The flipped classroom approach in adult pet education emphasizes interactive, hands-on learning outside traditional lecture hours, allowing learners to engage with the material at their own pace. In contrast, conventional classrooms rely on instructor-led sessions where information is primarily delivered during scheduled class time. This shift in methodology enhances adult learners' retention and application of practical pet care skills by fostering active participation and collaboration.
Table of Comparison
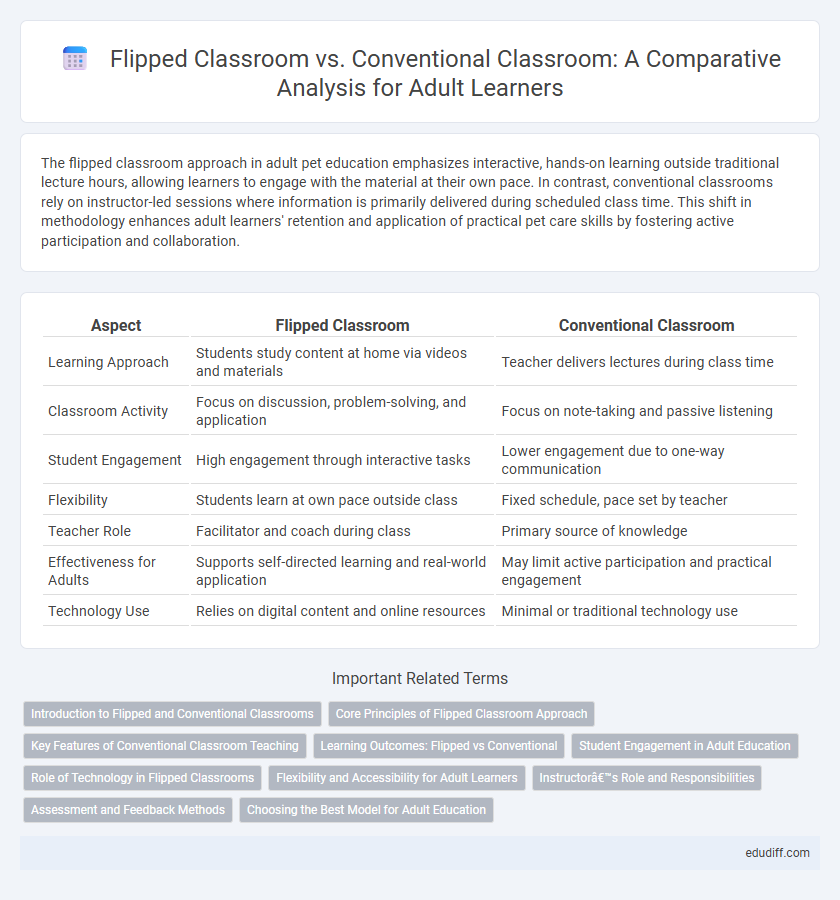
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Conventional Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Approach | Students study content at home via videos and materials | Teacher delivers lectures during class time |
| Classroom Activity | Focus on discussion, problem-solving, and application | Focus on note-taking and passive listening |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through interactive tasks | Lower engagement due to one-way communication |
| Flexibility | Students learn at own pace outside class | Fixed schedule, pace set by teacher |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach during class | Primary source of knowledge |
| Effectiveness for Adults | Supports self-directed learning and real-world application | May limit active participation and practical engagement |
| Technology Use | Relies on digital content and online resources | Minimal or traditional technology use |
Introduction to Flipped and Conventional Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class and engaging students in interactive activities during in-person sessions. Conventional classrooms rely on direct instruction delivered by the teacher in class, with students completing assignments independently at home. This shift in instructional design enhances active learning and student participation.
Core Principles of Flipped Classroom Approach
The Flipped Classroom approach centers on active learning by delivering instructional content online outside of class, freeing in-class time for interactive, problem-solving activities. Core principles include student-centered learning, where learners engage with material at their own pace, and collaborative peer discussions facilitated by the instructor. This method enhances comprehension and retention by shifting focus from passive lectures to hands-on application and critical thinking during class sessions.
Key Features of Conventional Classroom Teaching
Conventional classroom teaching centers on teacher-led instruction where educators deliver content directly to students in a structured setting, often using lectures and textbooks. It relies heavily on face-to-face interaction, fixed schedules, and standardized assessments to evaluate student performance. This traditional approach emphasizes passive learning through listening and note-taking, with limited opportunities for personalized pace or interactive engagement.
Learning Outcomes: Flipped vs Conventional
Flipped classrooms enhance learning outcomes by promoting active engagement and personalized pacing, leading to higher retention and improved critical thinking skills compared to conventional classrooms. Students in flipped settings demonstrate better problem-solving abilities and deeper conceptual understanding due to pre-class preparation and interactive in-class activities. Conventional classrooms often emphasize passive learning, resulting in lower student participation and less effective mastery of complex subjects.
Student Engagement in Adult Education
Flipped classrooms enhance student engagement in adult education by promoting active participation through pre-class content review and in-class collaboration. This model empowers adult learners to apply concepts in practical settings, increasing motivation and retention. Conventional classrooms often struggle to maintain the same level of interaction, resulting in lower engagement among adult students.
Role of Technology in Flipped Classrooms
Technology in flipped classrooms transforms traditional learning by providing students with interactive video lectures and digital resources accessible anytime, enhancing comprehension and engagement. Advanced platforms such as Learning Management Systems (LMS) and multimedia tools facilitate personalized learning, promote collaboration, and enable real-time feedback between instructors and adult learners. This integration of technology supports active learning environments, fostering critical thinking and allowing adults to balance education with other responsibilities effectively.
Flexibility and Accessibility for Adult Learners
Flipped classrooms offer adult learners enhanced flexibility by allowing them to access instructional materials at their own pace and on their own schedule, accommodating varying work and family commitments. Conventional classrooms typically require fixed attendance times, limiting accessibility and posing challenges for adults balancing multiple responsibilities. The asynchronous nature of flipped learning maximizes accessibility, enabling adults to revisit complex topics as needed and engage in more meaningful in-person interactions.
Instructor’s Role and Responsibilities
In a flipped classroom, the instructor's role shifts from delivering lectures to facilitating active learning by guiding discussions and providing personalized support, enhancing student engagement and comprehension. Responsibilities include designing pre-class materials such as videos and readings that students review independently, enabling the instructor to focus on clarifying doubts and encouraging critical thinking during in-person sessions. In contrast, conventional classrooms emphasize direct instruction and content delivery, with the instructor primarily responsible for presenting lectures and managing classroom activities in real time.
Assessment and Feedback Methods
Flipped classrooms leverage formative assessments such as quizzes and interactive activities to provide immediate feedback, enhancing adult learners' comprehension and engagement. Conventional classrooms often rely on summative assessments like exams and periodic tests, which delay feedback and may hinder real-time learning adjustments. Emphasizing continuous assessment and timely feedback in flipped models aligns with adult learning theories, promoting self-directed improvement and deeper understanding.
Choosing the Best Model for Adult Education
Choosing the best model for adult education requires evaluating the benefits of flipped classrooms versus conventional classrooms, where flipped classrooms enhance engagement by promoting active, self-paced learning supported by multimedia resources, while conventional classrooms rely on direct instruction and real-time interaction. Research indicates that flipped classrooms improve knowledge retention and critical thinking skills among adult learners due to increased autonomy and flexibility. Ultimately, tailoring the teaching model to adult learners' needs and learning preferences maximizes effectiveness in skill acquisition and course satisfaction.
Flipped Classroom vs Conventional Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com