries, ensuring career relevance and personal growth. Unlike initial education, which establishes foundational expertise, continuing education adapts to evolving professional demands and emerging technologies. This dynamic approach supports workforce adaptability, enhances employability, and fosters continuous intellectual development throughout an individual's life.
Benefits of Initial Education for Adult Learners
Initial education provides adult learners with foundational knowledge and skills crucial for career entry or advancement, establishing a solid base for lifelong learning. It enhances literacy, numeracy, and critical thinking abilities, which are essential for adapting to evolving job market demands and personal development. Access to certified initial education programs increases employability and opens opportunities for higher education pathways, significantly improving socioeconomic outcomes for adults.
Adaptability and Flexibility in Continuing Education
Continuing education enhances adaptability by offering learners the flexibility to update skills in response to evolving industry demands, unlike initial education which provides foundational knowledge. Courses in continuing education often feature modular designs and online accessibility, enabling professionals to balance learning with existing work commitments. This flexibility fosters lifelong learning, crucial for maintaining competitiveness in dynamic job markets.
Career Advancement Through Continuing Education
Career advancement through continuing education involves acquiring advanced skills and updated knowledge beyond initial education credentials, fostering adaptability in dynamic job markets. Professionals who engage in lifelong learning demonstrate enhanced expertise and qualifications, increasing their competitive edge for promotions and specialized roles. Employers often prioritize candidates who show commitment to ongoing development, aligning workforce capabilities with evolving industry standards and technologies.
Overcoming Barriers in Initial and Continuing Education
Overcoming barriers in initial education often requires addressing foundational challenges such as limited access, socioeconomic constraints, and language difficulties. In contrast, continuing education barriers focus on balancing work, family responsibilities, and motivation to re-engage with learning. Tailored support systems, flexible scheduling, and targeted resource allocation significantly enhance accessibility and completion rates in both educational stages.
Cost and Accessibility: Comparing Education Pathways
Continuing education often offers more flexible and affordable options compared to initial education, with many programs available online or part-time to accommodate working adults. Initial education typically requires a larger financial investment upfront, including tuition, fees, and living expenses, which can be a significant barrier for some learners. Accessibility in continuing education is enhanced by varied formats and scheduling, enabling broader participation among diverse adult populations.
Integration of Technology in Adult Education
Continuing education and initial education differ significantly in their integration of technology, with adult education increasingly leveraging digital tools to enhance learning engagement and flexibility. Platforms like online courses, virtual simulations, and mobile learning apps support adults in balancing education with work and personal commitments. This technological integration enables personalized learning pathways, real-time feedback, and access to diverse resources, pivotal for skill development in dynamic professional environments.
Choosing the Right Educational Path as an Adult
Choosing the right educational path as an adult involves evaluating whether continuing education meets current career goals or if pursuing initial education provides a foundational knowledge base. Continuing education offers flexible schedules, targeted skill development, and opportunities for professional advancement tailored to adult learners. Initial education often requires a longer commitment but delivers comprehensive credentials essential for entering new industries or changing career trajectories.
Continuing education vs Initial education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com