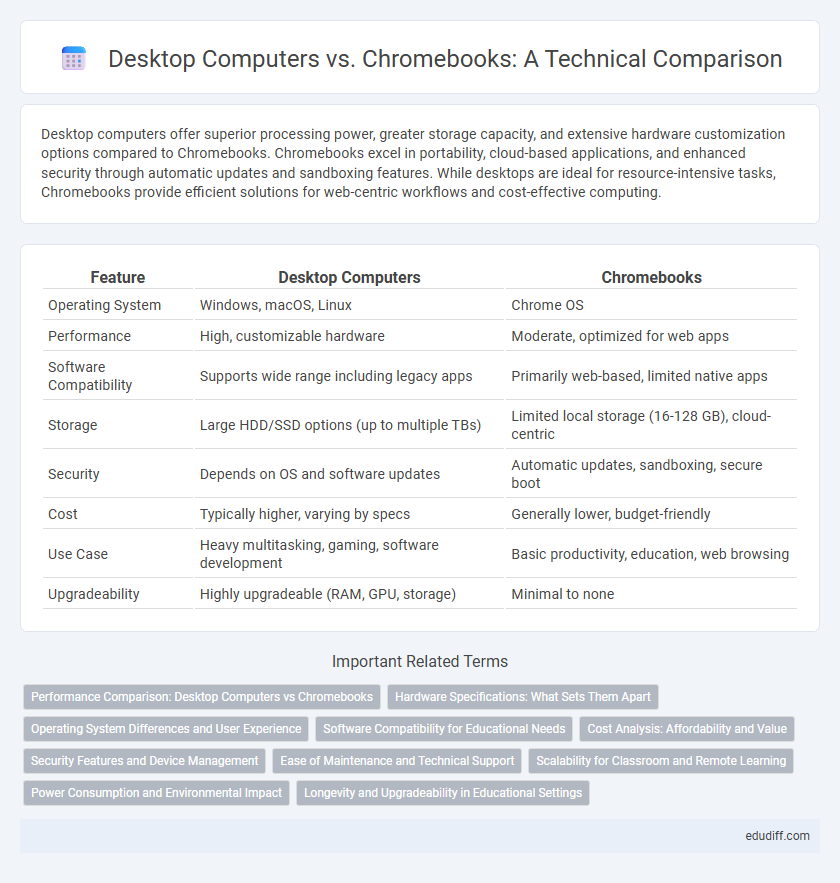
Desktop computers offer superior processing power, greater storage capacity, and extensive hardware customization options compared to Chromebooks. Chromebooks excel in portability, cloud-based applications, and enhanced security through automatic updates and sandboxing features. While desktops are ideal for resource-intensive tasks, Chromebooks provide efficient solutions for web-centric workflows and cost-effective computing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Desktop Computers | Chromebooks |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows, macOS, Linux | Chrome OS |
| Performance | High, customizable hardware | Moderate, optimized for web apps |
| Software Compatibility | Supports wide range including legacy apps | Primarily web-based, limited native apps |
| Storage | Large HDD/SSD options (up to multiple TBs) | Limited local storage (16-128 GB), cloud-centric |
| Security | Depends on OS and software updates | Automatic updates, sandboxing, secure boot |
| Cost | Typically higher, varying by specs | Generally lower, budget-friendly |
| Use Case | Heavy multitasking, gaming, software development | Basic productivity, education, web browsing |
| Upgradeability | Highly upgradeable (RAM, GPU, storage) | Minimal to none |
Performance Comparison: Desktop Computers vs Chromebooks
Desktop computers consistently outperform Chromebooks in raw processing power due to their ability to support higher-end CPUs like Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen 7, coupled with dedicated GPUs for intensive tasks. Chromebooks rely primarily on energy-efficient ARM or Intel Celeron processors, optimizing for web-based applications rather than demanding software. This performance distinction makes desktops ideal for gaming, video editing, and multitasking, while Chromebooks excel in lightweight, cloud-centric productivity.
