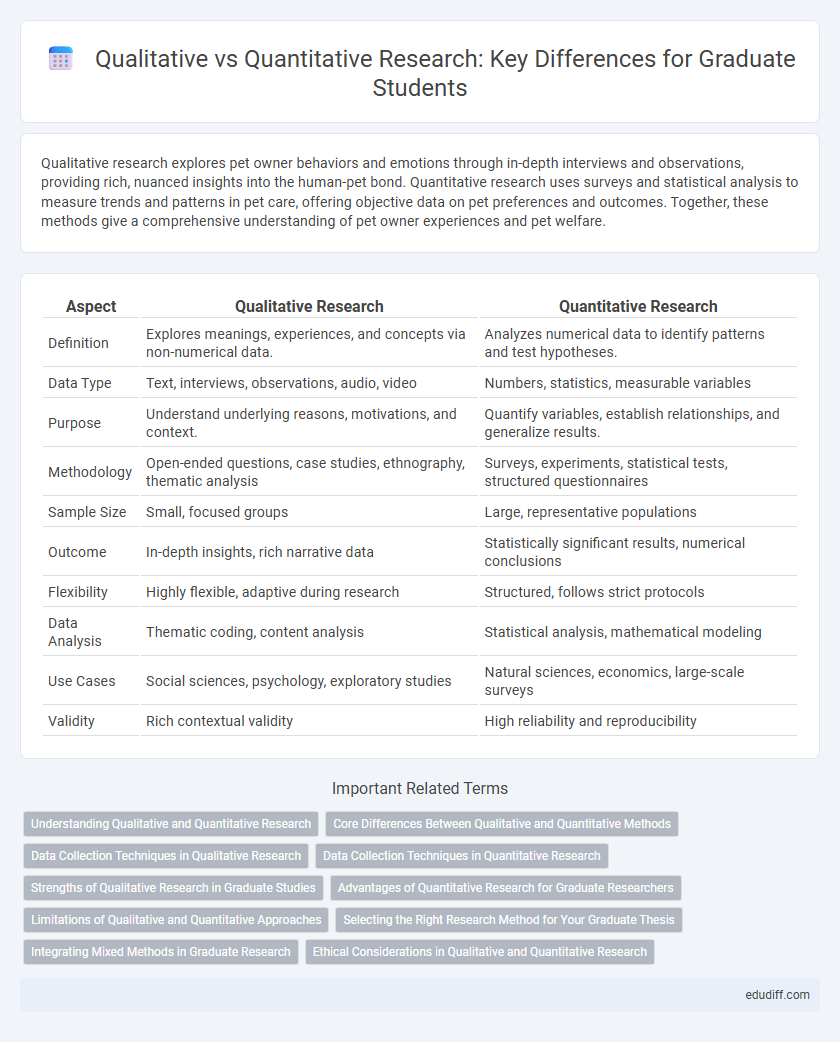
Qualitative research explores pet owner behaviors and emotions through in-depth interviews and observations, providing rich, nuanced insights into the human-pet bond. Quantitative research uses surveys and statistical analysis to measure trends and patterns in pet care, offering objective data on pet preferences and outcomes. Together, these methods give a comprehensive understanding of pet owner experiences and pet welfare.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explores meanings, experiences, and concepts via non-numerical data. | Analyzes numerical data to identify patterns and test hypotheses. |
| Data Type | Text, interviews, observations, audio, video | Numbers, statistics, measurable variables |
| Purpose | Understand underlying reasons, motivations, and context. | Quantify variables, establish relationships, and generalize results. |
| Methodology | Open-ended questions, case studies, ethnography, thematic analysis | Surveys, experiments, statistical tests, structured questionnaires |
| Sample Size | Small, focused groups | Large, representative populations |
| Outcome | In-depth insights, rich narrative data | Statistically significant results, numerical conclusions |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adaptive during research | Structured, follows strict protocols |
| Data Analysis | Thematic coding, content analysis | Statistical analysis, mathematical modeling |
| Use Cases | Social sciences, psychology, exploratory studies | Natural sciences, economics, large-scale surveys |
| Validity | Rich contextual validity | High reliability and reproducibility |
Understanding Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative research explores complex phenomena through non-numerical data, emphasizing context, meanings, and experiences collected via interviews, focus groups, and observations. Quantitative research relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and quantify variables using surveys, experiments, and longitudinal studies. Understanding these methodologies enables graduate students to select appropriate approaches based on research objectives, data types, and the depth of insight required.
