On-premises software offers greater control and security by hosting applications on local servers, ideal for organizations with strict compliance requirements. Cloud-based software provides scalability and remote accessibility, reducing IT maintenance costs through vendor-managed infrastructure. Choosing between the two depends on factors such as budget, data sensitivity, and desired flexibility.
Table of Comparison
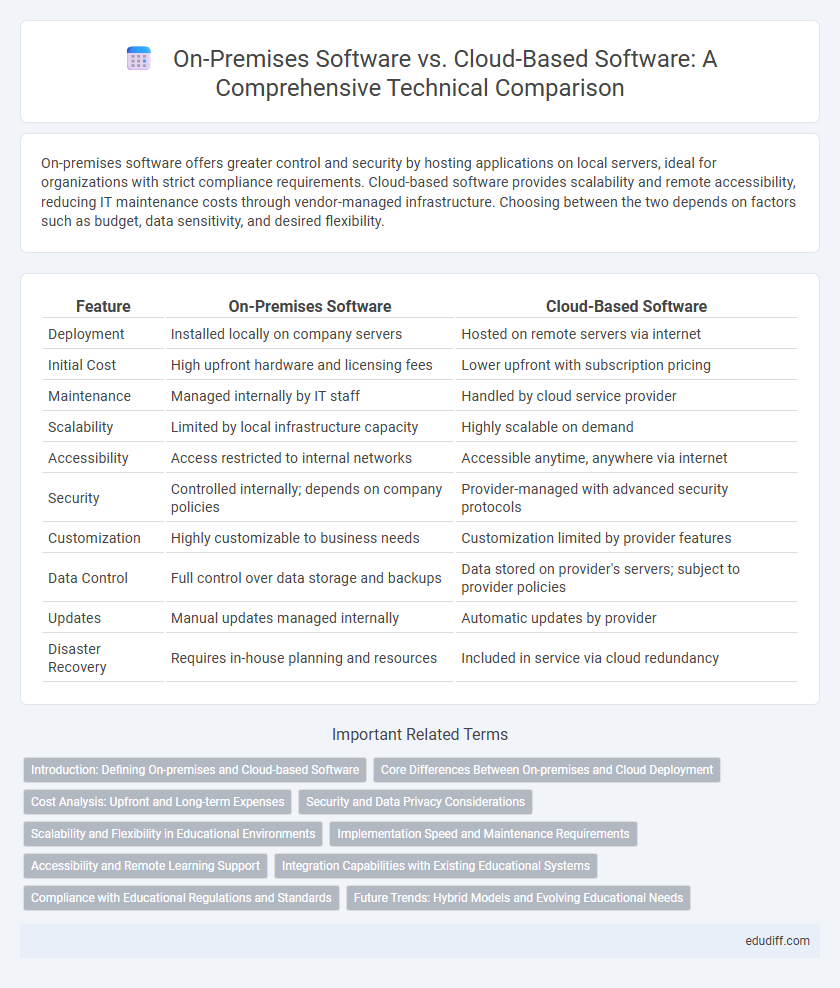
| Feature | On-Premises Software | Cloud-Based Software |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Installed locally on company servers | Hosted on remote servers via internet |
| Initial Cost | High upfront hardware and licensing fees | Lower upfront with subscription pricing |
| Maintenance | Managed internally by IT staff | Handled by cloud service provider |
| Scalability | Limited by local infrastructure capacity | Highly scalable on demand |
| Accessibility | Access restricted to internal networks | Accessible anytime, anywhere via internet |
| Security | Controlled internally; depends on company policies | Provider-managed with advanced security protocols |
| Customization | Highly customizable to business needs | Customization limited by provider features |
| Data Control | Full control over data storage and backups | Data stored on provider's servers; subject to provider policies |
| Updates | Manual updates managed internally | Automatic updates by provider |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires in-house planning and resources | Included in service via cloud redundancy |
Introduction: Defining On-premises and Cloud-based Software
On-premises software is deployed locally on a company's own servers, offering complete control over data security and customization. Cloud-based software operates on remote servers managed by third-party providers, enabling scalable access via the internet. These contrasting deployment models impact IT infrastructure, maintenance responsibilities, and operational flexibility.
