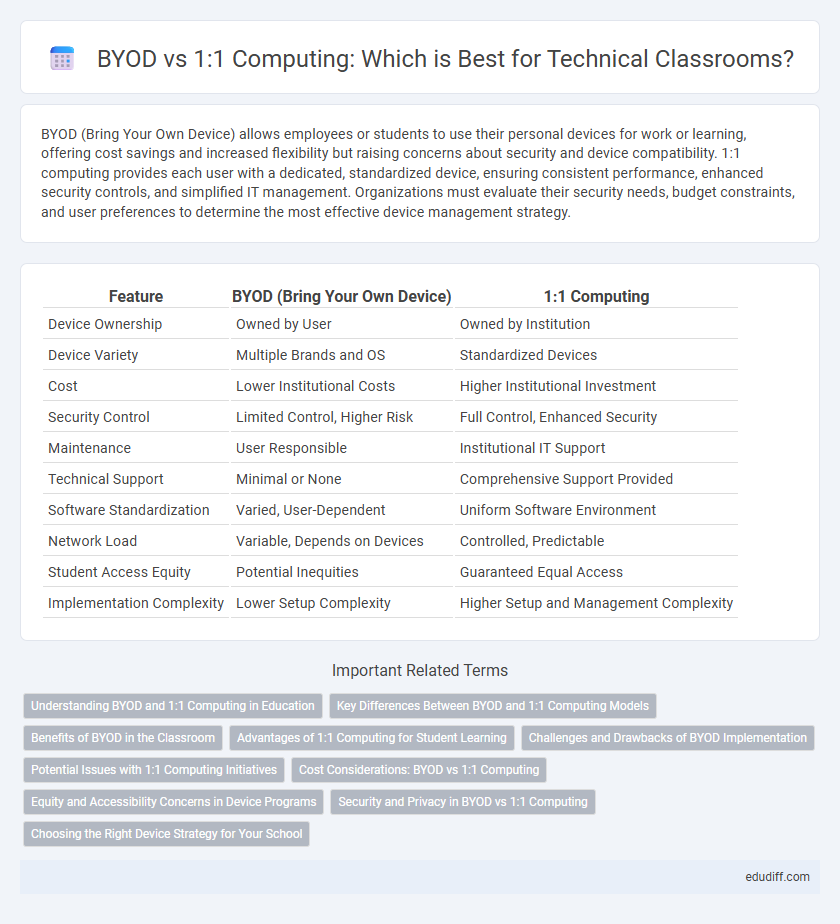
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) allows employees or students to use their personal devices for work or learning, offering cost savings and increased flexibility but raising concerns about security and device compatibility. 1:1 computing provides each user with a dedicated, standardized device, ensuring consistent performance, enhanced security controls, and simplified IT management. Organizations must evaluate their security needs, budget constraints, and user preferences to determine the most effective device management strategy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) | 1:1 Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Device Ownership | Owned by User | Owned by Institution |
| Device Variety | Multiple Brands and OS | Standardized Devices |
| Cost | Lower Institutional Costs | Higher Institutional Investment |
| Security Control | Limited Control, Higher Risk | Full Control, Enhanced Security |
| Maintenance | User Responsible | Institutional IT Support |
| Technical Support | Minimal or None | Comprehensive Support Provided |
| Software Standardization | Varied, User-Dependent | Uniform Software Environment |
| Network Load | Variable, Depends on Devices | Controlled, Predictable |
| Student Access Equity | Potential Inequities | Guaranteed Equal Access |
| Implementation Complexity | Lower Setup Complexity | Higher Setup and Management Complexity |
Understanding BYOD and 1:1 Computing in Education
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) enables students to use personal devices for educational purposes, promoting flexibility and cost savings for schools. In contrast, 1:1 computing provides each student with a dedicated school-issued device, ensuring standardized hardware and software for consistent learning experiences. Understanding these models helps educators balance accessibility, equity, and technological control in classrooms.
Key Differences Between BYOD and 1:1 Computing Models
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) allows employees or students to use their personal devices for work or learning, offering flexibility but raising security and compatibility issues. In contrast, 1:1 computing provides each user with a standardized device issued and managed by the organization, enhancing control over software, updates, and data protection. Key differences include device ownership, management policies, cost distribution, and the level of IT support required for maintaining consistent performance and security standards.
Benefits of BYOD in the Classroom
BYOD in the classroom enhances personalized learning by allowing students to use familiar devices, which increases engagement and productivity. It reduces the school's hardware costs and maintenance efforts compared to 1:1 computing programs. BYOD also promotes digital literacy by encouraging students to responsibly manage and secure their own technology.
Advantages of 1:1 Computing for Student Learning
1:1 computing ensures every student has equal access to personalized devices preloaded with educational software, enhancing engagement and tailored learning experiences. This standardized environment reduces technical disparities and simplifies IT support, allowing educators to focus more on instruction rather than troubleshooting. Consistent hardware and software facilitate seamless integration of digital tools, boosting collaborative projects and access to real-time assessment data.
Challenges and Drawbacks of BYOD Implementation
BYOD implementation poses significant security challenges, as personal devices often lack uniform security protocols, increasing vulnerabilities to data breaches and malware attacks. Device diversity complicates IT management and support, causing inconsistent user experiences and higher maintenance costs. Privacy concerns arise due to potential mixing of personal and corporate data, alongside difficulties in enforcing compliance with organizational policies.
Potential Issues with 1:1 Computing Initiatives
1:1 computing initiatives often face challenges such as inconsistent device quality, limited technical support, and increased maintenance costs. The demand for uniform software compatibility and security policies can strain IT resources, leading to potential breaches or system downtime. Furthermore, disparities in student digital literacy may result in unequal learning outcomes, complicating effective technology integration.
Cost Considerations: BYOD vs 1:1 Computing
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) significantly reduces upfront hardware expenditures by leveraging personal devices, but often incurs higher costs in security management, compatibility, and support infrastructure. In contrast, 1:1 computing requires substantial initial capital investment for device procurement, yet enables standardized maintenance and streamlined IT support, potentially lowering long-term operational expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO) for both models must consider hardware lifecycle, software licensing, network demands, and administrative overhead to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Equity and Accessibility Concerns in Device Programs
BYOD programs often exacerbate equity and accessibility challenges as they rely on students providing their own devices, leading to disparities based on socioeconomic status. In contrast, 1:1 computing initiatives provide every student with standardized devices, promoting equal access to technology and creating a more inclusive learning environment. Ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies and addressing connectivity issues remain critical factors in both models to support all learners effectively.
Security and Privacy in BYOD vs 1:1 Computing
BYOD policies introduce complexities in security and privacy due to diverse device management, inconsistent software updates, and variable user compliance, increasing vulnerability to data breaches and unauthorized access. In contrast, 1:1 Computing environments offer centralized control with uniform device configurations, standardized security protocols, and enforced privacy measures, reducing risks associated with malware and data leakage. Effective deployment requires robust encryption, mobile device management (MDM), and user training tailored to the specific challenges of each approach.
Choosing the Right Device Strategy for Your School
Choosing the right device strategy for your school involves evaluating the benefits and challenges of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) versus 1:1 computing programs. BYOD can reduce upfront costs and increase device variety, but it may introduce compatibility and security concerns, while 1:1 computing ensures uniformity, easier IT management, and consistent educational software use at a higher initial investment. Analyzing factors like budget constraints, infrastructure readiness, student needs, and long-term maintenance will guide schools in making data-driven decisions that align with their educational goals.
BYOD vs 1:1 Computing Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com