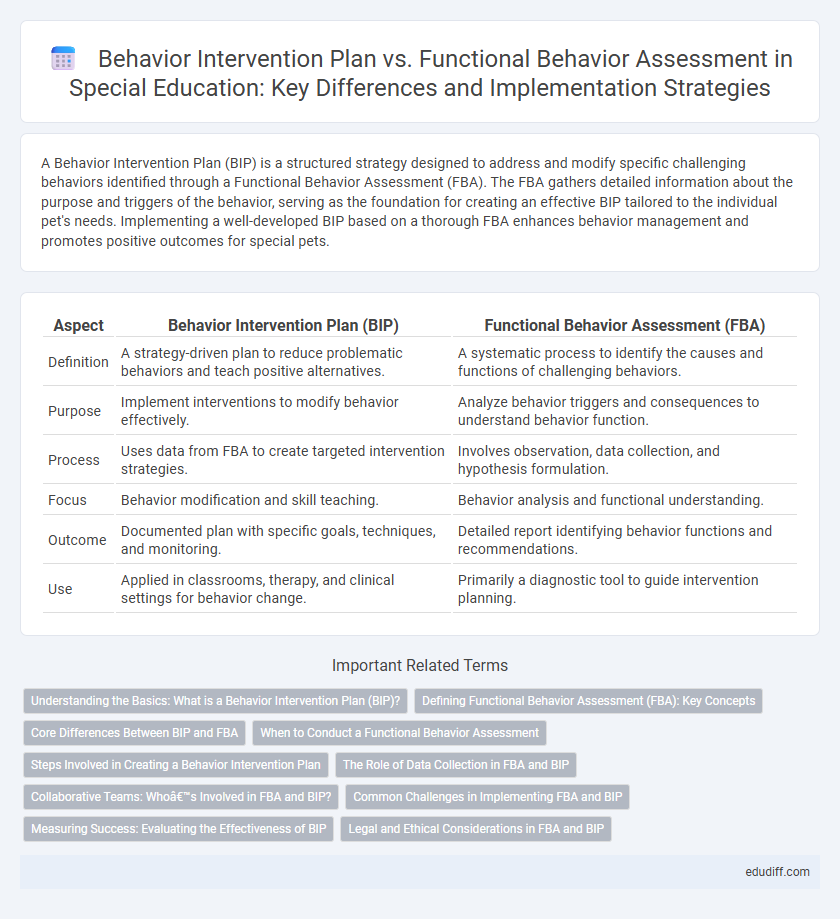
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a structured strategy designed to address and modify specific challenging behaviors identified through a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA). The FBA gathers detailed information about the purpose and triggers of the behavior, serving as the foundation for creating an effective BIP tailored to the individual pet's needs. Implementing a well-developed BIP based on a thorough FBA enhances behavior management and promotes positive outcomes for special pets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) | Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A strategy-driven plan to reduce problematic behaviors and teach positive alternatives. | A systematic process to identify the causes and functions of challenging behaviors. |
| Purpose | Implement interventions to modify behavior effectively. | Analyze behavior triggers and consequences to understand behavior function. |
| Process | Uses data from FBA to create targeted intervention strategies. | Involves observation, data collection, and hypothesis formulation. |
| Focus | Behavior modification and skill teaching. | Behavior analysis and functional understanding. |
| Outcome | Documented plan with specific goals, techniques, and monitoring. | Detailed report identifying behavior functions and recommendations. |
| Use | Applied in classrooms, therapy, and clinical settings for behavior change. | Primarily a diagnostic tool to guide intervention planning. |
Understanding the Basics: What is a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP)?
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a strategic, individualized plan designed to address challenging behaviors by implementing evidence-based interventions tailored to a student's specific needs. It is developed using data gathered from a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA), which identifies the underlying causes and functions of the behavior. The BIP outlines clear, measurable goals, positive reinforcement strategies, and supports to promote constructive behavior change in educational settings.
Defining Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA): Key Concepts
Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) is a systematic process used to identify the underlying causes and functions of challenging behaviors in individuals, particularly in educational and clinical settings. It involves data collection, observation, and analysis to determine antecedents, behaviors, and consequences that maintain the behavior. The goal of FBA is to develop effective, individualized Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) that address the root causes and promote positive behavioral changes.
Core Differences Between BIP and FBA
Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) outlines specific strategies and interventions designed to address targeted behaviors based on data collected, while Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) identifies the underlying causes and functions of those behaviors through systematic observation and analysis. BIP is action-oriented, focusing on prevention and skill-building, whereas FBA is diagnostic, emphasizing understanding the reasons behind behaviors. The core difference lies in FBA serving as the foundation for creating a tailored BIP informed by behavioral functions.
When to Conduct a Functional Behavior Assessment
Conduct a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) when a student exhibits challenging behaviors that interfere with learning or safety, and when previous interventions have failed or limited data exist about the behavior's function. An FBA identifies the underlying causes and triggers of behavior by collecting data on antecedents, behaviors, and consequences, guiding the development of an effective Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP). Implementing an FBA early ensures targeted, individualized strategies that improve behavioral outcomes in educational settings.
Steps Involved in Creating a Behavior Intervention Plan
Creating a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) involves first conducting a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) to identify the underlying causes and functions of challenging behaviors. The process includes collecting data on behavior patterns, defining target behaviors, and developing strategies tailored to address specific triggers and reinforcements. Implementing the BIP requires collaboration with educators, caregivers, and specialists to monitor progress and make data-driven adjustments for effective behavior management.
The Role of Data Collection in FBA and BIP
Data collection in Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) serves as the foundation for identifying the antecedents, behaviors, and consequences that influence student actions, enabling precise behavior analysis. Within a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP), continuous data tracking evaluates the effectiveness of personalized strategies and informs necessary adjustments to support behavior change. Accurate and ongoing data collection ensures that interventions are evidence-based, measurable, and responsive to student needs.
Collaborative Teams: Who’s Involved in FBA and BIP?
Collaborative teams involved in Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) include special educators, school psychologists, behavior analysts, and parents, ensuring diverse perspectives for accurate behavior analysis. Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) development engages these same professionals along with classroom teachers and related service providers who implement targeted strategies. Effective collaboration among these stakeholders promotes consistent behavior support tailored to the individual student's needs.
Common Challenges in Implementing FBA and BIP
Common challenges in implementing Functional Behavior Assessments (FBA) and Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) include insufficient training for educators, inconsistent data collection, and limited collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. Difficulty in accurately identifying the function of behavior often leads to ineffective BIP strategies, reducing the overall intervention's success. Resource constraints and time demands further hinder the consistent application and monitoring necessary for meaningful behavioral improvements in special education settings.
Measuring Success: Evaluating the Effectiveness of BIP
Measuring success in a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) involves systematically collecting data on target behaviors to assess changes over time and determine the plan's effectiveness. In contrast, a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) provides the foundational analysis by identifying antecedents, consequences, and functions of behavior that inform BIP development. Evaluating the effectiveness of a BIP requires ongoing progress monitoring using quantitative data aligned with the goals established through the initial FBA process.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in FBA and BIP
Legal and ethical considerations in Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) and Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) emphasize adherence to IDEA and Section 504 regulations to ensure students' rights and privacy are protected. Confidentiality protocols must be strictly followed during data collection and intervention implementation to maintain compliance with FERPA guidelines. Ethical practice mandates collaboration with families and multidisciplinary teams to develop culturally responsive, evidence-based interventions that respect the child's dignity and promote positive behavioral outcomes.
Behavior Intervention Plan vs Functional Behavior Assessment Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com