Hardware Specifications: What Sets Them Apart
Desktop computers boast powerful processors, extensive RAM options, and dedicated graphics cards, enabling high performance for demanding applications, while Chromebooks rely on energy-efficient ARM or Intel chips optimized for cloud-based tasks. Desktops typically provide substantial internal storage, ranging from HDDs to SSDs with terabyte capacities, whereas Chromebooks emphasize minimal local storage, often SSDs under 128GB, leveraging cloud storage solutions like Google Drive. The expandability of desktops allows for customizable hardware upgrades, contrasting with Chromebooks' fixed components designed for lightweight use and portability.
Operating System Differences and User Experience
Desktop computers typically run full-featured operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux, offering extensive software compatibility and powerful customization options for advanced users. Chromebooks operate on Chrome OS, a lightweight, cloud-centric system designed primarily for web applications and seamless integration with Google services, resulting in faster boot times and simpler maintenance. The user experience on desktops is more versatile for demanding tasks like video editing or gaming, while Chromebooks provide a streamlined, secure environment optimized for productivity and ease of use with internet-connected workflows.
Software Compatibility for Educational Needs
Desktop computers offer extensive software compatibility, supporting a wide array of educational programs including advanced simulation, CAD, and legacy software essential for specialized courses. Chromebooks rely primarily on web-based applications and Android apps through Chrome OS, restricting their use to cloud-dependent tools like Google Workspace and limited offline educational software. For institutions requiring comprehensive software installations and offline functionality, desktops provide a more versatile and powerful solution to meet diverse educational demands.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Desktop computers generally offer higher performance and upgradeability at a varied price range, making them suitable for users requiring long-term investment and robust computing power. Chromebooks present a more affordable alternative with lower upfront costs, simplified maintenance, and strong integration with cloud services, ideal for budget-conscious consumers and basic productivity tasks. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including software, hardware upgrades, and support, determines the best value between desktops and Chromebooks for specific user needs.
Security Features and Device Management
Desktop computers offer extensive security features such as advanced firewall configurations, antivirus software compatibility, and customizable encryption protocols tailored for enterprise environments. Chromebooks leverage cloud-based security, automatic updates, sandboxing, and verified boot processes, minimizing vulnerabilities and reducing reliance on local security management. Device management on desktops requires manual configuration and regular patching, while Chromebooks benefit from centralized administration through Google's Admin Console, providing streamlined policy enforcement and real-time monitoring.
Ease of Maintenance and Technical Support
Desktop computers offer greater ease of maintenance with accessible hardware components that can be individually upgraded or replaced, supported by widespread technical expertise and readily available spare parts. Chromebooks simplify software maintenance through automatic updates and cloud-based management, reducing the need for manual intervention but limiting hardware customization. Technical support for desktops benefits from diverse third-party options, whereas Chromebook support is primarily streamlined via Google's ecosystem and verified partners.
Scalability for Classroom and Remote Learning
Desktop computers offer substantial scalability for classroom settings due to their powerful hardware, upgrade options, and compatibility with diverse educational software, supporting resource-intensive applications and multiple user profiles. Chromebooks excel in remote learning scalability by providing lightweight, cloud-based platforms that facilitate easy device management, quick deployment, and seamless integration with Google Workspace for Education. Schools benefit from combining desktops for lab-based, high-performance tasks and Chromebooks for flexible, cost-effective remote access and collaborative learning environments.
Power Consumption and Environmental Impact
Desktop computers typically consume between 200 to 600 watts of power during operation, significantly higher than Chromebooks, which average around 15 to 30 watts. This increased energy consumption directly contributes to a larger carbon footprint, with desktops generating approximately 1,000 kg CO2e annually compared to Chromebooks' roughly 100 kg CO2e. Chromebooks' energy efficiency and reliance on cloud-based applications reduce environmental impact, making them a greener choice for users prioritizing sustainability.
Longevity and Upgradeability in Educational Settings
Desktop computers offer superior longevity and upgradeability in educational settings due to their modular components, allowing schools to replace or enhance parts like RAM, storage, and graphics cards to extend device lifespan. Chromebooks, favored for their affordability and ease of management, typically have limited upgrade options and shorter official support cycles, which may lead to earlier replacement. Prioritizing desktops can reduce total cost of ownership over time by enabling incremental hardware improvements aligned with evolving software requirements.
Desktop computers vs Chromebooks Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com