Comprehensive Exams assess a graduate student's mastery of the entire field, ensuring broad knowledge necessary for degree completion. Qualifying Exams evaluate a student's readiness to conduct independent research within a specific discipline or specialization. Both exams serve as critical milestones in graduate education but target different aspects of academic and research competencies.
Table of Comparison
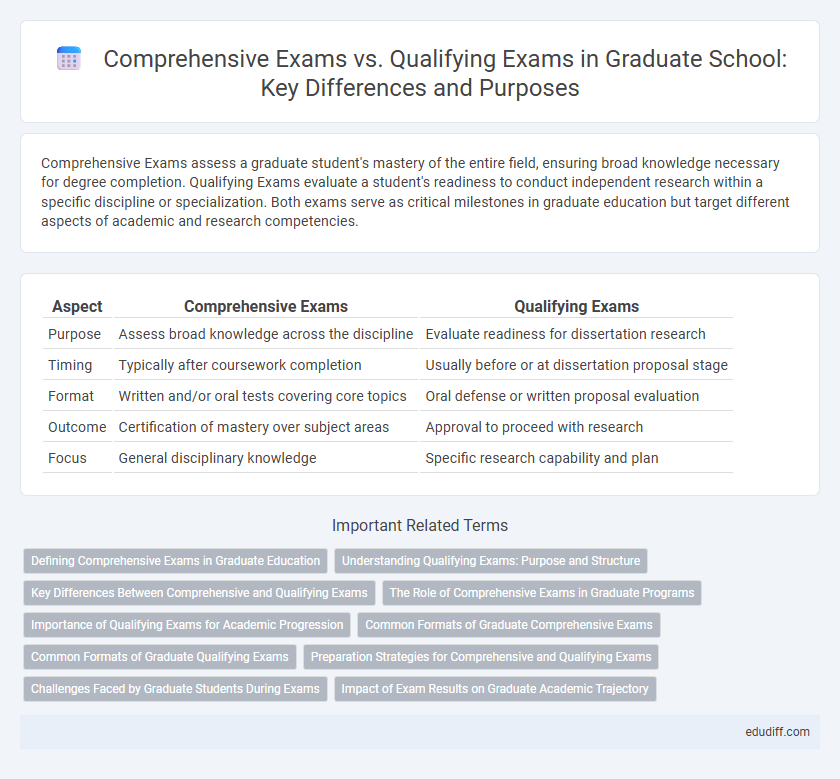
| Aspect | Comprehensive Exams | Qualifying Exams |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assess broad knowledge across the discipline | Evaluate readiness for dissertation research |
| Timing | Typically after coursework completion | Usually before or at dissertation proposal stage |
| Format | Written and/or oral tests covering core topics | Oral defense or written proposal evaluation |
| Outcome | Certification of mastery over subject areas | Approval to proceed with research |
| Focus | General disciplinary knowledge | Specific research capability and plan |
Defining Comprehensive Exams in Graduate Education
Comprehensive exams in graduate education assess a student's mastery of the core knowledge base within their field, ensuring readiness for advanced research and academic responsibilities. These exams typically cover a broad range of topics included in the graduate curriculum, testing analytical skills and subject integration rather than focusing on a narrow research area. Passing comprehensive exams is often a prerequisite for advancing to doctoral candidacy or beginning dissertation work.
Understanding Qualifying Exams: Purpose and Structure
Qualifying exams serve as a critical milestone in graduate education, designed to assess a student's mastery of core knowledge and readiness for independent research. These exams typically encompass written and oral components that evaluate both theoretical understanding and practical application within the discipline. Successfully passing qualifying exams allows doctoral candidates to advance to dissertation research, confirming their preparedness for specialized scholarship.
Key Differences Between Comprehensive and Qualifying Exams
Comprehensive exams assess a graduate student's mastery of broad subject knowledge across their field, ensuring readiness to proceed in the program. Qualifying exams evaluate a student's capability to conduct original research and determine their eligibility to enter candidacy for a doctoral degree. The key difference lies in comprehensiveness versus research focus, with comprehensive exams testing overall knowledge and qualifying exams emphasizing research potential and dissertation preparedness.
The Role of Comprehensive Exams in Graduate Programs
Comprehensive exams in graduate programs serve as a critical milestone to evaluate a student's mastery of core knowledge across their field, ensuring readiness for advanced research. These exams assess broad interdisciplinary understanding, reinforcing foundational concepts necessary for specialized study. Successful completion of comprehensive exams validates a candidate's preparedness to undertake dissertation work and contributes to graduate program progression and academic rigor.
Importance of Qualifying Exams for Academic Progression
Qualifying exams serve as a critical milestone in graduate education, assessing a student's mastery of foundational knowledge and readiness for advanced research. Successfully passing these exams enables progression to candidacy, allowing students to embark on dissertation work essential for degree completion. The rigor and significance of qualifying exams ensure that only those prepared for scholarly contribution advance, reinforcing academic standards across graduate programs.
Common Formats of Graduate Comprehensive Exams
Graduate comprehensive exams typically feature formats such as written essays, multiple-choice questions, and oral presentations designed to evaluate a student's mastery of core subject areas. These exams often assess critical thinking, synthesis of knowledge, and the ability to apply theories across disciplines relevant to the graduate program. Common formats may vary by department but consistently emphasize in-depth understanding and readiness for advanced research or professional practice.
Common Formats of Graduate Qualifying Exams
Graduate qualifying exams commonly include written tests, oral defenses, or a combination of both, designed to assess a student's mastery of core knowledge in their discipline. Formats often vary by institution but typically encompass subject-specific questions, problem-solving tasks, and critical analysis of relevant literature. These exams serve as a rigorous evaluation to determine readiness for dissertation research and candidacy advancement.
Preparation Strategies for Comprehensive and Qualifying Exams
Effective preparation for comprehensive exams involves thorough review of core coursework and mastery of broad subject knowledge, emphasizing synthesis and application of key concepts. Qualifying exams demand focused study on specialized research areas, critical analysis, and the ability to articulate original ideas, with targeted practice on potential exam questions and scholarly writing. Strategic time management, utilization of study groups, and consultation with advisors enhance readiness and confidence for both exam formats.
Challenges Faced by Graduate Students During Exams
Graduate students often face immense pressure during Comprehensive Exams and Qualifying Exams due to the extensive breadth of knowledge required and the high stakes involved in determining their academic progress. The challenges include mastering a wide range of subject areas, managing time effectively for preparation, and coping with anxiety and stress that can hinder performance. Balancing these exams with research responsibilities and teaching commitments further exacerbates the difficulty, impacting students' overall productivity and well-being.
Impact of Exam Results on Graduate Academic Trajectory
Comprehensive exams assess a graduate student's mastery of foundational knowledge across their discipline, determining eligibility for continued enrollment and research candidacy. Qualifying exams evaluate readiness for dissertation research, directly influencing a student's progression to candidacy status and shaping their academic timeline. Failure or underperformance in either exam can delay degree completion, limit funding opportunities, or result in academic dismissal, profoundly impacting the graduate's academic trajectory.
Comprehensive Exams vs Qualifying Exams Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com