Core Differences Between On-premises and Cloud Deployment
On-premises software requires local hardware installation and maintenance, giving organizations full control over data security and customization but demanding significant upfront capital investment. Cloud-based software operates on remote servers managed by providers, offering scalability, regular updates, and reduced IT overhead with subscription-based pricing models. The core differences lie in deployment location, management responsibility, cost structure, and flexibility in resource allocation.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term Expenses
On-premises software requires significant upfront capital expenditure for hardware, licenses, and infrastructure setup, with ongoing costs for maintenance, upgrades, and IT staff. Cloud-based software operates on a subscription or pay-as-you-go model, reducing initial costs but generating continuous operational expenses that scale with usage. Over the long term, cloud solutions often offer lower total cost of ownership through reduced capital investments, while on-premises installations may incur higher fixed costs but provide more control over expenses.
Security and Data Privacy Considerations
On-premises software grants organizations full control over security measures and data privacy protocols by housing data within their own infrastructure, reducing exposure to external cyber threats. Cloud-based software relies on providers' robust security frameworks, offering advanced encryption and compliance certifications such as GDPR and HIPAA, but requires trust in third-party vendor security and data handling practices. Evaluating encryption standards, access controls, and data residency regulations is critical when choosing between on-premises and cloud-based solutions for maintaining optimal security and privacy.
Scalability and Flexibility in Educational Environments
On-premises software in educational environments often limits scalability due to fixed hardware resources and high upfront costs for expansion. Cloud-based software offers dynamic scalability, enabling institutions to adjust computing power and storage based on fluctuating student enrollment and usage demands. Flexible deployment models in cloud solutions support seamless integration with various learning management systems and enable remote access, enhancing adaptability for diverse educational needs.
Implementation Speed and Maintenance Requirements
On-premises software typically requires longer implementation times due to hardware setup and in-house integration complexities, whereas cloud-based software deploys rapidly through internet access with minimal initial infrastructure. Maintenance for on-premises solutions involves ongoing in-house updates, patches, and hardware management, demanding dedicated IT resources. Conversely, cloud-based software providers manage maintenance and updates centrally, reducing organizational overhead and enabling seamless scalability.
Accessibility and Remote Learning Support
On-premises software requires direct access to the local network or physical devices, limiting accessibility primarily to on-site users, which constrains remote learning capabilities. Cloud-based software offers seamless access from any device with an internet connection, enhancing flexibility for remote learners and supporting virtual collaboration tools effectively. This broad accessibility significantly improves user experience and scalability in diverse educational environments.
Integration Capabilities with Existing Educational Systems
On-premises software offers direct integration with existing educational systems through local network connections, ensuring faster data transfer and enhanced security control. Cloud-based software provides scalable APIs and web services that facilitate seamless interoperability with various learning management systems (LMS) and student information systems (SIS). Both solutions require evaluating compatibility with legacy platforms and data synchronization protocols to optimize integration efficiency in educational environments.
Compliance with Educational Regulations and Standards
On-premises software offers greater control over data security and customization, which can facilitate adherence to strict educational regulations such as FERPA and GDPR. Cloud-based software providers often invest heavily in compliance certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2, ensuring regular audits and updates to meet evolving educational standards. Selecting a solution requires evaluating whether in-house infrastructure or cloud vendor policies better align with institutional compliance requirements and audit readiness.
Future Trends: Hybrid Models and Evolving Educational Needs
Hybrid models integrating on-premises software with cloud-based solutions are rapidly gaining traction in educational technology, enabling institutions to tailor infrastructure to specific needs while enhancing scalability and security. Advancements in AI-driven analytics and adaptive learning platforms rely on this hybrid approach to deliver personalized educational experiences and real-time data insights. The evolving demands for flexible access, data privacy compliance, and cost-efficiency are driving the adoption of hybrid architectures, positioning them as the future foundation for educational software ecosystems.
On-premises software vs Cloud-based software Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com