Pass/Fail grading reduces stress by emphasizing mastery of material rather than competition, fostering a more inclusive learning environment. Letter grades provide detailed feedback on student performance, motivating higher achievement and clearer academic standards. Balancing both systems can support diverse learning needs while maintaining rigorous assessment.
Table of Comparison
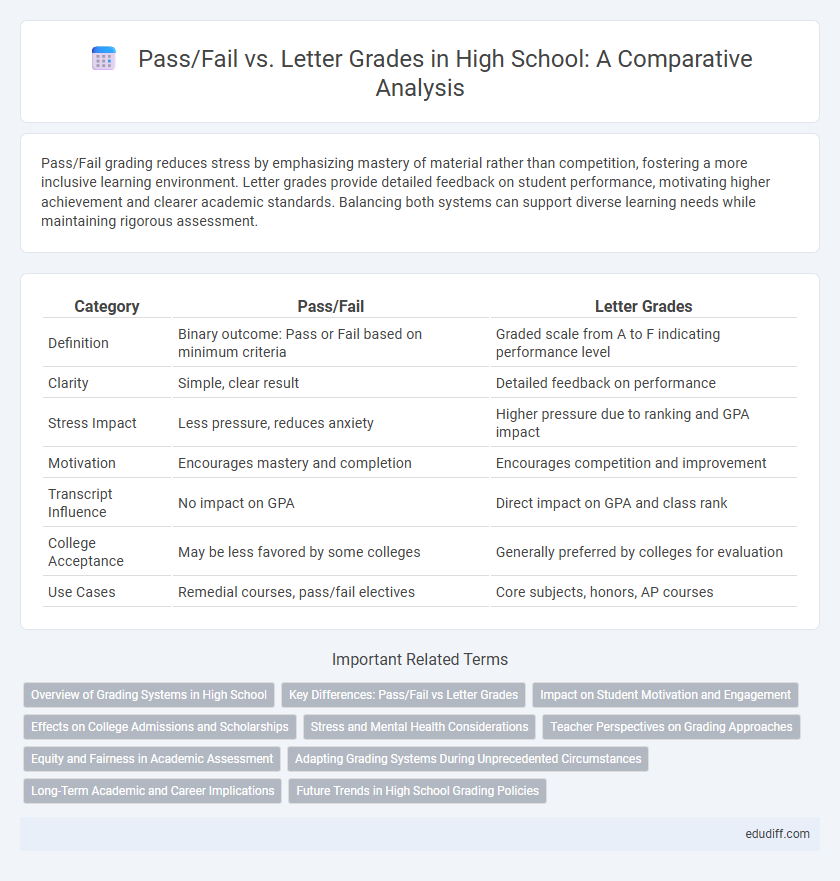
| Category | Pass/Fail | Letter Grades |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Binary outcome: Pass or Fail based on minimum criteria | Graded scale from A to F indicating performance level |
| Clarity | Simple, clear result | Detailed feedback on performance |
| Stress Impact | Less pressure, reduces anxiety | Higher pressure due to ranking and GPA impact |
| Motivation | Encourages mastery and completion | Encourages competition and improvement |
| Transcript Influence | No impact on GPA | Direct impact on GPA and class rank |
| College Acceptance | May be less favored by some colleges | Generally preferred by colleges for evaluation |
| Use Cases | Remedial courses, pass/fail electives | Core subjects, honors, AP courses |
Overview of Grading Systems in High School
High schools typically use two main grading systems: Pass/Fail and Letter Grades, each serving distinct educational purposes. Pass/Fail grading simplifies assessment by categorizing student performance into satisfactory or unsatisfactory, often reducing stress and encouraging learning mastery. Letter Grades provide detailed feedback with a scale from A to F, allowing precise measurement of student achievement and influencing GPA calculations and college admissions.
Key Differences: Pass/Fail vs Letter Grades
Pass/Fail grading evaluates student performance based on meeting minimum criteria without detailed distinctions, while letter grades provide a nuanced assessment ranging from A to F, reflecting varying levels of achievement. Letter grades impact GPA calculations and college admissions with precise academic performance indicators, whereas Pass/Fail simplifies evaluation but may limit differentiation in strengths and weaknesses. The choice between Pass/Fail and letter grades affects student motivation, stress levels, and transcript interpretation in high school academic environments.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Pass/fail grading systems reduce pressure, fostering intrinsic motivation and encouraging risk-taking, which enhances student engagement by prioritizing learning over competition. Letter grades, while providing clear performance benchmarks, may induce anxiety and promote extrinsic motivation, often leading to strategic studying rather than deep understanding. Research shows that pass/fail assessments can improve classroom participation and persistence, particularly in challenging subjects where fear of failure might otherwise diminish effort.
Effects on College Admissions and Scholarships
Pass/fail grading systems in high school can impact college admissions by limiting the ability to demonstrate academic rigor and mastery, as letter grades provide a detailed assessment of student performance. Many colleges rely on GPA and class rank calculated from traditional letter grades to evaluate applicants for scholarships, making pass/fail transcripts potentially less competitive. However, some institutions have adjusted their admissions criteria to accommodate pass/fail transcripts during exceptional circumstances, but letter grades generally remain crucial for scholarship eligibility and merit-based awards.
Stress and Mental Health Considerations
Pass/Fail grading systems in high schools can significantly reduce student stress by removing the pressure to achieve high letter grades, fostering a healthier learning environment. Letter grades often contribute to anxiety and mental health challenges due to their competitive nature and impact on college admissions. Implementing Pass/Fail options allows students to focus on mastery and personal growth rather than solely on performance metrics.
Teacher Perspectives on Grading Approaches
Teachers often view pass/fail grading as a method that reduces stress and encourages risk-taking among high school students, fostering a focus on learning rather than competition. However, many educators believe that letter grades provide clearer feedback on student performance and help identify areas needing improvement. Balancing these approaches requires consideration of academic standards, student motivation, and the ability to communicate achievement effectively.
Equity and Fairness in Academic Assessment
Pass/Fail grading systems promote equity by reducing stress and competition among high school students, enabling a focus on learning rather than ranking. Letter grades often amplify disparities linked to socio-economic background and resource availability, impacting fairness in academic assessment. Implementing Pass/Fail options can create a more inclusive environment that recognizes diverse learning styles and challenges.
Adapting Grading Systems During Unprecedented Circumstances
High schools adopted Pass/Fail grading systems to accommodate students' diverse challenges during unprecedented circumstances like the COVID-19 pandemic, promoting equity and reducing academic stress. This flexible approach prioritizes learning and mental health by minimizing the pressure associated with traditional letter grades such as A, B, or C. Schools continue to evaluate the effectiveness of Pass/Fail options in maintaining academic standards while supporting student well-being amid ongoing disruptions.
Long-Term Academic and Career Implications
Pass/Fail grading systems can reduce stress and promote learning curiosity but may limit the detailed performance feedback needed for college admissions and scholarships. Letter grades offer nuanced academic evaluation, influencing GPA, class rank, and competitive college applications critical for scholarships and career opportunities. Over time, consistent letter grades often enhance transcript clarity and bolster resumes in professional and academic settings.
Future Trends in High School Grading Policies
Emerging trends in high school grading policies indicate a shift from traditional letter grades to more holistic pass/fail systems emphasizing mastery and skills development. Data from education research suggests that pass/fail grading can reduce student stress and promote equity by focusing on learning outcomes rather than competition. Future policies are likely to integrate personalized assessment models leveraging technology to provide real-time feedback and support differentiated instruction.
Pass/Fail vs Letter Grades Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com