Teacher-centered classrooms rely on direct instruction where the teacher controls the learning process and delivers content to students. Student-centered classrooms emphasize active learning, encouraging students to participate, collaborate, and take responsibility for their own education. This approach promotes critical thinking and helps students develop problem-solving skills by engaging with the material in meaningful ways.
Table of Comparison
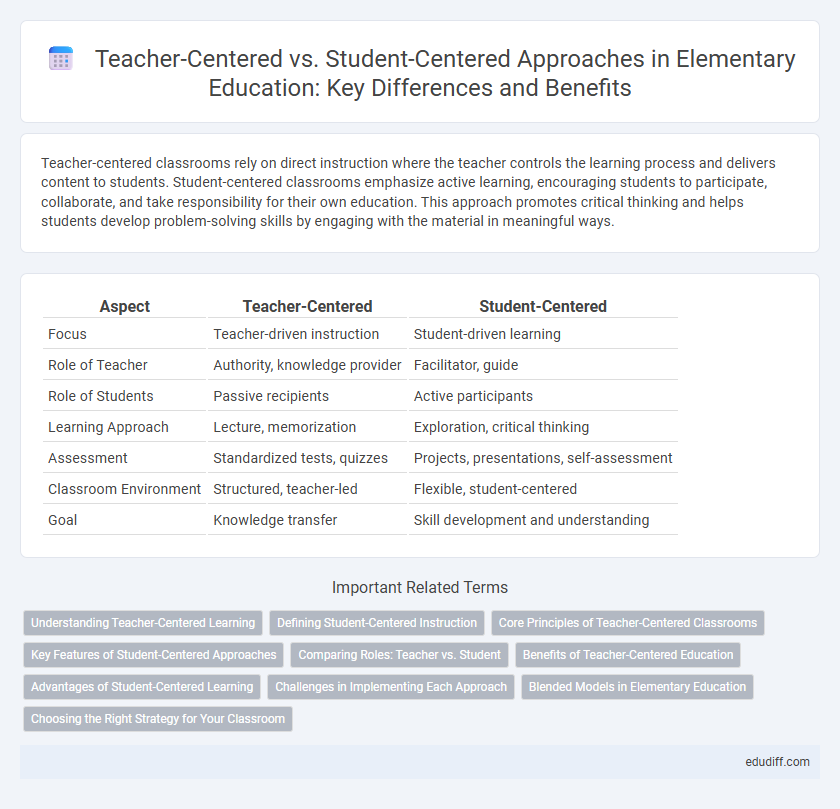
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered | Student-Centered |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Teacher-driven instruction | Student-driven learning |
| Role of Teacher | Authority, knowledge provider | Facilitator, guide |
| Role of Students | Passive recipients | Active participants |
| Learning Approach | Lecture, memorization | Exploration, critical thinking |
| Assessment | Standardized tests, quizzes | Projects, presentations, self-assessment |
| Classroom Environment | Structured, teacher-led | Flexible, student-centered |
| Goal | Knowledge transfer | Skill development and understanding |
Understanding Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes the role of the teacher as the primary source of knowledge, where students receive information passively through lectures and direct instruction. This approach prioritizes structured lessons, clear objectives, and standardized assessments to ensure content mastery. Understanding teacher-centered learning highlights its efficiency in delivering foundational knowledge but often limits student engagement and critical thinking opportunities.
Defining Student-Centered Instruction
Student-centered instruction prioritizes active learning by engaging students in critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving activities. It shifts the focus from teacher-led lectures to personalized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs and interests. This approach fosters autonomy and encourages students to take responsibility for their own learning outcomes.
Core Principles of Teacher-Centered Classrooms
Teacher-centered classrooms emphasize direct instruction, where the teacher controls the lesson content and pace, ensuring structured learning through lectures and demonstrations. The core principles include maintaining authority, promoting discipline, and delivering standardized curriculum to achieve predictable outcomes. This approach prioritizes efficiency in content delivery and clear expectations for student behavior and performance.
Key Features of Student-Centered Approaches
Student-centered approaches prioritize active learning, where students engage in critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving. This method encourages personalized instruction that adapts to individual student interests and needs, fostering autonomy and motivation. Technology integration and formative assessment are commonly used to support continuous feedback and dynamic learning experiences.
Comparing Roles: Teacher vs. Student
In teacher-centered classrooms, the teacher acts as the primary source of knowledge, directing lessons and controlling classroom activities, while students listen, absorb, and follow instructions. In student-centered environments, students take an active role, engaging in discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative learning, with the teacher serving as a facilitator and guide. This shift enhances student autonomy, critical thinking, and personalized learning experiences.
Benefits of Teacher-Centered Education
Teacher-centered education provides structured learning environments where instructors deliver clear and consistent information, helping students master foundational skills efficiently. This approach ensures standardized curriculum coverage, promoting uniform knowledge acquisition and easy assessment of student progress. It supports classroom management and discipline, creating an organized space conducive to focused learning.
Advantages of Student-Centered Learning
Student-centered learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills by actively engaging elementary students in the learning process. This approach promotes greater retention and understanding as children take ownership of their education through exploration and collaboration. It also supports diverse learning styles, making education more inclusive and motivating young learners to develop a lifelong love for learning.
Challenges in Implementing Each Approach
Teacher-centered approaches often face challenges such as limited student engagement and the difficulty of addressing diverse learning styles in a single authoritative delivery. Student-centered methods can struggle with classroom management and the need for extensive teacher training to effectively facilitate active learning. Both approaches require balancing instructional goals with practical constraints like time, resources, and varying student needs.
Blended Models in Elementary Education
Blended models in elementary education integrate teacher-centered instruction with student-centered activities, maximizing personalized learning while maintaining structured guidance. Technology-enhanced lessons facilitate interactive experiences, allowing students to engage actively and teachers to tailor support based on real-time assessments. This hybrid approach fosters collaboration, critical thinking, and individualized pacing crucial for foundational skill development.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Classroom
Choosing the right strategy for an elementary classroom involves understanding the key differences between teacher-centered and student-centered approaches. Teacher-centered methods emphasize structured lessons and direct instruction, promoting clear guidance and control. Student-centered strategies prioritize active learning and collaboration, fostering critical thinking and engagement tailored to individual student needs.
Teacher-Centered vs Student-Centered Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com