Core Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Qualitative research emphasizes exploratory analysis through methods such as interviews and focus groups to understand underlying motivations and meanings, while quantitative research relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to measure variables and test hypotheses. Qualitative data is often unstructured and subjective, capturing rich, detailed information, whereas quantitative data is structured, allowing for objective comparison and generalization. The core difference lies in the approach to data collection and analysis: qualitative methods interpret complex phenomena in context, while quantitative methods quantify relationships and patterns across larger samples.
Data Collection Techniques in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research employs data collection techniques such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and participant observation to gather rich, descriptive insights into participants' experiences and social contexts. These methods prioritize open-ended questions and flexible data collection processes to capture the depth and complexity of human behavior and cultural phenomena. Unlike quantitative research's reliance on structured surveys and statistical measurements, qualitative techniques emphasize thematic analysis and narrative data to explore meanings and patterns within the collected information.
Data Collection Techniques in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research employs structured data collection techniques such as surveys, questionnaires, and experiments to gather numerical data for statistical analysis. Standardized instruments and closed-ended questions are utilized to ensure consistency and objectivity during data collection. This method emphasizes measuring variables and quantifying relationships to produce replicable and generalizable findings.
Strengths of Qualitative Research in Graduate Studies
Qualitative research offers graduate students the strength of deep contextual understanding by exploring complex phenomena through interviews, focus groups, and observations. This method prioritizes rich, detailed data that uncover underlying motivations, attitudes, and behaviors, which quantitative methods might overlook. It also provides flexibility in data collection and analysis, allowing researchers to adapt to emerging themes and gain holistic insights critical for nuanced academic inquiries.
Advantages of Quantitative Research for Graduate Researchers
Quantitative research offers graduate researchers clear advantages by providing precise, numerical data that enables statistical analysis and objective measurement of variables. This research method facilitates large sample sizes, enhancing the generalizability and replicability of findings across diverse populations. Moreover, quantitative research supports hypothesis testing and theory validation, crucial for producing scientifically robust and evidence-based conclusions in graduate-level studies.
Limitations of Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches
Qualitative research faces limitations such as smaller sample sizes, which can restrict generalizability, and potential researcher bias affecting data interpretation. Quantitative research, despite its statistical rigor, may overlook contextual nuances and subjective experiences crucial for understanding complex social phenomena. Both approaches require careful consideration of validity and reliability issues to ensure robust and meaningful graduate-level research outcomes.
Selecting the Right Research Method for Your Graduate Thesis
Selecting the right research method for your graduate thesis depends on your research objectives and the nature of the data. Qualitative research excels at exploring complex phenomena and understanding participants' perspectives through interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis. Quantitative research suits hypotheses testing and statistical analysis, using surveys, experiments, and numerical data to produce generalizable results.
Integrating Mixed Methods in Graduate Research
Integrating mixed methods in graduate research enriches data interpretation by combining qualitative insights with quantitative metrics, fostering a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. This approach enhances validity and depth, enabling researchers to explore numerical trends alongside subjective experiences. Effective integration requires careful alignment of qualitative themes and quantitative variables to ensure cohesive analysis and robust conclusions.
Ethical Considerations in Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Ethical considerations in qualitative research prioritize informed consent, confidentiality, and the researcher-participant relationship to ensure trust and respect for personal narratives. Quantitative research emphasizes data integrity, participant anonymity, and the ethical use of statistical analysis to maintain validity and transparency. Both methodologies require adherence to institutional review board (IRB) standards and responsible reporting to protect human subjects and uphold research ethics.
Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com