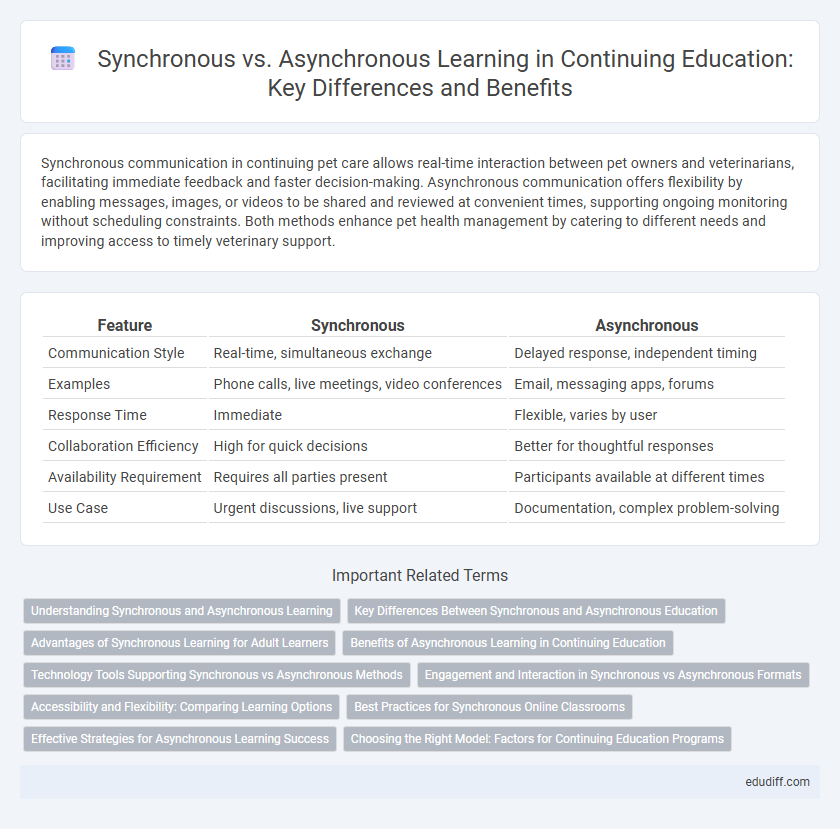
Synchronous communication in continuing pet care allows real-time interaction between pet owners and veterinarians, facilitating immediate feedback and faster decision-making. Asynchronous communication offers flexibility by enabling messages, images, or videos to be shared and reviewed at convenient times, supporting ongoing monitoring without scheduling constraints. Both methods enhance pet health management by catering to different needs and improving access to timely veterinary support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Real-time, simultaneous exchange | Delayed response, independent timing |
| Examples | Phone calls, live meetings, video conferences | Email, messaging apps, forums |
| Response Time | Immediate | Flexible, varies by user |
| Collaboration Efficiency | High for quick decisions | Better for thoughtful responses |
| Availability Requirement | Requires all parties present | Participants available at different times |
| Use Case | Urgent discussions, live support | Documentation, complex problem-solving |
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students, typically through live video sessions, allowing immediate feedback and collaboration. Asynchronous learning lets students access course materials, lectures, and assignments on their own schedule, fostering flexibility and self-paced study. Understanding these modes helps educators design effective curricula that balance engagement with convenience, catering to diverse learning needs.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Education
Synchronous education requires students and instructors to engage simultaneously through live lectures or real-time discussions, fostering immediate feedback and collaborative interaction. Asynchronous education allows learners to access course materials, submit assignments, and participate in discussions at their own pace, providing flexibility and accommodating diverse schedules. The key differences lie in timing, interaction dynamics, and adaptability, which significantly impact student engagement and learning outcomes.
Advantages of Synchronous Learning for Adult Learners
Synchronous learning provides adult learners with immediate interaction and real-time feedback, enhancing understanding and engagement. This approach fosters a structured learning environment that helps maintain discipline and motivation among busy adults. Collaborative discussions and instant clarification of doubts promote deeper comprehension and knowledge retention in synchronous settings.
Benefits of Asynchronous Learning in Continuing Education
Asynchronous learning in continuing education offers flexibility, allowing learners to access educational materials anytime, which accommodates diverse schedules and learning paces. This self-paced approach enhances knowledge retention by enabling repeated review of content and fosters greater autonomy in managing personal development. Furthermore, asynchronous environments often increase accessibility for remote learners, expanding opportunities for professional growth without geographical constraints.
Technology Tools Supporting Synchronous vs Asynchronous Methods
Technology tools supporting synchronous methods include video conferencing platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams, enabling real-time communication and collaboration. Asynchronous tools such as email, discussion boards, and project management software like Trello and Slack facilitate flexible communication without requiring immediate responses. These tools optimize workflow by catering to different interaction needs in remote and hybrid work environments.
Engagement and Interaction in Synchronous vs Asynchronous Formats
Synchronous formats foster real-time engagement, allowing participants to interact instantly through live discussions, video calls, or chat, which enhances immediate feedback and dynamic collaboration. Asynchronous formats support flexible interaction, enabling learners to contribute thoughtfully at their own pace through forums, emails, and recorded content, which promotes deeper reflection and personalized learning experiences. Both formats offer unique benefits for engagement, with synchronous boosting immediacy and social presence, while asynchronous enhances accessibility and thoughtful participation.
Accessibility and Flexibility: Comparing Learning Options
Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction, fostering immediate feedback and social engagement that enhances accessibility for students needing structured schedules and direct support. Asynchronous learning provides flexibility, allowing students to access materials anytime, which benefits those with irregular timetables or varying learning paces. Institutions optimizing accessibility and flexibility often implement hybrid models to accommodate diverse learner needs effectively.
Best Practices for Synchronous Online Classrooms
Effective best practices for synchronous online classrooms include establishing clear communication protocols to ensure active student engagement and timely feedback. Utilizing interactive tools like polls, breakout rooms, and real-time quizzes enhances participation and fosters collaboration among students. Consistent scheduling and maintaining a structured agenda support a productive learning environment tailored to synchronous session dynamics.
Effective Strategies for Asynchronous Learning Success
Effective strategies for asynchronous learning success include clear communication channels, structured timelines, and interactive content to maintain engagement. Utilizing robust learning management systems with consistent feedback mechanisms helps learners stay motivated and on track. Incorporating multimedia resources and peer collaboration opportunities further enhances understanding and retention in asynchronous environments.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors for Continuing Education Programs
Choosing between synchronous and asynchronous models for continuing education programs depends on factors such as learner flexibility, interaction requirements, and content complexity. Synchronous learning supports real-time engagement and immediate feedback, ideal for collaborative discussions and complex subjects requiring direct instructor support. Asynchronous learning offers flexibility and self-paced study, making it suitable for professionals balancing work commitments and seeking modular or on-demand course access.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com